Abstract
Background/Objectives
The reported risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection is conflicting. This meta-analysis was conducted to summarize all available data and to estimate the prevalence and association between H. pylori and kidney disease and CKD.
Methods
Comprehensive literature review was conducted using MEDLINE and EMBASE database through October 2016 to identify studies that reported the prevalence or the association between H. pylori infection and non-dialysis-dependent kidney diseases or CKD. Effect estimates from the individual study were extracted and combined using random-effect, generic inverse variance method of DerSimonian and Laird.
Results
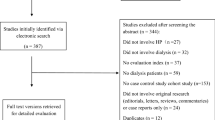
Of 4546 studies, nine cross-sectional studies met the eligibility criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. The estimated prevalence of H. pylori infection among subjects with kidney disease was 53% (95% CI 45–61%). The pooled OR of H. pylori in patients with non-dialysis-dependent kidney diseases was 1.20 (95% CI 0.73–1.97) when compared with the patients without kidney diseases. The meta-analysis was then limited to only studies evaluating the risk of H. pylori in CKD; the pooled OR of H. pylori in patients with CKD was 1.00 (95% CI 0.58–1.71).
Conclusions
The estimated prevalence of H. pylori in patients with non-dialysis-dependent kidney diseases is 53%. This study does not support the association between H. pylori infection and non-dialysis-dependent kidney diseases nor CKD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pounder RE, Ng D. The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in different countries. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995;9:33–39.
Siurala M, Sipponen P, Kekki M. Campylobacter pylori in a sample of Finnish population: relations to morphology and functions of the gastric mucosa. Gut. 1988;29:909–915.
Graham DY. Campylobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1989;96:615–625.
Jiang J, Chen Y, Shi J, Song C, Zhang J, Wang K. Population attributable burden of Helicobacter pylori-related gastric cancer, coronary heart disease, and ischemic stroke in China. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017;36:199–212.
Franceschi F, Gasbarrini A, Polyzos SA, Kountouras J. Extragastric diseases and Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter. 2015;20:40–46.
Goni E, Franceschi F. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases. Helicobacter. 2016;21:45–48.
Chang SS, Hu HY. Lower Helicobacter pylori infection rate in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease patients with peptic ulcer disease. J Chin Med Assoc: JCMA. 2014;77:354–359.
Gladziwa U, Haase G, Handt S et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1993;8:301–306.
Jaspersen D, Fassbinder W, Heinkele P et al. Significantly lower prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in uremic patients than in patients with normal renal function. J Gastroenterol. 1995;30:585–588.
Karari EM, Lule GN, McLigeyo SO, Amayo EO. Endoscopic findings and the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in chronic renal failure patients with dyspepsia. East Afr Med J. 2000;77:406–409.
Khedmat H, Ahmadzad-Asl M, Amini M et al. Gastro-duodenal lesions and Helicobacter pylori infection in uremic patients and renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2007;39:1003–1007.
Moriyama T, Kaneko T, Fujii M, Tsubakihara Y, Kawano S, Imai E. High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japanese patients with membranous nephropathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther Symp Ser. 2006;2:189–193.
Nakajima F, Sakaguchi M, Oka H et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori antibodies in long-term dialysis patients. Nephrology. 2004;9:73–76.
Nardone G, Rocco A, Fiorillo M et al. Gastroduodenal lesions and Helicobacter pylori infection in dyspeptic patients with and without chronic renal failure. Helicobacter. 2005;10:53–58.
Zhou F, Zhong X, Chen J et al. Helicobacter pylori infection associated with type 2 diabetic nephropathy in patients with dyspeptic symptoms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;110:328–334.
Ozgur O, Boyacioglu S, Ozdogan M, Gur G, Telatar H, Haberal M. Helicobacter pylori infection in haemodialysis patients and renal transplant recipients. Nephrol, Dial Transplant. 1997;12:289-291.
Shousha S, Arnaout AH, Abbas SH, Parkins RA. Antral Helicobacter pylori in patients with chronic renal failure. J Clin Pathol. 1990;43:397–399.
Ala-Kaila K. Upper gastrointestinal findings in chronic renal failure. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987;22:372–376.
Sotoudehmanesh R, Ali Asgari A, Ansari R, Nouraie M. Endoscopic findings in end-stage renal disease. Endoscopy. 2003;35:502–505.
Afsar B, Ozdemir FN, Elsurer R, Sezer S. Helicobacter pylori infection may increase renal resistive index. Med Hypotheses. 2007;69:956–957.
Ala-Kaila K, Vaajalahti P, Karvonen AL, Kokki M. Gastric Helicobacter and upper gastrointestinal symptoms in chronic renal failure. Ann Med. 1991;23:403–406.
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle–Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:603–605.
Herzog R, Alvarez-Pasquin MJ, Diaz C, Del Barrio JL, Estrada JM, Gil A. Are healthcare workers’ intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:154.
Barendregt J, Doi S. MetaXL User Guide: Version 1.0. Wilston: EpiGear International Pty Ltd; 2010.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–188.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560.
Hwang IR, Kodama T, Kikuchi S et al. Effect of interleukin 1 polymorphisms on gastric mucosal interleukin 1beta production in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1793–1803.
Wesdorp RI, Falcao HA, Banks PB, Martino J, Fischer JE. Gastrin and gastric acid secretion in renal failure. Am J Surg. 1981;141:334–338.
Borch K, Jonsson KA, Petersson F, Redeen S, Mardh S, Franzen LE. Prevalence of gastroduodenitis and Helicobacter pylori infection in a general population sample: relations to symptomatology and life-style. Dig Dis Sci. 2000;45:1322–1329.
Macenlle Garcia R, Gayoso Diz P, Sueiro Benavides RA, Fernandez Seara J. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the general adult population of the province of Ourense. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2006;98:241–248.
Tamadon MR, Saberi Far M, Soleimani A et al. Evaluation of noninvasive tests for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in hemodialysis patients. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:249–253.
Jalalzadeh M, Ghadiani MH, Mousavinasab N. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and body mass index, before and after eradication of infection in hemodialysis patients. J Nephropathol. 2012;1:170–176.
Authors’ contributions
All authors had access to the data and a role in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wijarnpreecha, K., Thongprayoon, C., Nissaisorakarn, P. et al. Association of Helicobacter pylori with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Dig Dis Sci 62, 2045–2052 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4516-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4516-z