Summary
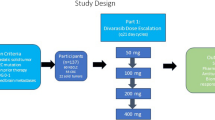
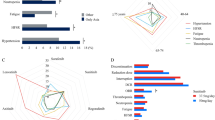
Objectives Sorafenib is a multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor of Raf kinase, VEGFR, and PDGFR. Angiogenesis is important for growth and progression of SCLC. This trial was conducted to evaluate whether the combination of cisplatin and etoposide plus concurrent and sequential sorafenib could prolong survival in patients with previously untreated SCLC. Methods Previously untreated patients with extensive stage SCLC were treated with cisplatin and etoposide days 1, 2, 3 for four cycles, concurrent with sorafenib 200 mg orally bid starting day 1 cycle 1. Patients with no disease progression after four cycles continued sorafenib 400 mg orally bid as maintenance for maximum of 12 months. The primary endpoint was 1 year survival with response rate and safety as secondary endpoints. Results A total of 18 patients were enrolled with 17 evaluable patients. One patient had a complete response, seven patients had a partial response (overall response rate of 47 %) and one patient had stable disease. Overall median survival was 7.4 months and 1 year survival was 25 %. The most common treatment-related adverse events included fatigue, anorexia, rash, diarrhea, neutropenia and weight loss. Grade 5 GI bleeding, pulmonary hemorrhage and neutropenia occurred in one pt (6 %) each. Accrual was halted on the basis of safety profile as well as preliminary efficacy data. Conclusions The combination of platinum based chemotherapy and sorafenib has significant toxicity at current dose levels and is associated with disappointing efficacy data.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61:212–236
Seifter EJ, Ihde DC (1988) Therapy of small cell lung cancer: a perspective on two decades of clinical research. Semin Oncol 15:278–299
Hanna N, Bunn PA Jr, Langer C et al (2006) Randomized phase III trial comparing irinotecan/cisplatin with etoposide/cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:2038–2043
Schiller JH, Adak S, Cella D, DeVore RF 3rd, Johnson DH (2001) Topotecan versus observation after cisplatin plus etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: E7593–a phase III trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 19:2114–2122
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D et al (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24:4539–4544
Braghiroli MI, Sabbaga J, Hoff PM (2012) Bevacizumab: overview of the literature. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 12:567–580
Lucchi M, Mussi A, Fontanini G, Faviana P, Ribechini A, Angeletti CA (2002) Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC): the angiogenic phenomenon. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 21:1105–1110
Ruotsalainen T, Joensuu H, Mattson K, Salven P (2002) High pretreatment serum concentration of basic fibroblast growth factor is a predictor of poor prognosis in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:1492–1495
Salven P, Ruotsalainen T, Mattson K, Joensuu H (1998) High pre-treatment serum level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with poor outcome in small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 79:144–146
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L et al (2004) BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:7099–7109
Zhang J, Gold KA, Kim E (2012) Sorafenib in non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21:1417–1426
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM et al (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:125–134
Litz J, Sakuntala Warshamana-Greene G, Sulanke G, Lipson KE, Krystal GW (2004) The multi-targeted kinase inhibitor SU5416 inhibits small cell lung cancer growth and angiogenesis, in part by blocking Kit-mediated VEGF expression. Lung Cancer 46:283–291
Abrams TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Pryer NK, Cherrington JM (2003) SU11248 inhibits KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta in preclinical models of human small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2:471–488
Ibrahim N, Yu Y, Walsh WR, Yang JL (2012) Molecular targeted therapies for cancer: sorafenib mono-therapy and its combination with other therapies (review). Oncol Rep 27:1303–1311
Gitlitz BJ, Moon J, Glisson BS et al (2010) Sorafenib in platinum-treated patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG 0435) phase II trial. J Thorac Oncol 5:1835–1840
Ready N, Dunphy F, Pang H et al (2010) Combination chemotherapy with sunitinib (IND 74019; NSC 736511) for untreated extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC): CALGB 30504 phase IB safety results. J Clin Oncol 28:15s (suppl, abstract 7056)
Ramalingam SS, Belani CP, Mack PC et al (2010) Phase II study of Cediranib (AZD 2171), an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, for second-line therapy of small cell lung cancer (National Cancer Institute #7097). J Thorac Oncol 5:1279–1284
Arnold AM, Seymour L, Smylie M et al (2007) Phase II study of vandetanib or placebo in small-cell lung cancer patients after complete or partial response to induction chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy: National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.20. J Clin Oncol 25:4278–4284
Schneider BJ, Gadgeel SM, Ramnath N et al (2011) Phase II trial of sunitinib maintenance therapy after platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6:1117–1120
Spigel DR, Greco FA, Rubin MS et al (2012) Phase II study of maintenance sunitinib following irinotecan and carboplatin as first-line treatment for patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 7:359–364
Horn L, Dahlberg SE, Sandler AB et al (2009) Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501. J Clin Oncol 27:6006–6011
Ready NE, Dudek AZ, Pang HH et al (2011) Cisplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: CALGB 30306, a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 29:4436–4441
Spigel DR, Greco FA, Zubkus JD et al (2009) Phase II trial of irinotecan, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in the treatment of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 4:1555–1560
Spigel DR, Townley PM, Waterhouse DM et al (2011) Randomized phase II study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: results from the SALUTE trial. J Clin Oncol 29:2215–2222
Goss GD, Arnold A, Shepherd FA et al (2010) Randomized, double-blind trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel with either daily oral cediranib or placebo in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: NCIC clinical trials group BR24 study. J Clin Oncol 28:49–55
Baselga J, Segalla JG, Roche H et al (2012) Sorafenib in combination with capecitabine: an oral regimen for patients with HER2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 30:1484–1491
Kim ES, Herbst RS, Wistuba II et al (2011) The BATTLE trial: personalizing therapy for lung cancer. Cancer Discov 1:44–53
Mok TS, Paz-Ares L, Wu YL et al (2012) Association between tumor EGFR and KRAS mutation status and clinical outcomes in NSCLC patients randomized to sorafenib plus best supportive care (BSC) or BSC alone: subanalysis of the phase III MISSION trial. Ann Oncol 23:9s (suppl, abstract LBA9-PR)
Waterhouse DM, Morgan SK, Spigel DR et al (2010) Phase II study of oral topotecan plus bevacizumab (topo-bev) for second-line treatment of small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:15s (suppl, abstract 7055)
Allen JW, Moon J, Gadgeel SM et al (2012) SWOG 0802: A randomized phase II trial of weekly topotecan with and without AVE0005 (aflibercept) in patients with platinum-treated extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (E-SCLC). J Clin Oncol 30:15s (suppl, abstract 7005)
Conflict of interest
Nathan A. Pennell received research funding from Genentech and served as a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim and Oncogenex. Balazs Halmos received research funding from Daiichi Sankyo; Eli Lilly and Oncothyreon. All other authors declare no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N., Pennell, N., Nickolich, M. et al. Phase II trial of Sorafenib in conjunction with chemotherapy and as maintenance therapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs 32, 362–368 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0061-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0061-6