Abstract
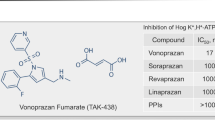
Although proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have been used widely, acid-related diseases are still associated with a huge burden on the health care system. Recently, the efficacy and safety of a new acid suppressant named vonoprazan in the treatment of acid-related diseases have been evaluated by a series of studies. As a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vonoprazan may provide reversible acid suppression by preventing K+ from binding to gastric H+/K+-ATPase. It has been clinically used for the short-term treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in Japan. The healing rate of GERD and gastric ulcers by vonoprazan is more than 95 and 90%, respectively; also, it is effective in curing PPI-resistant GERD. It increases H. pylori eradication rate to more than 88% as part of both first-line and second-line therapy. It is also effective in the eradication of clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori strains. All of these short-term studies show vonoprazan is safe and well-tolerated. As a safe and effective acid inhibitor, vonoprazan might be a novel alternative in the treatment of acid-related diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mejia A, Kraft WK. Acid peptic diseases: pharmacological approach to treatment. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2009;2:295–314.
Ganser AL, Forte JG. K+-stimulated ATPase in purified microsomes of bullfrog oxyntic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.. 1973;307:169–180.
Malfertheiner P. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of H. pylori infection. MMW Fortschr Med. 2003;145:42–45.
Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut. 2017;66:6–30.
Fallone CA, Chiba N, van Zanten SV, et al. The Toronto consensus for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in adults. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:e14.
Sakurai Y, Mori Y, Okamoto H, et al. Acid-inhibitory effects of vonoprazan 20 mg compared with esomeprazole 20 mg or rabeprazole 10 mg in healthy adult male subjects–a randomised open-label cross-over study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42:719–730.
Chey WD, Mody RR, Izat E. Patient and physician satisfaction with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): are there opportunities for improvement? Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:3415–3422.
Sachs G, Shin JM, Munson K, et al. Review article: the control of gastric acid and Helicobacter pylori eradication. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.. 2000;14:1383–1401.
Kondo M, Kawamoto M, Hasuoka A, Kajino M, Inatomi N, Tarui N. High-throughput screening of potassium-competitive acid blockers. J Biomol Screen. 2012;17:177–182.
Garnock-Jones KP. Vonoprazan: first global approval. Drugs. 2015;75:439–443.
Keeling DJ, Taylor AG, Schudt C. The binding of a K+ competitive ligand, 2-methyl,8-(phenylmethoxy)imidazo(1,2-a)pyridine 3-acetonitrile, to the gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:5545–5551.
Scott DR, Munson KB, Marcus EA, Lambrecht NW, Sachs G. The binding selectivity of vonoprazan (TAK-438) to the gastric H+, K+-ATPase. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42:1315–1326.
Shin JM, Kim N. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the proton pump inhibitors. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;19:25–35.
Shin JM, Inatomi N, Munson K, et al. Characterization of a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker of the gastric H, K-ATPase, 1-[5-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanamine monofumarate (TAK-438). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;339:412–420.
Hori Y, Imanishi A, Matsukawa J, et al. 1-[5-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanamine monofumarate (TAK-438), a novel and potent potassium-competitive acid blocker for the treatment of acid-related diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;335:231–238.
Jenkins H, Sakurai Y, Nishimura A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repeated doses of TAK-438 (vonoprazan), a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, in healthy male subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:636–648.
Arikawa Y, Nishida H, Kurasawa O, et al. Discovery of a novel pyrrole derivative 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanamin e fumarate (TAK-438) as a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB). J Med Chem. 2012;55:4446–4456.
Sakurai Y, Nishimura A, Kennedy G, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of single rising TAK-438 (vonoprazan) doses in healthy male Japanese/non-Japanese subjects. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2015;6:e94.
Inatomi N, Matsukawa J, Sakurai Y, Otake K. Potassium-competitive acid blockers: advanced therapeutic option for acid-related diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;168:12–22.
Kagami T, Sahara S, Ichikawa H, et al. Potent acid inhibition by vonoprazan in comparison with esomeprazole, with reference to CYP2C19 genotype. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:1048–1059.
Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol.. 2013;108:308–328. (quiz 329).
El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J. Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2014;63:871–880.
Ashida K, Sakurai Y, Nishimura A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: a dose-ranging study of vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. lansoprazole for the treatment of erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42:685–695.
Ashida K, Sakurai Y, Hori T, et al. Randomised clinical trial: vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. lansoprazole for the healing of erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:240–251.
Iwakiri K, Umegaki E, Hiramatsu N, et al. Su1119 A Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study to evaluate the dose-response relationships of acid-inhibitory effect of vonoprazan (20 mg, 40 mg) in patients with proton pump inhibitor-resistant erosive esophagitis [Abstract]. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:S475–S475.
Hanada Y, Hoshino S, Hoshikawa Y, et al. Su1120 efficacy of vonoprazan on PPI-resistant reflux esophagitis [Abstract]. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:S475–S475.
Koike T, Saito M, Kikuchi H, et al. Vonoprazan reduces the GERD symptoms in the symptom index positive PPI-refractory NERD. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:21.
Asaoka D, Nagahara A, Hojo M, et al. Efficacy of a potassium-competitive acid blocker for improving symptoms in patients with reflux esophagitis, non-erosive reflux disease, and functional dyspepsia. Biomed Rep. 2017;6:175–180.
Maruoka D, Arai M, Kasamatsu S, et al. Vonoprazan is superior to proton pump inhibitors in healing artificial ulcers of the stomach post-endoscopic submucosal dissection: A propensity score-matching analysis. Dig Endosc. 2017;29:57–64.
Kagawa T, Iwamuro M, Ishikawa S, et al. Vonoprazan prevents bleeding from endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced gastric ulcers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44:583–591.
Tsuchiya I, Kato Y, Tanida E, et al. Effect of vonoprazan on the treatment of artificial gastric ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection: prospective randomized controlled trial. Dig Endosc. 2017;29:576–583.
Takahashi K, Sato Y, Kohisa J, et al. Vonoprazan 20 mg vs lansoprazole 30 mg for endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced gastric ulcers. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;8:716–722.
Hiroyuki K, Hiroya U, Akihito N, et al. # 1505 Vonoprazan versus rabeprazole for the healing effect of gastric ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:291.
Mizokami Y, Ashida K, Soen S, et al. Tu1054 TAK-438 versus lansoprazole 15 mg for secondary prevention of peptic ulcers associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) therapy: results of a Phase 3 trial. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:S739.
Kawai T, Ashida K, Mizokami Y, et al. Tu1055 TAK-438 versus lansoprazole 15 mg for secondary prevention of peptic ulcers associated with low-dose aspirin therapy: results of a Phase 3 trial [Abstract]. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:S739.
Sakurai Y, Shiino M, Horii S, et al. Pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions between vonoprazan and low-dose aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a Phase 2, open-label, study in healthy Japanese men. Clin Drug Invest. 2017;37:39–49.
Miwa H, Uedo N, Watari J, et al. Randomised clinical trial: efficacy and safety of vonoprazan vs. lansoprazole in patients with gastric or duodenal ulcers—results from two phase 3, non-inferiority randomised controlled trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45:240–252.
Suzuki S, Gotoda T, Kusano C, Iwatsuka K, Moriyama M. The efficacy and tolerability of a triple therapy containing a potassium-competitive acid blocker compared with a 7-day PPI-based low-dose clarithromycin triple therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:949–956.
Shinozaki S, Nomoto H, Kondo Y, et al. Comparison of vonoprazan and proton pump inhibitors for eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016;32:255–260.
Shichijo S, Hirata Y, Niikura R, et al. Vonoprazan versus conventional proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy as first-line treatment against Helicobacter pylori: a multicenter retrospective study in clinical practice. J Dig Dis. 2016;17:670–675.
Noda H, Noguchi S, Yoshimine T, et al. A novel potassium-competitive acid blocker improves the efficacy of clarithromycin-containing 7-day triple therapy against Helicobacter pylori. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2016;25:283–288.
Yamada S, Kawakami T, Nakatsugawa Y, et al. Usefulness of vonoprazan, a potassium ion-competitive acid blocker, for primary eradication of Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016;7:550–555.
Murakami K, Sakurai Y, Shiino M, Funao N, Nishinura A, Asaka M. Vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, as a component of first-line and second-line triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a phase III, randomised, double-blind study. Gut. 2016;65:1439–1446.
Maruyama M, Kubota D, Miyajima M, et al. Tu2083 A randomized controlled trial comparing the first-line eradication rate using vonoprazan or PPI for Helicobacter pylori infectious gastritis [Abstract]. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:S1269–S1269.
Matsumoto H, Shiotani A, Katsumata R, Fujita M, Nakato R, Murao T. Helicobacter pylori Eradication with proton pump inhibitors or potassium-competitive acid blockers: the effect of clarithromycin resistance. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61:3215–3220.
Sakurai Y, Shiino M, Okamoto H, Nishimura A, Nakamura K, Hasegawa S. Pharmacokinetics and safety of triple therapy with vonoprazan, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin or metronidazole: a Phase 1, open-label, randomized, crossover study. Adv Ther. 2016;33:1519–1535.
Yamasaki T, Owari M, Amano Y, et al. High dose CAM with vonoprazan (P-CAB) plus AMX regimen is the strongest H. pylori eradication triple therapy regimens to improve success rate of CAM based regimens. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:61.
Graham DY. Vonoprazan Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: ethical and interpretation issues. Gut. 2017;66:384–386.
Furuta T, Shu S, Ichikawa H, et al. Tu1333 dual therapy with vonoprazan and amoxicillin is as effective as standard PPI-based triple therapy with amoxicillin and clarithromycin or metronidazole in Japan [Abstract]. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:S877–S877.
Sato Yu, Yamamoto K, Onishi Y, et al. Efficacy of the vonoprazan (VPZ)-based second line therapy for Helicobacter pylori (HP) eradication. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:67.
Okimoto K, Arai M, Kasamatsu S, et al. Su1027 efficacy of sitafloxacin-based triple therapy for eradication-refractory Helicobacter pylori and salvage therapy with the new potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan [Abstract]. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:S447–S447.
Kawashima K, Ishihara S, Kinoshita Y. Successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection with vonoprazan-based triple therapy after failure of PPI-based triple therapy. Dig Liver Dis. 2016;48:688–689.
Ono S, Kato M, Nakagawa S, Mabe K, Sakamoto N. Vonoprazan improves the efficacy of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy with a regimen consisting of clarithromycin and metronidazole in patients allergic to penicillin. Helicobacter. 2017;22:e12374.
Jung YS, Kim EH, Park CH. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the efficacy of vonoprazan-based triple therapy on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14130.
Dong SQ, Singh TP, Wei X, Yao H, Wang HL. A Japanese population-based meta-analysis of vonoprazan versus PPI for Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: is superiority an illusion? Helicobacter. 2017;22. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12438.
Fraser AG. Editorial: replacing standard proton pump inhibitors with vonoprazan may breathe new life into triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:550–551.
Jung YS, Kim EH, Park CH. Editorial: replacing standard proton pump inhibitors with vonoprazan may breathe new life into triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori-authors’ reply. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:551–552.
Me P, Dj K. Novel approaches to the pharmacological blockade of gastric acid secretion. Expert Opin Invest Drugs. 2005;14:411–421.
Kahrilas PJ, Dent J, Lauritsen K, Malfertheiner P, Denison H, Franzén S. A randomized, comparative study of three doses of AZD0865 and esomeprazole for healing of reflux esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:1385–1391.
Kamiya K, Nishio E, Horio A, Tokura Y. Erythema multiforme caused by triple therapy with amoxicillin, clarithromycin and vonoprazan for Helicobacter pylori. J Dermatol. 2016;43:340–341.
Johnson DA, Katz PO, Armstrong D, et al. The safety of appropriate use of over-the-counter proton pump inhibitors: an evidence-based review and Delphi consensus. Drugs. 2017;77:547–561.
Abe K, Tani K, Fujiyoshi Y. Systematic comparison of molecular conformations of H+, K+-ATPase reveals an important contribution of the A-M2 linker for the luminal gating. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:30590–30601.
Acknowledgments
No financial support was received for this work from any company. This study was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (no. 81330012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Li, Y., Sun, Y. et al. Vonoprazan: A Novel and Potent Alternative in the Treatment of Acid-Related Diseases. Dig Dis Sci 63, 302–311 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4866-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4866-6