Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the characteristics of the late foveal response component (lfrc) that presents on the first slice of the second-order kernel (K2.1) in multifocal electroretinograms (mfERGs).
Methods
mfERGs with 37 hexagonal stimulus elements were obtained from 27 healthy subjects under a stimulus intensity of 2.67 cds/m2, base rate of 75 Hz, and a net recording time of 1 min 49.2 s, using bipolar contact lens electrodes. The responses on the centermost hexagon (with a diameter of 4.5°–5.2°) were designated as foveal mfERGs.
Results
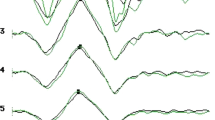
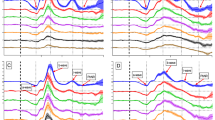
The foveal mfERG of the first-order kernel (K1) was shaped similarly to the K1 of the surrounding mfERGs. The foveal mfERG of K2.1 differed from the K2.1s of the surrounding mfERGs. This difference varied among subjects; however, the potential (0.34 ± 0.10 µV: mean ± SD) of the lfrc acutely changed at approximately 50 ms (range 48.56 ± 1.02–56.86 ± 1.99 ms). Whereas the amplitudes of the other major components of K1 and K2.1 significantly decreased with increasing refractive error, the amplitude of lfrc was not significantly correlated with refraction in this cohort.
Conclusions
The lfrc was obtained only on the centermost hexagon within an appropriate recording time (<2 min). This finding reflects the particular structure and peculiar adaptiveness of the fovea, a specialized area of the human retina, and enables the estimation of foveal function in clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutter EE, Tran D (1992) The field topography of ERG components in man—I. The photopic luminance response. Vis Res 32:433–446
Wu S, Sutter EE (1995) A topographic study of oscillatory potentials in man. Vis Neurosci 12:1013–1025
Bearse MA, Shimada Y, Sutter EE (2000) Distribution of oscillatory components in the central retina. Doc Ophthalmol 100:185–205
Palmowski AM, Allgayer R, Heinemann-Vemaleken B (2000) The multifocal ERG in open angle glaucoma—a comparison of high and low contrast recordings in high- and low-tension open angle glaucoma. Doc Ophthalmol 101:35–49
Sutter EE (2001) Imaging visual function with the multifocal m-sequence technique. Vis Res 41:1241–1255
Chan HL, Mohidin N (2003) Variation of multifocal electroretinogram with axial length. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 23:133–140
Hood DC, Odel JG, Chen CS, Winn BJ (2003) The multifocal electroretinogram. J Neuroophthalmol 23:225–235
Lai TY, Chan WM, Lai RY, Ngai JW, Li H, Lam DS (2007) The clinical applications of multifocal electroretinography: a systematic review. Surv Ophthalmol 52:61–96
Langrová H, Zrenner E, Kurtenbach A, Seeliger MW (2008) Age-related changes in retinal functional topography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:5024–5032
Hogan MJ, Alvarado JA, Weddell JE (1971) Histology of the human eye: an atlas and textbook. Saunders, Philadelphia. ISBN-13: 978-0721647203
Rodieck RW (1998) The first steps in seeing. Sinauer, Sunderland. ISBN-13: 978-0878937578
Shimada Y, Horiguchi M, Tanikawa A (2012) P50: a foveal wavelet in the nonlinear component of multifocal electroretinogram. Folia Japonica Ophthalmol Clin 5:669–673
Yamamoto S, Arai M, Kondo M, Machida S, Shinoda K (2015) Practical guide to ERG updated: from recording to analysis. Medical View, Tokyo. ISBN978-4-7583-1092-5
Kawabata H, Adachi-Usami E (1997) Multifocal electroretinogram in myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 38:2844–2851
Luu CD, Lau AM, Lee SY (2006) Multifocal electroretinogram in adults and children with myopia. Arch Ophthalmol 124:328–334
Miyake Y (2006) Electrodiagnosis of retinal diseases. Springer, Tokyo. ISBN-13: 978-4431998099
Seeliger MW, Kretschmann UH, Apfelstedt-Sylla E, Zrenner E (1998) Implicit time topography of multifocal electroretinograms. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 39:718–723
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements) or nonfinancial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Statement on the welfare of animals
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kariman, G.T.A., Shimada, Y. & Horiguchi, M. A late foveal response component of multifocal electroretinograms in healthy subjects. Doc Ophthalmol 133, 121–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-016-9562-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-016-9562-x