Abstract
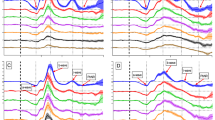
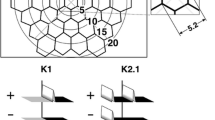
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of reference electrode location on the multifocal electroretinographic waveform. Multifocal electroretinograms (mfERGs) were recorded from 20 ocularly normal cynomolgus monkeys. The corneal electrode was an ERG-jetTM referenced to an ipsilaterally (outer canthus) situated subdermal needle electrode and to the contralateral corneal electrode. Testing was monocular and recordings from both montages were obtained simultaneously. The stimulus array consisted of 103 equal-sized hexagonal elements, which subtended ±44° about the central visual axis. Mean luminance of the display was 100 cd/m2. First-order (K1) and second-order (first slice) kernels (K2.1) of the mfERG were grouped in (a) 4 rings, representing the central 56° of visual field and (b) in 15-element quadrants. The mfERG waveform measures included amplitude, implicit time, and root mean square (RMS) of the oscillatory potentials (OP) and response waveform. K1 and K2.1 ring and quadrant amplitudes were larger with the contralateral than with the ipsilateral reference, but more notably signal-to-noise ratios (S:N) of the response waveform were always larger with the ipsilateral reference. Implicit times were longer for the contralateral than ipsilateral reference montage. K1 and K2.1 implicit times in males were longer than in females. Quadrant groupings revealed generally larger K1 and K2.1 amplitudes in nasal than in temporal retina.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- K1:
-
first-order kernel
- K2.1:
-
second-order (first slice) kernel
- mfERG:
-
multifocal electroretinogram
- OP:
-
oscillatory potentials
- RMS:
-
root mean square
- S:N:
-
signal-to-noise ratio
References
LJ Frishman S Saszik RS Harwerth S Viswanathan Y Li EL Smith JG Robson G Barnes et al. (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of experimental glaucoma in macaques on the multifocal ERG Multifocal ERG in laser-induced glaucoma Doc Ophthalmol 100 231–51 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FptVWjtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1002735804029
DC Hood LJ Frishman S Saszik S Viswanathan (2002) ArticleTitleRetinal origins of the primate multifocal ERG: implications for the human response Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43 1673–85 Occurrence Handle11980890
D Raz MW Seeliger AB Geva CL Percicot GN Lambrou R Ofri (2002) ArticleTitleThe effect of contrast and luminance on mfERG responses in a monkey model of glaucoma Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43 2027–35 Occurrence Handle12037015
D Raz I Perlman CL Percicot GN Lambrou R Ofri (2003) ArticleTitleFunctional damage to inner and outer retinal cells in experimental glaucoma Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44 3675–84 Occurrence Handle12882823 Occurrence Handle10.1167/iovs.02-1236
Vaegan PJ Anderton TJ Millar (2000) ArticleTitleMultifocal, pattern, full field electroretinograms in cats with unilateral optic nerve section Doc Ophthalmol 100 207–29 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FptVWjtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11142747 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1002793004609
CBY Kim JN Ver Hoeve PL Kaufman TM Nork (2004) ArticleTitleInterspecies and gender differences in multifocal electroretinograms of cynomolgus and rhesus macaques Doc Ophthalmol 109 73–86 Occurrence Handle15675202 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10633-004-2630-7
WW Dawson GL Trick CA Litzkow (1979) ArticleTitleImproved electrode for electroretinography Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 18 988–91 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi%2BD3cros1Q%3D Occurrence Handle478786
EE Sutter MA Bearse (1999) ArticleTitleThe optic nerve head component of the human ERG Vision Res 39 419–36 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3ntlGhsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10341974
B Fortune G Cull L Wang EM Buskirk ParticleVan GA Cioffi (2002) ArticleTitleFactors affecting the use of multifocal electroretinography to monitor function in a primate model of glaucoma Doc Ophthalmol 105 151–78 Occurrence Handle12462442 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020548919355
EE Sutter (2000) ArticleTitleThe interpretation of multifocal binary kernels Doc Ophthalmol 100 49–75 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FptVWjtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1002702917233
JV Odom TM Maida WW Dawson R Hobson (1987) ArticleTitlePattern electroretinogram: effects of reference electrode position Doc Ophthalmol 65 297–306 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieD2Mvksl0%3D Occurrence Handle3678002 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00149936
TC Prager N Saad FC Schweitzer CA Garcia GB Arden (1992) ArticleTitleElectrode comparison in pattern electroretinography Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33 390–4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2C2MrptVU%3D Occurrence Handle1740370
DL McCulloch GB Boemel ParticleVan MS Borchert (1998) ArticleTitleComparisons of contact lens, foil, fiber and skin electrodes for pattern electroretinograms Doc Ophthalmol 94 327–40 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2Fntlyjtg%3D%3D
DC Hood LJ Frishman S Viswanathan JG Robson J Ahmed (1999) ArticleTitleEvidence for a ganglion cell contribution to the primate electroretinogram (ERG): effects of TTX on the multifocal ERG in macaque Vis Neurosci 16 411–6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3nslCltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10349962 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0952523899163028
B Vainio-Mattila (1951) ArticleTitleThe clinical electroretinogram. II. The difference between the electroretinogram in men and in women Acta Ophthalmol 29 25–32 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Cy6D28jis1I%3D
I Zeidler (1959) ArticleTitleThe clinical electroretinogram. IX. The normal electroretinogram. Value of the b-potential in different age groups and its differences in men and women Acta Ophthalmol 37 294–301 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CC%2BB3Mjps1w%3D
DG Birch JL Anderson (1992) ArticleTitleStandardized full-field electroretinography. Normal values and their variation with age Arch Ophthalmol 110 1571–6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD2svls1c%3D Occurrence Handle1444914
GG Celesia D Kaufman S Cone (1987) ArticleTitleEffects of age and sex on pattern electroretinograms and visual evoked potentials Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 68 161–71 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiC1M%2FgtFc%3D Occurrence Handle2436875
PL Kaufman BT Calkins KA Erickson (1981) ArticleTitleOcular biometry of the cynomolgus monkey Curr Eye Res 1 307–9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2D2s7kvVY%3D Occurrence Handle7307539
MP Hennessy Vaegan (1995) ArticleTitleAmplitude scaling relationships of Burian–Allen, gold foil and Dawson, Trick and Litzkow electrodes Doc Ophthalmol 89 235–48 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymD2MzmvVc%3D Occurrence Handle7555591 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01203377
AM Komáromy DE Brooks WW Dawson ME Källberg FJ Ollivier R Ofri (2002) ArticleTitleTechnical issues in electrodiagnostic recording Vet Ophthalmol 5 85–91 Occurrence Handle12071864
D Keating S Parks A Evans (2000) ArticleTitleTechnical aspects of multifocal ERG recording Doc Ophthalmol 100 77–98 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FptVWjug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1002723501303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C.B.Y., VerHoeve, J.N., Kaufman, P.L. et al. Effects of Reference Electrode Location on Monopolar-derived Multifocal Electroretinograms in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Doc Ophthalmol 111, 113–125 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-005-4781-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-005-4781-6