Abstract
Introduction
A same-day low-volume 1 L polyethylene glycol (PEG) for bowel preparation before colonoscopy was developed to improve patients’ compliance. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of this regimen especially for the elderly and patients with renal dysfunction.
Methods
All consecutive patients who underwent colonoscopy in our center from November 2014 to September 2015 were included. Patients undertook a low-residue diet with 10 mL sodium picosulfate 1 day before colonoscopy. Subsequently, they had 1 L low-volume PEG (MoviPrep) and 0.5 L water 4 h before the examination. Clinical outcomes, including cleansing level using the Boston bowel preparation score (BBPS), in the elderly and special-elderly (65–79 and ≥80 years old) were analyzed and compared with the non-elderly (18–64 years old). Additionally, patients with renal dysfunction were analyzed with respect to both complications and changes in blood parameters.
Results
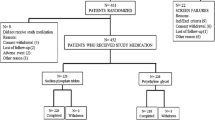
A total of 5427 patients (mean age: 64.5 ± 13.8) were analyzed. The rate of BBPS ≥ 6 in the elderly (2761 patients), special-elderly (565 patients), and non-elderly (2101 patients) was 94.1, 91.8, and 94.6 %, respectively. In the special-elderly, the rate of renal dysfunction was 14.8 %, and no severe complications were detected after colonoscopy. Additionally, there were no severe complications in 86 patients with renal dysfunction, though elevation of hematocrit was shown after intake of 1 L PEG (before, 36.7 ± 6.1 vs. after, 39.0 ± 5.7, P = 0.006).
Conclusions
Our study shows the safety and efficacy of same-day low-volume 1 L PEG bowel preparation in colonoscopy for the elderly and patients with renal dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:687–696.
Yoshida N, Wakabayashi N, Kanemasa K, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors: technical difficulties and rate of perforation. Endoscopy. 2009;41:758–761.
Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:100–107.
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:1217–1225.
Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Kajiyama M, et al. Removal of small colorectal polyps in anticoagulated patients: a prospective randomized comparison of cold snare and conventional polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:417–423.
Yoshida N, Naito Y, Kugai M, et al. Efficacy of hyaluronic acid in endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal tumors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:286–291.
Yoshida N, Yagi N, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T. Safe procedure in endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors focused on preventing complications. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1688–1695.
Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, et al. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European Multicenter Study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;6:378–384.
Harewood GC, Sharma VK, de Garmo P. Impact of colonoscopy preparation quality on detection of suspected colonic neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:76–79.
Johnson DA, Barkun AN, Cohen LB, et al. Optimizing adequacy of bowel cleansing for colonoscopy: recommendations from the US multi-society task force on colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:903–924.
Corporaal S, Kleibeuker JH, Koornstra JJ. Low-volume PEG plus ascorbic acid versus high-volume PEG as bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:1380–1386.
Gentile M, De Rosa M, Cestaro G, Forestieri P. 2 L PEG plus ascorbic acid versus 4 L PEG plus simethicone for colonoscopy preparation: a randomized single-blind clinical trial. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2013;23:276–280.
Mathus-Vliegen EM, van der Vliet K. Safety, patient’s tolerance, and efficacy of a 2-liter vitamin C-enriched macrogol bowel preparation: a randomized, endoscopist-blinded prospective comparison with a 4-liter macrogol solution. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:1002–1012.
Ponchon T, Boustière C, Heresbach D, et al. A low-volume polyethylene glycol plus ascorbate solution for bowel cleansing prior to colonoscopy: the NORMO randomised clinical trial. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45:820–826.
Pontone S, Angelini R, Standoli M, et al. Low-volume plus ascorbic acid vs high-volume plus simethicone bowel preparation before colonoscopy. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:4689–4695.
Tajika M, Tanaka T, Ishihara M, et al. A randomized controlled trial evaluating a low-volume PEG solution plus ascorbic acid versus standard PEG solution in bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:326581.
Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G, et al. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:620–625.
Valiante F, Pontone S, Hassan C, et al. A randomized controlled trial evaluating a new 2-L PEG solution plus ascorbic acid vs 4-L PEG for bowel cleansing prior to colonoscopy. Dig Liver Dis. 2012;44:224–227.
Seo EH, Kim TO, Park MJ, et al. Low-volume morning-only polyethylene glycol with specially designed test meals versus standard-volume split-dose polyethylene glycol with standard diet for colonoscopy: a prospective, randomized trial. Digestion. 2013;88:110–118.
Hookey LC, Depew WT, Vanner SJ. Combined low volume polyethylene glycol solution plus stimulant laxatives versus standard volume polyethylene glycol solution: a prospective, randomized study of colon cleansing before colonoscopy. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006;20:101–105.
Hassan C, Fuccio L, Bruno M, et al. A predictive model identifies patients most likely to have inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:501–506.
Lebwohl B, Wang TC, Neugut AI. Socioeconomic and other predictors of colonoscopy preparation quality. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:2014–2020.
Ness RM, Manam R, Hoen H, Chalasani N. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:1797–1802.
Borg BB, Gupta NK, Zuckerman GR, et al. Impact of obesity on bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:670–675.
Taylor C, Schubert ML. Decreased efficacy of polyethylene glycol lavage solution (golytely) in the preparation of diabetic patients for outpatient colonoscopy: a prospective and blinded study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:710–714.
Lim SW, Seo YW, Sinn DH, et al. Impact of previous gastric or colonic resection on polyethylene glycol bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:1554–1559.
Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, et al. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:1197–1203.
Horimatsu T, Sano Y, Tanaka S, et al. Next-generation narrow band imaging system for colonic polyp detection: a prospective multicenter randomized trial. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015;30:947–954.
Yoshida N, Hisabe T, Hirose R, et al. 2015) Improvement in the visibility of colorectal polyps by using blue laser imaging (with video. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:542–549.
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of the Department of Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, for helping with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yoshito Itoh received a research grant from Ajinomoto Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Yuji Naito received research grants from Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, N., Naito, Y., Murakami, T. et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Same-Day Low-Volume 1 L PEG Bowel Preparation in Colonoscopy for the Elderly People and People with Renal Dysfunction. Dig Dis Sci 61, 3229–3235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4262-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4262-7