Abstract
Introduction
The etiologies of functional dyspepsia symptoms, including postprandial distress syndrome, remain unknown. We tested the hypothesis that neonatal colon inflammation induces postprandial distress syndrome-like symptoms in adult life that associate with increased activation of vagal afferent pathways and forebrain limbic regions.
Results
These rats showed a significant decrease in nutrient meal consumption to satiety after an overnight fast, decrease in gastric emptying, decrease in total distance traveled, and decrease in percent distance traveled in midfield versus control rats in open field test, indicating postprandial anxiety- and depression-like behaviors. Adult naïve rats treated with oral iodoacetamide to induce H. pylori-like mild gastritis demonstrated similar postprandial effects as the above rats.
Conclusions
We concluded that neonatal colon inflammation is a risk factor for the development of postprandial distress syndrome-like symptoms. While mild gastritis can induce symptoms similar to those of neonatal colon inflammation, gastritis in these rats does not worsen the symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is characterized by a cluster of diverse symptoms, including epigastric pain, burning, discomfort, early satiety, impaired gastric emptying, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, and depression [1, 2]. These symptoms are heterogeneous among cohorts and may occur intermittently or continuously in individual patients. Rome III criteria classified these symptoms into two categories: postprandial distress syndrome (PDS) and epigastric pain syndrome (EPS). PDS constitutes bothersome postprandial fullness and early satiety, whereas EPS constitutes epigastric pain and burning. The temporal variation and diversity of symptoms in individual patients and their heterogeneity among cohorts suggest potential biological abnormalities of the neuromuscular apparatus in the gastric wall, afferent sensory neurons, autonomic neurons, spinal cord transmission to the CNS and central processing of the signals reaching the CNS. The temporal variations suggest sensitivity of the biological abnormalities to environmental and psychological factors. The underlying cellular mechanisms of these abnormalities remain unknown primarily because of lack of availability of live tissues from human internal organs as well as limitations of the use of interventional approaches in humans because of ethical and safety considerations.
On the other hand, epidemiological studies have identified adverse early-life experiences as risk factors for the development of FD symptoms [3, 4]. In addition, experimental clinical studies have identified hypersensitivity to gastric balloon distension, which contributes to epigastric pain in FD patients [5–8]. Taking cues from the epidemiological findings, animal studies in rodents demonstrated that neonatal colon or gastric inflammation is one of the adverse early-life experiences that upregulate sensitivity to gastric balloon distension [9, 10]. It was also demonstrated that the upregulation of nerve growth factor (NGF) in the gastric fundus and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the thoracic dorsal root ganglia and LS spinal cord as well as downregulation of Kv1.1 channels in the dorsal root ganglia underlies hypersensitivity to gastric distension [9].
Together, the above clinical and basic science findings support a potential role of splanchnic pathway sensitization in generating the symptom of epigastric pain. Less than half of FD patients demonstrate hypersensitivity to gastric distension that correlates with postprandial epigastric pain [6]. By contrast, the non-painful symptoms of PDS, such as early satiety, discomfort, and altered gastric emptying, occur following a meal [11, 12] and they may not necessarily utilize the splanchnic neuronal pathway. In this study, we investigated whether the preclinical model of neonatal colon inflammation also mimics the non-painful symptoms of FD patients, such as early satiety, discomfort, delayed gastric empting, and anxiety- and depression-like behaviors; if so which afferent neuronal pathways underlie these symptoms.
A subset of FD patients is diagnosed with H. pylori infection that causes mild chronic gastritis [13–15]. The resulting innate and adaptive immune response impairs the gastric epithelium and causes peptic ulcer disease, gastric adenocarcinoma, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Therefore, it was postulated that H. pylori infection may also target the other types of effector cells in the gastric wall, such as the afferent nerve terminals, smooth muscle cells, and enteric neurons to induce or contribute to FD-like symptoms. However, H. pylori eradication in FD patients produces little or modest improvement in symptoms in FD patients [16–18]. Accordingly, a potential role of H. pylori infection in the pathology of FD has remained uncertain. We will induce mild gastritis with oral iodoacetamide treatment in adult rats subjected previously to neonatal colon inflammation to investigate whether it contributes to the PDS symptoms, such as early satiety, discomfort, delayed gastric emptying, and anxiety-like behavior.
Overall, we will test the hypothesis that neonatal colon inflammation sensitizes the interoception circuits so that ingestion of a meal in adult life over activates the hypothalamus and limbic regions that associate with early satiety, discomfort, anxiety-like behavior, and delayed gastric emptying. We will investigate also whether mild gastritis induced by oral iodoacetamide induces similar symptoms in naïve adult rats as neonatal colon inflammation does or worsens them in rats subjected previously to neonatal colon inflammation.
Methods
Animals
Male Sprague–Dawley rats, each weighing 300–350 g, and 10-day-old male pups were used in these studies. The IACUC at UTMB approved all procedures performed on these animals.
Experimental Groups
The rats were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups: intracolonic administration of saline in 10-day-old rat pups, which received regular drinking water as adults (control rats); neonatal colon inflammation (NCI) induced by intracolonic administration of 0.2 ml of 130 mg/kg trinitrobenzene sulfonic (TNBS) acid in 10% ethanol through a catheter inserted 2 cm into the colon (NCI rats); adult gastritis (AG) induced by seven-day treatment with 0.1% iodoacetamide in drinking water (AG rats), and 10-day-old neonatal rats treated with 130 mg/kg TNBS followed by treatment with 0.1% iodoacetamide as above at 6–8 weeks of age (NCI + AG rats). Experiments were performed 7 days after the end of the above adult treatments.
Liquid Nutrient Meal Test
We investigated the effects of neonatal colon inflammation and adult gastritis on consumption volumes of liquid nutrient meals (Ensure®, homemade vanilla; Abbott Nutrition, Columbus, OH) consumed to satiety within 30 min in overnight fasted un-entrained rats. Enough Ensure® was provided to enable each rat to reach satiety. The rats were pre-exposed to the test diet to reduce neophobia and acclimatize them to wire bottom cages for 48 h before subjecting them to an overnight fast. Tissues were collected 60 min after end of the meal. Gastric emptying rates and magnitude of neuronal activation revealed by c-Fos IR in the dorsal vagal complex (DVC), central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA), and the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) were measured [19]. Stomachs were removed and contents weighed. Gastric emptying rate was expressed as: [volume of Ensure® consumed (ml)-volume of stomach contents (ml)]/Ensure® consumed (ml) × 100. A total of 47 adult rats were used, n = 11–12 in each group.
Full thickness duodenum and gastric fundus tissues were frozen for measurement of inflammatory cytokines. The numbers of c-Fos IR nuclei were counted in thoracic spinal cord segments T7-T12, DVC, CeA, and PVN by laboratory staff blinded to experimental groups. Three to five rats per group were examined (Table 1).
c-Fos and CGRP Immunohistochemistry
The rats were anaesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (100 mg/kg body weight) and were perfused transcardially with 50 ml PBS + 5U heparin/ml and then with 150 ml ice cold 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. The brains were left overnight at 4 °C in the fixative, then kept in 20% sucrose in 1× PBS at 4 °C for 24 h, and then rapidly frozen on dry ice and stored at −80 °C. The frozen brains were cut into 40-μm coronal slices using a sliding microtome (Leica SM200R, Buffalo Grove, IL). The brain sections obtained from the free-floating sections were rinsed three times in PBS, incubated for 2 h at room temperature in a blocking solution of PBS containing 5% normal goat serum, 0.3% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and were incubated with c-Fos Ab-5 1/20,000 in the blocking solution for 72 h at 4 °C with gentle agitation (EMD Chemicals, San Diego, CA). The sections were then rinsed with PBS + 0.3% Triton X-100, incubated with biotinylated secondary antibody against rabbit [1:600, Vectastin ABC kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) in the blocking solution, rinsed in PBS, incubated in avidin–peroxidase complex (ABC, reagent; Vector Laboratories), and rinsed in PBS. Neurons immunoreactive for c-Fos were visualized as brown color after a 10-min incubation in 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (SK-4100; Vector Laboratories). The brain sections were then rinsed three times in water, mounted on SuperFrost slides (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA), dried, dehydrated through graded alcohols, washed in xylenes, and cover-slipped with Organo/Limonene Mount, Sigma]. Serial sections were probed with Rabbit anti-CGRP, 1/4000, Calbiochem PC205L, and same secondary antibody procedures as used for c-Fos staining.
c-Fos Quantitation
Cells were considered c-Fos positive if their nuclei contained detectable brown immunolabeling, regardless of labeling intensity. The cells were considered c-Fos negative, if they displayed no visible nuclei or the nuclei were lacking c-Fos immunolabeling. DVC c-Fos was counted bilaterally in tissue sections through the rostro-caudal extent of the area postrema. In each rat, four tissue sections through the PVN (spaced by 80 μm) that were obtained from bregma −1 to −2 mm were selected for analysis. CGRP fiber immunolabeling was used to distinguish the boundaries of the CeA in sections between bregma −2.3 and −3 mm. c-Fos-positive profiles were counted in 4–6 sections/rat. Regional cell count data for each rat are expressed as the number of cells counted in each region unilaterally divided by the number of analyzed tissue sections through the region (Table 1).
Evaluation of Gastric Inflammation
Gastric tissues were evaluated for inflammation by measuring expression of inflammatory cytokines by quantitative RT-PCR. RNA was isolated using Qiagen RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). RT was performed using super script III kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) followed by SYBR green PCR (Life technologies, Grand Island, NY). PCR was performed on a Step One Plus (Applied Biosystems now Thermo Fisher), and fold change relative to control was calculated with the DDCt method with 18S as the normalizer. Primer sequences are: IL-12 F-GCACTTCAGAGCCACAATCA R-GGAGCTTTCTGGTGCAGAGT, IL-1β F-TGAAGCAGCTATGGCAACTG R-ATCTTTTGGGGTCTGTCAGC, TNF-α F-GCCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCT R-GATCTGAGTGTGAGGGTCTGG, IL-10 F-TTTGAATTCCCTGGGAGAGA R-TCTTCACCTGCTCCACTGC, INF-γ F-CGAATCGCACCTGATCACTA R-CTGGATCTGTGGGTTGTTCA, IL-6 F-TCCAGAAATACAAAGAAATGAT R-GGTAGAAACGGAACTCCAGAA.
Open Field Test
We used open field test (OFT) to measure the effects of Ad lib nutrient meal consumption after an overnight fast on open field activity in Ctr., NCI, and NCI + AG rats. The rats were placed in an open field consisting of a 60 × 60 cm box with 30-cm-high walls around. The floor was divided into a center (20 × 20 cm) and peripheral areas. The rats were placed individually in the center always facing the same direction, and they were video-recorded for 10 min. The recordings were evaluated in a blinded fashion. The locomotor activity was measured by the total distance traveled. For anxiety, distance traveled in the center area of the field expressed as a percentage of the total distance traveled was measured. Separate groups of naïve adult rats received either 0.2 ml of 0.15 M LiCl or 0.9% saline (control) 30 min prior to testing.
Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed using Sigmaplot 12.0. The treatment group data are expressed as mean ± SE. Meal consumption, gastric emptying, and c-Fos data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. Otherwise, t-test was used where appropriate. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Early Satiety, Delayed Gastric Emptying, and Discomfort in NCI, AG, and NCI + AG Rats
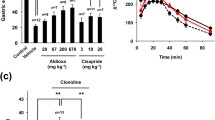
The volume of Ensure consumed to satiety after an overnight fast was significantly less in NCI than in control rats (Fig. 1a; 14.6 ± 1 ml vs. 20.6 ± 1 ml, p < 0.001, F 1,46 = 14.0, p < 0.001). The percent gastric emptying was significantly reduced in NCI rats versus control rats (Fig. 1b; 20.6 ± 3% vs. 34.6 ± 2%, p < 0.001, F 1,51 = 8.0, p = 0.007). The induction of adult gastritis by iodoacetamide in naïve rats decreased Ensure consumption to satiety by the same degree as that in NCI rats (Fig. 1a). However, the reduction in gastric emptying by adult gastritis in naïve rats was significantly greater than in NCI rats (p = 0.001); AG in NCI rats did not decrease gastric emptying greater than that in AG rats (Fig. 1b).
Nutrient meal test results. a The volumes of Ensure consumed to satiety after an overnight fast by NCI, AG, and NCI + AG rats were significantly less than those consumed by control rats (two-way ANOVA: neonatal treatment, F 1.,46 = 14.0, p < 0.001, adult gastritis, F 1.,46 = 6.75, p < 0.013; Ctr. vs. NCI, p < 0.001; Ctr. vs. AG, p < .001; Ctr. vs. NCI + AG, p < 0.001). b Graphs showing the percent of Ensure emptied from the stomach at 1.5 h after the start of meal consumption (two-way ANOVA, F 1,51 = 8.0, p = 0.007 for NCI–AG interaction; Ctr. vs. NCI, p < 0.001; NCI vs. NCI + IAG, p < 0.001). *p < 0.01 versus Ctr.; # p < 0.01 versus NCI, n = 12
Open field test results following the consumption of Ensure meal to satiety after an overnight fast indicated discomfort/anxiety/fear in NCI rats. The NCI and NCI + AG rats traveled significantly shorter total distances than the control rats (Fig. 2a; p = 0.038 and p = 0.004, respectively, F 2,54 = 3.26, p = 0.049 and F 1,54 = 7.68, p = 0.008, respectively). In addition, the NCI and NCI + AG rats traveled significantly less percent distances in the midfield compared to that of the control rats (Fig. 2b; p = 0.043 and p = 0.005, respectively; F 2,54 = 3.26, p = 0.049 and F 1,54 = 7.92, p = 0.007, respectively). By contrast, the total distance traveled and the percent distance traveled midfield by the NCI or NCI + AG rats fed Ad lib overnight were not significantly different from those by the control rats (Fig. 2c, d), suggesting that the behavioral changes in NCI and NCI + AG rats were in response to meal ingestion after an overnight fast.
Open field test results. a Bar graphs showing mean total distances traveled in the open field by Ctr., NCI, and NCI + AG rats following Ensure meal consumption. b Bar graphs showing the mean percent distance traveled in the midfield of the open field by Ctr., NCI, and NCI + AG rats following nutrient meal consumption; p = 0.043 and p = 0.005, respectively; F 2,54 = 3.26, p = 0.049 and F 1,54 = 7.92, p = 0.007, respectively). c Bar graphs showing mean total distances traveled Ctr., NCI, and NCI + AG rats fed Ad lib. d Bar graphs showing the percent distance traveled in the middle field by Ctr., NCI, and NCI + AG rats fed Ad lib
c-Fos Activity in Brain Regions
We investigated whether the consumption of Ensure meal to satiety activated c-Fos IR neurons in the DVC, CeA, and PVN of control, NCI, AG, and NCI + AG rats. The c-Fos reactive neurons in these regions were undetectable after an overnight fast in each group of rats (data not shown). The average numbers of c-Fos IR nuclei/section were significantly greater in NCI, AG, and NI + AG rats compared to controls in DVC, CeA, and PVN (Table 1; Figs. 3a–c, 4). The c-Fos IR in AG rats was significantly greater than that in NCI rats only in the DVC. The activation of c-Fos IR neurons in NCI + AG rats was greater than in Ctr. and NCI rats in all three brain regions. However, activation of c-Fos IR in NCI + AG rats was greater than that in AG rats only in the DVC and PVN. We noted that regardless of the different average volumes of Ensure consumed by the four groups of rats in c-Fos studies, the average volumes of liquid retained in the stomach were not significantly different among the different groups at euthanasia, primarily because of concurrent decreases in meal consumption and rate of gastric emptying. Negligible c-Fos IR was detected in spinal cord segments T9–T12 (Fig. 3d).
Bar graphs depicting the numbers of c-Fos IR neurons in a DVC (neonatal treatment F 1,15 = 11.3, p = 0.006; adult gastritis F 1,15 = 46, p < 0.001), b CeA (neonatal treatment F 1,15 = 20.3, p < 0.001; adult gastritis F 1,15 = 23.3, p < 0.001), and c PVN (neonatal treatment F 1,15 = 30.7, p < 0.001; adult gastritis F 1,15 = 21.8, p < 0.001). *p < 0.05 versus Ctr.; @ p < 0.05 versus NCI; # p < 0.05 versus AG
Interoceptive Neural Circuit Activation and Early Satiety and Discomfort-/Fear-/Anxiety-Like Behaviors
Lithium chloride (LiCl) activates interoceptive neural circuits in the brain, including DVC, CeA, and PVN [20]. We investigated whether LiCl-induced activation of interoceptive neural circuits was associated with early satiety and discomfort-/fear-/anxiety-like behaviors in naïve adult rats. LiCl was administered to naïve adult rats 30 min before nutrient meal consumption and open field test. LiCl treatment significantly decreased Ensure meal consumption (Fig. 5a, p < 0.02, t-test) and the total distance traveled (Fig. 5b, p < 0.001, t-test) as well as the percent distance traveled in midfield (Fig. 5c, p < 0.001, t-test) vs. saline-treated control rats.
Effects of LiCl treatment on meal consumption and open field activity. a Bar graphs showing mean volumes of ensure consumed by naïve adult control rats treated i.p. with 0.15 M NaCl or 0.15 M LiCl (n = 6, *p < 0.02). b Bar graph showing mean total distances traveled in the open field by control rats treated i.p. with 0.15 M NaCl or 0.15 M LiCl (n = 6, *p < 0.001) following nutrient meal consumption. c Bar graph showing the mean percent distance traveled in the middle of the open field by control rats treated i.p. with 0.15 M NaCl or 0.15 M LiCl (n = 6, *p < 0.001) following nutrient meal consumption
Gastric Fundus and Duodenal Inflammation in Ctr., NCI, AG and NCI + AG Rats
We investigated whether the upregulation of some of the key classical proinflammatory cytokines were associated with gastric emptying, and discomfort and anxiety-like behavior. The mRNA levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-12 were not significantly different between the gastric fundi of the NCI and NCI + AG versus the control rats (Fig. 6a–c). However, INF-γ and IL-6 mRNAs were significantly increased in the gastric fundus of the NCI versus the control rats (Fig. 6d). In NCI + AG rats, only IL-6 was upregulated versus the control rats (Fig. 6e). In the duodenum, NCI or NCI + AG caused no significant change in the expression of cytokines mRNAs we investigated, except that NCI + AG suppressed the expression of IL-1β mRNA (Fig. 7).
Bar graphs showing cytokine mRNA levels normalized to 18S RNA in the fundus of control, NCI, AG, and NCI + AG rats, n = 6. a IL-1β. (F = 1.98, p = 0.15). b TNF-α (F = 0.86, p = 0.48). c IL-10 (F = 1.9, p = 0.17). d IL-12 (F = 1.2, p = 0.354). e INF-γ (F = 4.23, p = 0.019). f IL-6 (F = 12.8, p < 0.001)
Bar graphs showing cytokine mRNA levels normalized to 18S RNA in the duodenum of control, NI, adult gastritis, and NI + IA rats, n = 6. a IL-1β (F = 4.91, p = 0.01). b TNF-α (F = 1.55, p = 0.233). c IL-10 (F = 0.9, p = 0.42). d IL-12 (F = 1.1, p = 0.383). e INF-γ (F = 0.095, p = 0.962). f IL-6 (F = 0.63, p = 0.6)
Discussion
Previous preclinical studies [9, 10, 21] support epidemiological findings that adverse early-life experiences are risk factors for the development of functional dyspepsia [3, 4]. The preclinical studies demonstrated that neonatal colon or gastric inflammation/irritation enhances sensitivity to gastric balloon distention, and it induces anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in response to psychological stress in later life [9, 10, 21]. However, the PDS symptoms in FD patients occur following the ingestion of a meal that only modestly distends the gastric wall as compared with balloon distension to induce the sensation of epigastric pain [8, 22]. Our findings advance the field by demonstrating that neonatal colon inflammation induces the symptoms of postprandial distress syndrome, including early satiety, reduced meal consumption, delayed gastric emptying, and anxiety-like and depression-like behaviors in response to the ingestion of a nutrient meal to satiety after an overnight fast in later life.
Experimental clinical studies showed that ingestion of a large nutrient meal initially relaxes the proximal stomach followed by a modest increase in wall tension that generates intra-gastric pressures of about 10 mm Hg [5, 8]. The suppression of this wall tension by sumatriptan or clonidine relieved some FD symptoms [23]. Our findings agree with the clinical findings. We noted that the postprandial affective disorders were present in rats subjected previously to neonatal colon inflammation only after the consumption of a nutrient meal to satiety after an overnight fast; they were absent when these rats were fed Ad lib overnight. Together, the clinical and preclinical findings suggest that consumption of small meals at a time may suppress some of the aversive postprandial symptoms.
Our findings show that mild gastritis induced by iodoacetamide decreases nutrient meal consumption, rate of gastric emptying; these effects are similar to those in adult rats subjected previously to neonatal colon inflammation, except that decrease in gastric emptying rate was greater in AG than in NCI rats. The notable finding was that the induction of gastritis in NCI rats did not significantly enhance the above adverse effects of NCI, which suggests that each insult may induce nearly maximal adverse effects and their individual contributions to the symptoms are not additive. The eradication of H. pylori infection in a wide majority of FD patients with this infection makes little or minimal improvement in FD symptoms [16, 24, 25]. Our findings may explain the lack of symptom improvements at least in those FD patients with childhood infections as their underlying etiology. The modest, but significant, improvement in symptoms in about 10% of the FD patients might be because these patients had a greater severity of H. pylori infection, which was not recorded in those studies.
The open field test measures general locomotor activity and willingness to explore; both relate to anxiety levels [26], spontaneous discomfort or pain-like behavior [27]. We found that the total distance traveled and the percent distance traveled in the midfield were significantly reduced in NCI rats following a nutrient meal ingestion to satiety versus those in control rats, suggesting that exposure to robust neonatal colon inflammation induces postprandial anxiety-like and aversive behaviors in later life. Another publication reported that psychological stress induces anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in rats when exposed to neonatal gastric irritation followed psychological stress in later life [21].
The patterns of regional brain activation and deactivation differ between FD patients and healthy controls during gastric balloon distention [28–30], suggesting that CNS processing of gastric afferent information is different in FD patients compared to controls. These findings highlight the importance of investigating the effects of meal consumption on regional brain activity in patients and in preclinical models. Ingestion of food activates spinal and vagal afferents that project, respectively, to the second order neurons in the spinal cord and the dorsal vagal complex, which then convey the information to various forebrain and limbic areas involved in the regulation of visceral functions and exploratory behavior [31, 32].
The postprandial effects of decrease in meal consumption, delay in gastric emptying, and increase in anxiety-like and depression-like behaviors appear to be induced by vagal afferents. The postprandial gastric afferent signals did not activate spinal cord c-Fos IR neurons. A large nutrient meal provides both mechanical and chemical stimulations (e.g., lipids evoke release of CCK that activates vagal afferents to reduce food intake. By contrast, the noxious mechanical response is mediated primarily by spinal afferents [33]. Noxious balloon distention activates the vagal afferents as well since c-Fos in DVC was reduced, but not absent, after splanchnicectomy [34].
During the ingestion of a meal, the neuronal and endocrine signals from the stomach and the duodenum are integrated in the homeostatic control regions of the brainstem, such as the amygdala and the hypothalamus [31, 32, 35]. The activation of these regions can affect eating behavior, exploratory behavior, and anxiety. We found significantly greater neuronal activation in the DVC, CeA, and PVN following nutrient meal consumption to satiety in overnight fasted NCI, AG, and NCI + AG rats. These increases in c-Fos may be due to increased afferent sensitization of the vagal afferents and/or due to local sensitization of the forebrain (DVC)-limbic circuits by neonatal colon inflammation and adult gastritis. Adverse early-life experiences can sensitize gastric afferents [9, 10] as well as the central nervous system leading to adverse effects on behavioral indices of anxiety in adult rats [21].
The pattern of c-Fos activation in response to acid infusion [36] is similar to that we observed for a large nutrient meal intake in NCI rats, suggesting that meal ingestion activates circuits that are activated by noxious as well as physiological gastroduodenal stimuli. A previous study reported a significant positive correlation between postmortem weight of gastric contents and the proportion of DVC catecholaminergic neurons expressing c-Fos in naive rats, indicating that activation of these cells is quantitatively related to the magnitude of feeding-induced gastric distension [19]. In healthy rats, regional brain activation patterns mapped by c-Fos immunohistochemistry after meal consumption showed activation in the DVC, CeA, and PVN [19, 32]. Our c-Fos data indicated that adult gastritis or neonatal colon inflammation each enhances the central postprandial c-Fos activation.
As stated earlier, both NCI and adult gastritis induce adverse effects on meal consumption, rate of gastric emptying, and aversive behaviors in open field test of similar magnitudes, which are not enhanced with a combination of both insults. On the other hand, gastritis in NCI rats significantly enhanced c-Fos activation in DVC, CeA, and PVN. These findings suggest that the observed behavior changes, decrease in meal consumption, and delay in gastric emptying may occur at a given level of c-Fos activation; any additional c-Fos activation may not further deteriorate the adverse effects we examined. These findings may explain the clinical findings that treatment of H. pylori infection in FD patients may have marginal effects on symptoms [16, 24, 37].
LiCl is an established activator of interoceptive circuits [20]. Our goal in using LiCl was to show that chemical activation of the interoceptive circuits produces changes in behavior and food consumption similar to those in rats subjected to neonatal colon inflammation. We did not notice diarrhea or any visual peripheral symptom of LiCl in our experiments. However, we cannot rule out that an unknown peripheral effect of LiCl may also have contributed to decrease in nutritional food conniption. The LiCl experiments also validated the open field test as a measure of postprandial aversive behavior.
Low-grade inflammation as well as increase in mast cell infiltration has been reported in the duodenal mucosa of FD patients including patients [38]. Although we did not investigate the mast cell numbers or mucosal inflammation in the duodenum in this study, we found no significant indication of inflammation as revealed by lack of inflammatory cytokine upregulation in our experimental groups. In a previous study, we found that mast cell numbers in the fundus were not significantly different between the control and NCI rats [9].
FD is defined by the lack of detectable organic pathophysiology [39], although there are reports of low-grade non-specific immune response in the stomach and/or the duodenum of FD patients [38]. We reported previously that adult rats subjected to prior neonatal colon inflammation demonstrate no detectable classic inflammatory cytokine expression in the gastric fundus, while they demonstrate significant hypersensitivity to gastric distension [9]. Iodoacetamide treatment in adult rats produces mild mucosal gastritis that is characterized by a mild increase in gastric tissue MPO activity [40]. In this study, we found no significant differences in the four major inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels between the fundi of the control, NCI, AG, or NCI + AG rats. The exception was the higher levels of IL-6 in the fundus of NCI and NCI + AG rats and of INF-γ in the fundus of NCI rats. This upregulation may be due to stress on the fundus smooth muscle layers [41, 42]. Unlike IL-6 signaling in macrophages that requires activation of NF-κB, intramuscular IL-6 expression is regulated by the Ca2+/NFAT and glycogen/p38 MAPK pathways [43]. We found no significant differences in expression of the five cytokines in the duodenum among our four experimental groups although there was a small but significant decline in IL-1β mRNA in the duodenum of adult gastritis rats. These findings suggest that the postprandial adverse effects on meal consumption, gastric emptying, and exploratory behaviors induced by central c-Fos activation may not be affected by mild immune response in the stomach or the duodenum.
In conclusion, our findings show that exposure to neonatal colon inflammation is a risk factor not only for the induction of gastric hypersensitivity to balloon distension that relates to epigastric pain, but also for the symptoms of postprandial distress syndrome, such as early satiety, decrease in food consumption, aversive behavior, and delayed gastric emptying. The postprandial interoceptive signals are transmitted to the central limbic systems through the vagal nerve. These signals may not originate from any overt mild inflammation in the gastric fundus or the duodenum. One cannot rule out that additional factors such as postprandial release of CCK and ghrelin and alterations in the enteric neuronal and smooth muscle regulation of gastric contractions may also contribute to some of the postprandial symptoms. Identification of the brain-gut axis circuits altered by adverse early-life experiences implicated in symptom generation, and the cellular and molecular changes responsible for these alterations in preclinical models will provide a greater understanding of disease mechanisms and identify targets for therapeutic intervention. These findings suggest that in the absence of readily apparent organic pathophysiology in the stomach and the duodenum, FD may be defined by cellular biological abnormalities in the central circuits that process gastric interoceptive information.
References
Tack J, Talley NJ. Functional dyspepsia–symptoms, definitions and validity of the Rome III criteria. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:134–141.
Piessevaux H, De Winter B, Louis E, et al. Dyspeptic symptoms in the general population: a factor and cluster analysis of symptom groupings. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;21:378–388.
Geeraerts B, Van Oudenhove L, Fischler B, et al. Influence of abuse history on gastric sensorimotor function in functional dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;21:33–41.
Saps M, Lu P, Bonilla S. Cow’s-milk allergy is a risk factor for the development of FGIDs in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52:166–169.
Farre R, Vanheel H, Vanuytsel T, et al. In functional dyspepsia, hypersensitivity to postprandial distention correlates with meal-related symptom severity. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:566–573.
Tack J, Caenepeel P, Fischler B, Piessevaux H, Janssens J. Symptoms associated with hypersensitivity to gastric distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:526–535.
Di Stefano M, Miceli E, Tana P, et al. Fasting and postprandial gastric sensorimotor activity in functional dyspepsia: postprandial distress vs. epigastric pain syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1631–1639.
Mertz H, Fullerton S, Naliboff B, Mayer EA. Symptoms and visceral perception in severe functional and organic dyspepsia. Gut. 1998;42:814–822.
Winston JH, Sarna SK. Developmental origins of functional dyspepsia-like gastric hypersensitivity in rats. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:570 e573–579 e573.
Liu LS, Winston JH, Shenoy MM, Song GQ, Chen JD, Pasricha PJ. A rat model of chronic gastric sensorimotor dysfunction resulting from transient neonatal gastric irritation. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:2070–2079.
Vanheel H, Vanuytsel T, Van Oudenhove L, Farre R, Verbeke K, Tack J. Postprandial symptoms originating from the stomach in functional dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25:911-e703.
Delgado-Aros S, Camilleri M, Cremonini F, Ferber I, Stephens D, Burton DD. Contributions of gastric volumes and gastric emptying to meal size and postmeal symptoms in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1685–1694.
Wilson KT, Crabtree JE. Immunology of Helicobacter pylori: insights into the failure of the immune response and perspectives on vaccine studies. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:288–308.
Bamford KB, Fan X, Crowe SE, et al. Lymphocytes in the human gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori have a T helper cell 1 phenotype. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:482–492.
Sundquist M, Quiding-Jarbrink M. Helicobacter pylori and its effect on innate and adaptive immunity: new insights and vaccination strategies. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;4:733–744.
Blum AL, Talley NJ, O’Morain C, et al. Lack of effect of treating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. Omeprazole plus Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin Effect One Year after Treatment (OCAY) Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1875–1881.
McColl K, Murray L, El-Omar E, et al. Symptomatic benefit from eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1869–1874.
Miwa H, Hirai S, Nagahara A, et al. Cure of Helicobacter pylori infection does not improve symptoms in non-ulcer dyspepsia patients-a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000;14:317–324.
Kreisler AD, Davis EA, Rinaman L. Differential activation of chemically identified neurons in the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract in non-entrained rats after intake of satiating vs. non-satiating meals. Physiol Behav. 2014;136:47–54.
Koehnle TJ, Rinaman L. Progressive postnatal increases in Fos immunoreactivity in the forebrain and brain stem of rats after viscerosensory stimulation with lithium chloride. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R1212–R1223.
Liu L, Li Q, Sapolsky R, et al. Transient gastric irritation in the neonatal rats leads to changes in hypothalamic CRF expression, depression- and anxiety-like behavior as adults. PLoS One. 2011;6:e19498.
Lee KJ, Vos R, Janssens J, Tack J. Differences in the sensorimotor response to distension between the proximal and distal stomach in humans. Gut. 2004;53:938–943.
Tack J, Caenepeel P, Corsetti M, Janssens J. Role of tension receptors in dyspeptic patients with hypersensitivity to gastric distention. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1058–1066.
Talley NJ, Janssens J, Lauritsen K, Racz I, Bolling-Sternevald E. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial with 12 months’ follow up. The Optimal Regimen Cures Helicobacter Induced Dyspepsia (ORCHID) Study Group. BMJ. 1999;318:833–837.
Moayyedi P, Deeks J, Talley NJ, Delaney B, Forman D. An update of the Cochrane systematic review of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in nonulcer dyspepsia: resolving the discrepancy between systematic reviews. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:2621–2626.
Prut L, Belzung C. The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;463:3–33.
Kline RH, Exposto FG, O’Buckley SC, Westlund KN, Nackley AG. Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibition alters pain and anxiety-related volitional behaviors through activation of beta-adrenergic receptors in the rat. Neuroscience. 2015;290:561–569.
Vandenberghe J, Dupont P, Van Oudenhove L, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow during gastric balloon distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1684–1693.
Geeraerts B, Van Oudenhove L, Dupont P, et al. Different regional brain activity during physiological gastric distension compared to balloon distension: a H2 15O-PET study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;23:533-e203.
Van Oudenhove L, Vandenberghe J, Dupont P, et al. Abnormal regional brain activity during rest and (anticipated) gastric distension in functional dyspepsia and the role of anxiety: a H(2)(15)O-PET study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:913–924.
Rinaman L. Ascending projections from the caudal visceral nucleus of the solitary tract to brain regions involved in food intake and energy expenditure. Brain Res. 2010;1350:18–34.
Rinaman L, Baker EA, Hoffman GE, Stricker EM, Verbalis JG. Medullary c-Fos activation in rats after ingestion of a satiating meal. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:R262–R268.
Ozaki N, Gebhart GF. Characterization of mechanosensitive splanchnic nerve afferent fibers innervating the rat stomach. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G1449–G1459.
Traub RJ, Sengupta JN, Gebhart GF. Differential c-fos expression in the nucleus of the solitary tract and spinal cord following noxious gastric distention in the rat. Neuroscience. 1996;74:873–884.
Olson BR, Freilino M, Hoffman GE, Stricker EM, Sved AF, Verbalis JG. c-Fos expression in rat brain and brainstem nuclei in response to treatments that alter food intake and gastric motility. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1993;4:93–106.
Lamb K, Kang YM, Gebhart GF, Bielefeldt K. Gastric inflammation triggers hypersensitivity to acid in awake rats. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1410–1418.
Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J et al. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002096.pub2.
Vanheel H, Vicario M, Vanuytsel T, et al. Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia. Gut. 2014;63:262–271.
Miwa H. Why dyspepsia can occur without organic disease: pathogenesis and management of functional dyspepsia. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:862–871.
Ozaki N, Bielefeldt K, Sengupta JN, Gebhart GF. Models of gastric hyperalgesia in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G666–G676.
Petersen AM, Pedersen BK. The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol 1985. 2005;98:1154–1162.
Febbraio MA, Pedersen BK. Contraction-induced myokine production and release: is skeletal muscle an endocrine organ? Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2005;33:114–119.
Brandt C, Pedersen BK. The role of exercise-induced myokines in muscle homeostasis and the defense against chronic diseases. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:520258.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported in part by NIDDK Grants 5R01DK088796 (SKS) and DK 32346 (SKS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors had any conflict of interest in performing the scientific experiments and did not use any outside assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Additional information
It is with a heavy heart that we publish this paper in memory of our colleague Dr. Sushil K. Sarna, one of the pioneer investigators in neurogastroenterology and motility, who passed away on February 27, 2017, after a short illness.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Winston, J.H., Aguirre, J.E., Shi, XZ. et al. Impaired Interoception in a Preclinical Model of Functional Dyspepsia. Dig Dis Sci 62, 2327–2337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4487-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4487-0