Abstract
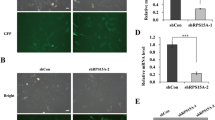
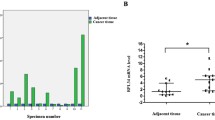
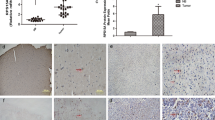
To explore the role of ribosomal protein S15A (RPS15A) in breast cancer. The Oncomine database was used to compare the expression of RPS15A in human breast cancer tissues and normal tissues. RPS15A in breast cancer cell line ZR-75-30 and BT474 was specifically knocked down using lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs). RPS15A knockdown efficiency was validated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis. Subsequently, the functional effects of RPS15A on proliferation of breast cancer cells were investigated by MTT, colony formation and flow cytometry assays. Functional analysis indicated that RPS15A knockdown could inhibit cell proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mechanism analysis revealed RPS15A mediated apoptosis via activating of caspase-3 and PARP cleavage, upregulating of Bad and BAX and downregulating of Bcl-2. Our preliminary study highlighted the importance of RPS15A in breast cancer growth. The inhibition of RPS15A may be a promising therapeutic target for breast cancer treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama N, Matsuo Y, Sai H, Noda M, Kizakakondoh S (2000) Identification of a series of transforming growth factor Β-responsive genes by retrovirus-mediated gene trap screening. Mol Cell Biol 20:3266–3273
Amsterdam A, Sadler KC, Lai K, Farrington S, Bronson RT, Lees JA, Hopkins N (2004) Many ribosomal protein genes are cancer genes in zebrafish. PLoS Biol 2:0690–0698
Besbes S, Mirshahi M, Pocard M, Billard C (2015) New dimension in therapeutic targeting of BCL-2 family proteins. Oncotarget 6:12862–12871
Bonham-Smith PC, Moloney MM (1994) Nucleotide and protein sequences of a cytoplasmic ribosomal protein S15a gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 106:401–402
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR (2010) The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell 37:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.025
Hannemann J, Velds A, Halfwerk JB, Kreike B, Peterse JL, Vijver MJVD (2006) Classification of ductal carcinoma in situ by gene expression profiling. Breast Cancer Res 8:R61
Heeres JT, Hergenrother PJ (2007) Poly(ADP-ribose) makes a date with death. Curr Opin Chem Biol 11:644–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.08.038
Jimenez L, Becerra A, Landa A (2004) Cloning, expression and partial characterization of a gene encoding the S15a ribosomal protein of Taenia solium. Parasitol Res 92:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-1021-4
Karagianni M, Kaitelidou D, Kalokairinou A, Mantas J (2014) Breast cancer in social media: a literature review. Stud Health Technol Inform 202:321
Kavak E, Unlu M, Nister M, Koman A (2010) Meta-analysis of cancer gene expression signatures reveals new cancer genes, sage tags and tumor associated regions of co-regulation. Nucl Acids Res 38:7008–7021
Kelly GL, Strasser A (2011) The essential role of evasion from cell death in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 111:39–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385524-4.00002-7
Lavoie C, Tam R, Clark M, Lee H, Sonenberg N, Lasko P (1994) Suppression of a temperature-sensitive cdc33 mutation of yeast by a multicopy plasmid expressing a Drosophila ribosomal protein. J Biol Chem 269:14625–14630
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Maiyu X et al (2014) Down-regulation of ribosomal protein S15A mRNA with a short hairpin RNA inhibits human hepatic cancer cell growth in vitro. Gene 536:84–89
Mazumder S, Plesca D, Almasan A (2008) Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol 414:13–21
Ottolini D, Calì T, Negro A, Brini M (2013) The Parkinson disease-related protein DJ-1 counteracts mitochondrial impairment induced by the tumour suppressor protein p53 by enhancing endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria tethering. Hum Mol Genet 22:2152–2168
Rhodes D et al (2007) Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia 9:166–180
Ruggero D, Pandolfi PP (2003) Does the ribosome translate cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 3:179–192
Shen XC, Valencia CA, Szostak JW, Dong B, Liu R (2005) Scanning the human proteome for calmodulin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5969–5974
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM (2011) Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J 30:3667–3683. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.307
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucl Acids Res 45:W98–W102
Yu X (2014) Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit D inhibits proliferation of HCT116 colon cancer cells. Biosci Rep 34:e00161–e00161
Zeller KI, Jegga AG, Aronow BJ, O’Donnell KA, Chi VD (2003) An integrated database of genes responsive to the Myc oncogenic transcription factor: identification of direct genomic targets. Genome Biol 4:54–56
Zhang C et al (2014a) HSPC111 governs breast cancer growth by regulating ribosomal biogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 12:583–594
Zhang C, Zhang T, Song E, Swa H, Chen X, Zheng L (2014b) Ribosomal protein S15A augments human osteosarcoma cell proliferation in vitro. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 29:451–456
Zhang GQ, He C, Tao L, Liu F (2015) Role of DJ-1 siRNA in reverse sensitivity of breast cancer cells to chemotherapy and its possible mechanism. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:6944–6951
Zhao X et al (2015) Decreased expression of RPS15A suppresses proliferation of lung cancer cells. Tumor Biol 36:6733–6740
Zhou W, Shi G, Zhang Q, Wu Q, Li B, Zhang Z (2014) MicroRNA-20b promotes cell growth of breast cancer cells partly via targeting phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN). Cell Biosci 4:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-4-62
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Project from Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY18H160033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, W., Liang, C., Wang, C. et al. Knockdown of ribosomal protein S15A inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells through induction of apoptosis in vitro. Cytotechnology 70, 1315–1323 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-018-0221-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-018-0221-9