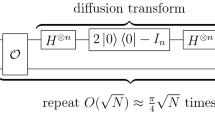
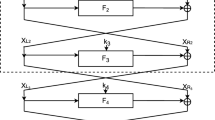
Abstract
Farfalle is a permutation-based construction for building a pseudorandom function which has been proposed by Bertoni et al. in 2017. In this work, we show that by observing suitable inputs to Farfalle, one can derive various constructions of a periodic function with a period that involves a secret key. As this admits the application of Simon’s algorithm in the so-called Q2 attack model, we further show that in the case when internal rolling function is linear, then the secret key can be extracted under feasible assumptions. Furthermore, using the provided constructions of periodic functions for Farfalle, we show that one can mount forgery attacks on the session-supporting mode for authenticated encryption (Farfalle-SAE) and the synthetic initial value AE mode (Farfalle-SIV). In addition, as the wide block cipher mode Farfalle-WBC is a 4-round Feistel scheme, a quantum distinguisher is constructed in the case when input branches are containing at last two blocks, where length of one block corresponds to the size of a permutation employed in Farfalle (a similar attack can be mounted to Farfalle-WBC-AE). And finally, we consider the problem of extracting a secret round key out of different periods obtained from a (Generalized) Feistel scheme (GFN), which has not been addressed in any of the previous works which consider the application of Simon’s (or Simon-Grover) algorithm to round reduced versions of GFNs. In this part, we assume that the key is added to an input of an inner function utilized in the round function of a given GFN. By applying two different interpolation formulas, we show that one can extract the round key by utilizing amount of different periods which is closely related to the polynomial/algebraic degree of underlying inner function. Our methods can be seen as an extension of existing quantum attacks on key-alternating GFNs based on Simon’s or Simon-Grover algorithms.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Figure generated with modified TikZ script from [22]
Let g be a Boolean function. A fast point, say \(\sigma \), is a vector for which \(deg_{alg}(D_{\sigma }g)=deg_{alg}(g)-2.\)
References
Bernstein D.J.: Some challenges in heavyweight cipher design. Presented at Dagstuhl seminar on Symmetric Cryptography, Schloss Dagstuhl (2016).
Bertoni G., Daemen J., Peeters M., Van Assche G.: The Keccak reference. http://keccak.noekeon.org/ , Available at: https://keccak.team/files/Keccak-reference-3.0.pdf.
Bertoni G., Daemen J., Hoffert S., Peeters M., Van Assche G., Keer R.V.: Farfalle: parallel permutation-based cryptography. IACR Trans. Symmetric Cryptol. 2017(4), 1–38 (2017).
Bogdanov A., Knudsen L.R., Leander G., Paar C., Poschmann A., Robshaw M.J.B., Seurin Y., Vikkelsoe C.: PRESENT: An ultra-lightweight block cipher. Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES, LNSC, Vol. 4727, pp. 450–466 (2007).
Bonnetain X., Hosoyamada A., Plasencia M.N., Sasaki Y., Schrottenloher A.: Quantum Attacks without superposition queries: The offline Simon algorithm. In: Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2019, LNCS, Vol. 11921, pp. 552–583 (2019).
Bonnetain X., Leurent G., Plasencia M.N., Schrottenloher A.: Quantum linearization attacks. Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2021, LNCS, Vol. 13090, pp. 422–452 (2021).
Bonnetain X.: Quantum key-recovery on full AEZ. Security and Cryptology, Selected Areas in Cryptography—SAC,: 24th International Conference. Ottawa, ON, Canada 2017, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72565-9, 16–18, pp. 3941–406.
Carlet C.: Boolean functions for cryptography and coding theory. Cambridge University Press, New York (2020). https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108606806.
Carlet C., Charpin P., Zinoviev V.: Codes, bent functions and permutations suitable for DES-like cryptosystems. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 15, 125–156 (1998).
Childs A.M., van Dam W., Hung S.-H., Shparlinski I.E.: Optimal quantum algorithm for polynomial interpolation. In: 43rd International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming, ICALP 2016—Rome, Italy, LIPIcs Vol. 55, pp. 1–13 (2016).
Cid C., Hosoyamada A., Liu Y., Sim S.M.: Quantum cryptanalysis on contracting Feistel structures and observation on related-key settings. In: Progress in Cryptology—INDOCRYPT 2020: 21st International Conference on Cryptology in India, Bangalore, India, December 13–16, pp. 373–394 (2020).
Daemen J., Hoffert S., Assche G.V., Keer R.V.: Xoodoo cookbook. In: IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive (2018). https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/767.
Daemen J., Hoffert S., Assche G.V., Keer R.V.: The design of Xoodoo and Xoofff. IACR Trans. Symmetric Cryptol. 2018(4), 1–38 (2018).
Dong X., Li Z., Wang X.: Quantum cryptanalysis on some generalized Feistel schemes. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 62, 22501 (2019).
Dong X., Dong B., Wang X.: Quantum attacks on some Feistel block ciphers. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 88(6), 1179–1203 (2020).
Feistel H., Notz W.A., Smith J.L.: Some cryptographic techniques for machine-to-machine data communications. Proc. IEEE 63(11), 1545–1554 (1975).
Ghosh S., Sarkar P.: Breaking tweakable enciphering schemes using Simon’s algorithm. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 89, 1907–1926 (2021).
Grover L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, May 22–24, pp. 212–219 (1996).
Hodžić S., Knudsen L.R., Kidmose A.B.: On quantum distinguishers for Type-3 Generalized Feistel Network based on separability. In: International Conference on Post-Quantum Cryptography, PQCrypto 2020, LNCS vol. 12100, pp. 461–480 (2020).
Hodžić S., Knudsen L.R.: A quantum distinguisher for 7/8-round SMS4 block cipher. Quant. Inf. Process. 19(11), 411 (2020).
Ito G., Hosoyamada A., Matsumoto R., Sasaki Y., Iwata T.: Quantum chosen-ciphertext attacks against Feistel ciphers. In: Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference, CT-RSA 2019: Topics in Cryptology—CT-RSA 2019, LNCS vol. 11405, pp. 391–411 (2019).
Jérémy Jean TikZ for Cryptographers https://www.iacr.org/authors/tikz/.
Kaplan M., Leurent G., Leverrier A., -Plasencia M.N.: Breaking symmetric cryptosystems using quantum period finding. In: CRYPTO 2016: Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2016, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, LNCS Vol. 9815, pp. 207–237 (2016).
Kuwakado H., Morii M.: Security on the quantum-type Even-Mansour cipher. In: International Symposium on Information Theory and its Applications, October 28–31, Honolulu, HI, USA (2012).
Kuwakado H., Morii M.: Quantum distinguisher between the 3-round Feistel cipher and the random permutation. IEEE Int. Symp. Inf. Theory (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISIT.2010.5513654.
Lai X.: Higher order derivatives and differential cryptanalysis. Commun. Cryptogr. SECS 276, 227–233 (1994).
Leander G., May A.: Grover meets Simon—quantumly attacking the FX-construction. In: Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2017, International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, LNCS, Vol. 10625, pp. 161–178 (2017).
Liskov M., Rivest R.L., Wagner D.: Tweakable block ciphers. J. Cryptol. 24(3), 588–613 (2011).
Miller K.S.: On the inverse of the sum of matrices. Math. Mag. 54(2), 67–72 (1981).
Mullen G.L., Panario, D.: Handbook of finite fields. Published by Chapman and Hall/CRC, ISBN 9781439873786, July 18 (2013).
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).: SHA-3 Standard: Permutation-based hash and extendable-output functions. In: Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 202. https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.FIPS.202.
Simon D.R.: On the power of quantum computation. SIAM J. Comput. 26(5), 1474–1483 (1997).
Stoss H.J.: The complexity of evaluating interpolation polynomials. Theor. Comput. Sci. 41, 319–323 (1985).
Wu C.-K., Feng D.: Boolean functions and their applications in cryptography. In: Advances in Computer Science and Technology. Springer, Berlin (2016).
Xu L., Guo J., Cui J., Li M.: Key-recovery attacks on LED-like block ciphers. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 24(5), 585–595 (2019).
Xu Y., Liu W., Yu W.: Quantum forgery attacks on COPA, AES-COPA and marble authenticated encryption algorithms. Quant. Inf. Process. 20(4), 1–21 (2021).
Youssef A.M., Gong G.: On the interpolation attacks on block ciphers. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, pp. 109–120 (2000).
Zhongya Z., Wenling W., Han S., Bolin W.: Quantum attacks on Type-3 generalized Feistel scheme and unbalanced Feistel scheme with expanding functions. Chin. J. Electron. 31(4), 1–9 (2022).
Zhou B.-M., Yuan Z.: Quantum key-recovery attack on Feistel constructions: Bernstein-Vazirani meet Grover algorithm. Quant. Inf. Process. 20(330), 1–14 (2021).
Acknowledgements
Samir Hodžić is supported by the Slovenian Research Agency (research program P1-0404 and research projects J1-4084 and N1-1059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Iwata.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hodžić, S., Roy, A. & Andreeva, E. Quantum cryptanalysis of Farfalle and (generalised) key-alternating Feistel networks. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 92, 227–257 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-023-01305-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-023-01305-6