Abstract
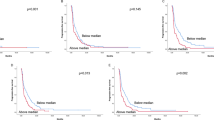
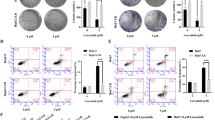
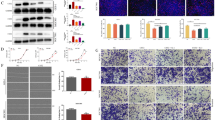
Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma (OTSCC) is the most common oral cancer with a low overall survival rate, necessitating effective treatments. This study reports the anti-OTSCC effect of vorinostat and selinexor. OTSCC cell lines SCC-4 and SCC-25 were cultured to determine the effects of vorinostat and/or selinexor on cell survival, invasion, migration, and apoptosis. The transplanted tumor model of SCC-25 in nude mice was established to observe the therapeutic effects of vorinostat and/or selinexor. Western blotting was used to determine protein expressions in tumor cells. The results showed that histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and exportin 1 (XPO1) were highly expressed, while nuclear maspin was expressed at a low rate in SCC-4 and SCC-25 compared to the normal tongue tissue. In vitro, both vorinostat and selinexor effectively inhibited cell viability, invasion, and migration, promoted cell apoptosis, down-regulated HDAC1, Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), and B cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), and up-regulated nuclear maspin and cleaved caspase 3. In vivo, both vorinostat and selinexor inhibited the growth of SCC-25-bearing tumors, down-regulated the expression of Ki67, HDAC1, MMP2, and Bcl-2, and promoted the expression of nuclear maspin and cleaved caspase 3. The combination of these two drugs exhibited synergistic effects both in vivo and in vitro. Our evidence shows that vorinostat combined with selinexor is an effective treatment for OTSCC. The mechanism may be that selinexor promotes the accumulation of maspin in the nucleus, an endogenous HDAC1 inhibitory protein to inhibit the HDAC1 activity of vorinostat and exert a synergistic anti-OTSCC effect.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bethesda (2021) LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury [Internet]. LiverTox, 2012
Bruzzese F, Leone A, Rocco M, Carbone C, Piro G, Caraglia M, Gennaro ED, Budillon A (2011) HDAC inhibitor vorinostat enhances the antitumor effect of gefitinib in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck by modulating ErbB receptor expression and reverting EMT. J Cell Physiol 226:2378–2390
Chang H-H, Chiang C-P, Hung H-C, Lin C-Y, Deng Y-T, Kuo MY-P (2009) Histone deacetylase 2 expression predicts poorer prognosis in oral cancer patients. Oral Oncol 45:610–614
Chang C-C, Lin B-R, Chen S-T, Hsieh T-H, Li Y-J, Kuo MYP (2011) HDAC2 promotes cell migration/invasion abilities through HIF-1α stabilization in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 40:567–575
Chi AC, Day TA, Neville BW (2015) Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma—an update. CA Cancer J Clin 65:401–421
Frey A, Soubani AO, Adam AK, Sheng S, Pass HI, Lonardo F (2010) Nuclear, compared with combined nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of maspin, is linked in lung adenocarcinoma to reduced VEGF-A levels and in stage I, improved survival. Histopathology 54:590–597
Goulet B, Kennette W, Ablack A, Postenka CO, Hague MN, Mymryk JS, Tuck AB, Giguère V, Chambers AF, Lewis JD (2011) Nuclear localization of maspin is essential for its inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis. Lab Investig 91:1181–1187
Kasamon YL, Price LSL, Okusanya OO, Richardson NC, Li R-J, Ma L, Wu Y-T, Theoret M, Pazdur R, Gormley NJ (2021) FDA approval summary: selinexor for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncologist 26:879–886
Kumar B, Yadav A, Lang JC, Teknos TN, Kumar P (2015) Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) reverses chemoresistance in head and neck cancer cells by targeting cancer stem cells via the downregulation of nanog. Genes Cancer 6:169–181
Li X, Yin S, Meng Y, Sakr W, Sheng S (2006) Endogenous inhibition of histone deacetylase 1 by tumor-suppressive maspin. Cancer Res 66:9323–9329
Longhi MT, Silva LE, Pereira M, Magalhães M, Reina J, Vitorino FN, Gumbiner BM, Da Cunha JP, Cella N (2021) PI3K-AKT, JAK2-STAT3 pathways and cell–cell contact regulate maspin subcellular localization. Cell Commun Signal 19:86
Mărăşescu FIIC, Marasescu PC, Matei M, Florescu AM, Margaritescu C, Petrescu SMS, Dumitrescu CI (2018) Epidemiological and histopathological aspects of tongue squamous cell carcinomas-retrospective study. Curr Health Sci J 44:211–224
Marioni G, Blandamura S, Giacomelli L, Calgaro N, Segato P, Leo G, Fischetto D, Staffieri A, De Filippis C (2010) Nuclear expression of maspin is associated with a lower recurrence rate and a longer disease-free interval after surgery for squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Histopathology 46:576–582
Marra A, Violati M, Broggio F, Codecà C, Blasi M, Luciani A, Zonato S, Rabbiosi D, Moneghini L, Saibene A, Maccari A, Felisati G, Ferrari D (2019) Long-term disease-free survival in surgically-resected oral tongue cancer: a 10-year retrospective study. Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica 39:84–91
McClure JJ, Li X, Chou CJ (2018) Advances and challenges of HDAC inhibitors in cancer therapeutics. Adv Cancer Res 138:183–211
Nakajima H (2007) A mammalian histone deacetylase related to the yeast transcriptional regulator Rpd3p. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso 52:1790–1791
Ng JH, Iyer NG, Tan M-H, Edgren G (2017) Changing epidemiology of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: a global study. Head Neck 39:297–304
Nosaka K, Horie Y, Shiomi T, Itamochi H, Oishi T, Shimada M, Sato S, Sakabe T, Harada T, Umekita Y (2015) Cytoplasmic maspin expression correlates with poor prognosis of patients with adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix. Yonago Acta Med 58:151–156
Richard S, Jagannath S (2022) Targeting nuclear export proteins in multiple myeloma therapy. BioDrugs 36:13–25
Rodriguez CP, Wu QV, Voutsinas J, Fromm JR, Jiang X, Pillarisetty VG, Lee SM, Santana-Davila R, Goulart B, Baik CS, Chow LQM, Eaton K, Martins R (2019) A phase II trial of pembrolizumab and vorinostat in recurrent metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinomas and salivary gland cancer. Clin Cancer Res 26:837–845
Saenz-Ponce N, Pillay R, Long LM, d., Kashyap T, Argueta C, Landesman Y, Hazar-Rethinam M, Boros S, Panizza B, Jacquemyn M, Daelemans D, Gannon OM, Saunders NA (2019) Targeting the XPO1-dependent nuclear export of E2F7 reverses anthracycline resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Sci Transl Med 10:eaar7223
Sajnani AK, Shah SG, Rashid M, Natu A, Gera PB, Gupta S (2021) In-silico analysis of chromatin modifiers and profiling of histone deacetylases (HDAC’s) in human oral cancer. Chonnam Med J 57:176–184
Shankar E, Pandey M, Verma S, Abbas A, Candamo M, Kanwal R, Shukla S, MacLennan GT, Gupta S (2020) Role of class I histone deacetylases in the regulation of maspin expression in prostate cancer. Mol Carcinog 59:955–966
Takagi Y, Matsuoka Y, Shiomi T, Nosaka K, Takeda C, Haruki T, Araki K, Taniguchi Y, Nakamura H, Umekita Y (2014) Cytoplasmic maspin expression is a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma measuring less than 3 cm. Histopathology 66:732–739
Tang S, Lian X, Jiang J, Cheng H, Guo J, Huang C, Meng H, Li X (2020) Tumor suppressive maspin-sensitized prostate cancer to drug treatment through negative regulating androgen receptor expression. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:573820
Taunton J, Hassig CA, Schreiber SL (1996) A mammalian histone deacetylase related to the yeast transcriptional regulator Rpd3p. Science 272:408–411
Teknos TN, Grecula J, Agrawal A, Old MO, Ozer E, Carrau R, Kang S, Rocco J, Blakaj D, Diavolitsis V, Kumar B, Kumar P, Pan Q, Palettas M, Wei L, Baiocchi R, Savvides P (2016) A phase 1 trial of vorinostat in combination with concurrent chemoradiation therapy in the treatment of advanced staged head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Investig New Drugs 37:702–710
Theocharis S, Klijanienko J, Giaginis C, Rodriguez J, Jouffroy T, Girod A, Alexandrou P, Sastre-Garau X (2011) Histone deacetylase-1 and -2 expression in mobile tongue squamous cell carcinoma: associations with clinicopathological parameters and patients survival. J Oral Pathol Med 40:706–714
Yasumatsu R, Nakashima T, Hirakawa N, Kumamoto Y, Kuratomi Y, Tomita K, Komiyama S (2001) Maspin expression in stage I and II oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 23:962–966
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FY: Conceptualization, Visualization, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Formal analysis. JY: Project Administration, Investigation, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Writing—review & editing. Xl: Visualization, Methodology, Data curation. YW: Formal analysis, Project Supervision. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, F., Yong, J., Liu, X. et al. Selinexor assists vorinostat in inhibiting HDAC activity via promoting the accumulation of maspin in the nucleus of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cytotechnology 75, 1–16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00555-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00555-x