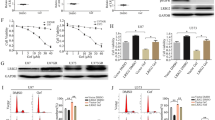
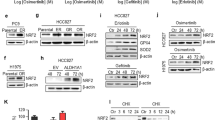
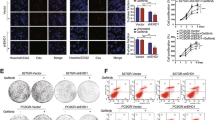
Summary
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) have led to great advances in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but the emergence of drug resistance severely limits their clinical use. Thus, elucidation of the mechanism underlying resistance to EGFR-TKIs is of great importance. In our study, sustained activation of STAT3 was confirmed to be involved in resistance to EGFR-TKIs, and this resistance occurred regardless of exposure time, EGFR-TKIs type, and even cancer cell type. Mechanistically, the sustained activation of STAT3 was not related to gp130/JAK signalling pathway or HER2/EGFR heterodimer formation, while related to the expression and activation levels of STAT3. Furthermore, FGFR was shown to bind more strongly to STAT3 after gefitinib treatment, and the inhibition of FGFR reduced the phosphorylation of STAT3, thereby counteracting the effects of EGFR-TKIs and resulting in the synergistic inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. Taken together, the FGFR/STAT3 axis mediates the sustained activation of STAT3 upon EGFR-TKI treatment. This finding elucidates a new mechanism underlying drug resistance to EGFR-TKIs that the FGFR/STAT3 axis mediates the sustained activation of STAT3, providing theoretical support for considering the combination of TKIs and FGFR inhibitors in clinical cancer treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, Chao TY, Nakagawa K, Chu DT, Saijo N, Duffield EL, Rukazenkov Y, Speake G, Jiang H, Armour AA, To KF, Yang JC, Mok TS (2011) Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). J Clin Oncol 29:2866–2874. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235
Thongprasert S, Duffield E, Saijo N, Wu YL, Yang JC, Chu DT, Liao M, Chen YM, Kuo HP, Negoro S, Lam KC, Armour A, Magill P, Fukuoka M (2011) Health-related quality-of-life in a randomized phase III first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients from Asia with advanced NSCLC (IPASS) J Thorac Oncol 6:1872–1880. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e31822adaf7
Song X, Qi X, Wang Q, Zhu W, Li J (2017) A novel multi-target inhibitor harboring selectivity of inhibiting EGFR T790M sparing wild-type EGFR. Am J Cancer Res 7:1884-1898
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, Orme JP, Finlay MR, Ward RA, Mellor MJ, Hughes G, Rahi A, Jacobs VN, Red Brewer M, Ichihara E, Sun J, Jin H, Ballard P, Al-Kadhimi K, Rowlinson R, Klinowska T, Richmond GH, Cantarini M, Kim DW, Ranson MR, Pao W (2014) AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov 4:1046–1061. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0337
Wu K, Chang Q, Lu Y, Qiu P, Chen B, Thakur C, Sun J, Li L, Kowluru A, Chen F (2013) Gefitinib resistance resulted from STAT3-mediated Akt activation in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 4:2430–2438. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1431
Chou TC (2010) Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 15:440–446. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1947
Codony-Servat C, Codony-Servat J, Karachaliou N, Molina MA, Chaib I, Ramirez JL, de Los Llanos Gil M, Solca F, Bivona TG, Rosell R (2017) Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling in EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Oncotarget 18:47305–47316. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17625
Zhao C, Li H, Lin HJ, Yang S, Lin J, Liang G (2016) Feedback activation of STAT3 as a cancer drug-resistance mechanism. Trends Pharmacol Sci 37:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2015.10.001
Alvarez JV, Greulich H, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Frank DA (2006) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for the oncogenic effects of non-small-cell lung cancer-associated mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 66:3162–3168. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3757
Greulich H, Chen TH, Feng W, Jänne PA, Alvarez JV, Zappaterra M, Bulmer SE, Frank DA, Hahn WC, Sellers WR, Meyerson M (2005) Oncogenic transformation by inhibitor-sensitive and -resistant EGFR mutants. PLoS Med 2:e313. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020313
Song L, Rawal B, Nemeth JA, Haura EB (2011) JAK1 activates STAT3 activity in non-small-cell lung cancer cells and IL-6 neutralizing antibodies can suppress JAK1-STAT3 signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 10:481–494. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0502
Sun J, Blaskovich MA, Jove R, Livingston SK, Coppola D, Sebti SM (2005) Cucurbitacin Q: a selective STAT3 activation inhibitor with potent antitumor activity. Oncogene 24:3236–3245. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208470
Hedvat M, Huszar D, Herrmann A, Gozgit JM, Schroeder A, Sheehy A, Buettner R, Proia D, Kowolik CM, Xin H, Armstrong B, Bebernitz G, Weng S, Wang L, Ye M, McEachern K, Chen H, Morosini D, Bell K, Alimzhanov M, Ioannidis S, McCoon P, Cao ZA, Yu H, Jove R, Zinda M (2009) The JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently blocks Stat3 signaling and oncogenesis in solid tumors. Cancer Cell 16:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.10.015
Wang Y, van Boxel-Dezaire AH, Cheon H, Yang J, Stark GR (2013) STAT3 activation in response to IL-6 is prolonged by the binding of IL-6 receptor to EGF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:16975–16980. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1315862110
Grant SL, Hammacher A, Douglas AM, Goss GA, Mansfield RK, Heath JK, Begley CG (2002) An unexpected biochemical and functional interaction between gp130 and the EGF receptor family in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21:460–474. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205100
Arcila ME, Nafa K, Chaft JE, Rekhtman N, Lau C, Reva BA, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Ladanyi M (2013) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol Cancer Ther 12:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0620
Hart KC, Robertson SC, Kanemitsu MY, Meyer AN, Tynan JA, Donoghue DJ (2000) Transformation and Stat activation by derivatives of FGFR1, FGFR3, and FGFR4. Oncogene 19:3309–3320. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203650
Ware KE, Marshall ME, Heasley LR, Marek L, Hinz TK, Hercule P, Helfrich BA, Doebele RC, Heasley LE (2010) Rapidly acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC cell lines through de-repression of FGFR2 and FGFR3 expression. PLoS One 5:e14117. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014117
Sharma SV, Settleman J (2007) Oncogene addiction: setting the stage for molecularly targeted cancer therapy. Genes Dev 21:3214–3231. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1609907
Xu AM, Huang PH (2010) Receptor tyrosine kinase coactivation networks in cancer. Cancer Res 70:3857–3860. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0163
Gao SP, Chang Q, Mao N, Daly LA, Vogel R, Chan T, Liu SH, Bournazou E, Schori E, Zhang H, Brewer MR, Pao W, Morris L, Ladanyi M, Arcila M, Manova-Todorova K, de Stanchina E, Norton L, Levine RL, Altan-Bonnet G, Solit D, Zinda M, Huszar D, Lyden D, Bromberg JF (2016) JAK2 inhibition sensitizes resistant EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Sci Signal 9:ra33. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aac8460
Kim HP, Han SW, Kim SH, Im SA, Oh DY, Bang YJ, Kim TY (2008) Combined lapatinib and cetuximab enhance cytotoxicity against gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:607–615. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2068
Lee HJ, Zhuang G, Cao Y, Du P, Kim HJ, Settleman J (2014) Drug resistance via feedback activation of Stat3 in oncogene-addicted cancer cells. Cancer Cell 26:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.019
Ochi N, Takigawa N, Harada D, Yasugi M, Ichihara E, Hotta K, Tabata M, Tanimoto M, Kiura K (2014) Src mediates ERK reactivation in gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Cell Res 322:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.007
Noro R, Gemma A, Kosaihira S, Kokubo Y, Chen M, Seike M, Kataoka K, Matsuda K, Okano T, Minegishi Y, Yoshimura A, Kudoh S (2006) Gefitinib (IRESSA) sensitive lung cancer cell lines show phosphorylation of Akt without ligand stimulation. BMC Cancer 6:277. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-6-277
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Dr. Heidi Greulich’s generous help for providing the plasmids (EGFR D770-N771 insNPG, gag/pol and VSV-G).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 81673450] and the NSFC Shandong Joint Fund [U1606403, U1906212]; the Scientific and Technological Innovation Project was financially supported by Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology [No. 2015ASKJ02], the National Science and Technology Major Project for Significant New Drugs Development (2018ZX09735-004),Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (major basic research projects, ZR2019ZD18) and Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (Program No. 19JK0850).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Xiaoping Song, Wei Tang, Hui Peng, Xin Qi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xiaoping Song and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of this report to the journal.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Tang, W., Peng, H. et al. FGFR leads to sustained activation of STAT3 to mediate resistance to EGFR-TKIs treatment. Invest New Drugs 39, 1201–1212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01061-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01061-1