Abstract
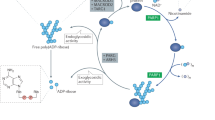
The urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) system is a complex regulator of extracellular proteolysis which is involved in various physiological and pathological processes. The major components of this system are the serine protease uPA, two inhibitors PAI-1 and PAI-2, and the receptor uPAR. It has been previously shown by several groups that the uPA system has an important role in cancer progression and therefore its possible prognostic and therapeutic value has been evaluated. The aim of this study is to tackle the role of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in the induction of uPA activity in a glioblastoma cell line, A1235. This cell line is sensitive to alkylation damage and is a model for drug treatment. The components of the uPA system and the level of DNA damage were analyzed after alkylation agent treatment in combination with poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibition. Here we show that the increase in uPA activity results from the net balance change between uPA and its inhibitor at mRNA level. Further, PARP-1 inhibition exerts its influence on uPA activity through DNA damage increase. Involvement of several signaling pathways, as well as cell specific regulation influencing the uPA system are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- uPA:
-
Urokinase
- PAI:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor
- uPAR:
-
Urokinase receptor
- PARP-1:
-
Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
- MNNG:
-
N′-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine
- 3-ABA:
-
3-Aminobenzamide
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- MGMT:
-
O6-Methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
References
Aguirre Ghiso JA, Alonso DF, Farias EF, Gomez DE, de Kier Joffe EB (1999) Deregulation of the signaling pathways controlling urokinase production. Its relationship with the invasive phenotype. Eur J Biochem 263:295–304
Brdar B (1986) Induction of plasminogen activator by alkylating agents in a repair defective human glioblastoma cell strain. Cancer Res 46:2282–2284
Brdar B, Matulic M (1988) Induction of plasminogen activator by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in mer + and mer-human tumour cell strains. Carcinogenesis 9:2191–2195
Caldini R, Barletta E, Del Rosso M, Giovannelli L, Chevanne M (2005) FGF2-mediated upregulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression requires a MAP-kinase dependent activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Cell Physiol 202:125–134. doi:10.1002/jcp.20096
Caldini R, Fanti E, Magnelli L, Barletta E, Tanganelli E, Zampieri M, Chevanne M (2011) Low doses of 3-aminobenzamide, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, stimulate angiogenesis by regulating expression of urokinase type plasminogen activator and matrix metalloprotease 2. Vasc Cell 3:12. doi:10.1186/2045-824X-3-12
Conese M, Blasi F (1995) Urokinase/urokinase receptor system: internalization/degradation of urokinase–serpin complexes: mechanism and regulation. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 376:143–155
Dano K, Andreasen PA, Grondahl-Hansen J, Kristensen P, Nielsen LS, Skriver L (1985) Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 44:139–266
de Vries TJ, van Muijen GN, Ruiter DJ (1996) The plasminogen activation system in tumour invasion and metastasis. Pathol Res Pract 192:718–733
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O, Peacocke M, Campisi J (1995) A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367
Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt ANJ, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, Santarosa M, Dillon KJ, Hickson I, Knights C, Martin NMB, Jackson SP, Smith GCM, Ashworth A (2005) Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 434:917–921. doi:10.1038/Nature03445
Giard DJ, Aaronson SA, Todaro GJ, Arnstein P, Kersey JH, Dosik H, Parks WP (1973) In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 51:1417–1423
Hagelgans A, Menschikowski M, Fuessel S, Nacke B, Arneth BM, Wirth MP, Siegert G (2013) Deregulated expression of urokinase and its inhibitor type 1 in prostate cancer cells: role of epigenetic mechanisms. Exp Mol Pathol 94:458–465. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.03.006
He WC, Tan RY, Dai CS, Li YJ, Wang D, Hao S, Kahn M, Liu YH (2010) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a transcriptional target of the canonical pathway of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem 285:24665–24675. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.091256
Hochegger H, Dejsuphong D, Fukushima T, Morrison C, Sonoda E, Schreiber V, Zhao GY, Saberi A, Masutani M, Adachi N, Koyama H, de Murcia G, Takeda S (2006) Parp-1 protects homologous recombination from interference by Ku and Ligase IV in vertebrate cells. EMBO J 25:1305–1314
Huang D, Wang Y, Yang C, Liao Y, Huang K (2009) Angiotensin II promotes poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of c-Jun/c-Fos in cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46:25–32. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.10.019
Ibanez-Tallon I, Caretti G, Blasi F, Crippa MP (1999) In vivo analysis of the state of the human uPA enhancer following stimulation by TPA. Oncogene 18:2836–2845. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202644
Irigoyen JP, Munoz-Canoves P, Montero L, Koziczak M, Nagamine Y (1999) The plasminogen activator system: biology and regulation. Cell Mol Life Sci 56:104–132
Knizhnik AV, Roos WP, Nikolova T, Quiros S, Tomaszowski KH, Christmann M, Kaina B (2013) Survival and death strategies in glioma cells: autophagy, senescence and apoptosis triggered by a single type of temozolomide-induced DNA damage. PLoS ONE 8:e55665. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055665
Konakova M, Hucho F, Schleuning WD (1998) Downstream targets of urokinase-type plasminogen-activator-mediated signal transduction. Eur J Biochem 253:421–429
Krishnakumar R, Kraus WL (2010) The PARP side of the nucleus: molecular actions, physiological outcomes, and clinical targets. Mol Cell 39:8–24. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.06.017
Lee JS, Favre B, Hemmings BA, Kiefer B, Nagamine Y (1994) Okadaic acid-dependent induction of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene associated with stabilization and autoregulation of c-Jun. J Biol Chem 269:2887–2894
Legrand AJ, Choul-Li S, Spriet C, Idziorek T, Vicogne D, Drobecq H, Dantzer F, Villeret V, Aumercier M (2013) The level of Ets-1 protein is regulated by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) in cancer cells to prevent DNA damage. PLoS One 8:e55883. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055883
Lengyel E, Stepp E, Gum R, Boyd D (1995) Involvement of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in the regulation of urokinase promoter activity by c-Ha-ras. J Biol Chem 270:23007–23012
Lengyel E, Gum R, Stepp E, Juarez J, Wang H, Boyd D (1996) Regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression by an ERK1-dependent signaling pathway in a squamous cell carcinoma cell line. J Cell Biochem 61:430–443. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19960601)61:3<430:AID-JCB10>3.0.CO;2-N
Loncarek J, Soric J (1998) Bacterial O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase reduces N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induction of plasminogen activator in Mer- human glioblastoma A1235 cell line. Mutat Res 408:47–54
Matulic M, Brdar B (2002) Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor induction by etoposide in a glioblastoma cell strain. Food Technol Biotechnol 40:1–7
Miceli F, Tropea A, Minici F, Orlando M, Lamanna G, Gangale MF, Panetta B, Tiberi F, Vaccari S, Canipari R, Lanzone A, Apa R (2005) Effects of insulin-like growth factor I and II on prostaglandin synthesis and plasminogen activator activity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:372–378
Miskin R, Ben-Ishai R (1981) Induction of plasminogen activator by UV light in normal and xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:6236–6240
Moreau M, Mourah S, Dosquet C (2011) beta-Catenin and NF-kappaB cooperate to regulate the uPA/uPAR system in cancer cells. Int J Cancer 128:1280–1292. doi:10.1002/ijc.25455
Nagamine Y, Medcalf RL, Munoz-Canoves P (2005) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of the plasminogen activator system. Thromb Haemost 93:661–675
Noonan EM, Shah D, Yaffe MB, Lauffenburger DA, Samson LD (2012) O6-Methylguanine DNA lesions induce an intra-S-phase arrest from which cells exit into apoptosis governed by early and late multi-pathway signaling network activation. Integr Biol 4:1237–1255. doi:10.1039/c2ib20091k
Parra M, Lluis F, Miralles F, Caelles C, Munoz-Canoves P (2000) The cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway mediates induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) by the alkylating agent MNNG. Blood 96:1415–1424
Rohwer N, Lobitz S, Daskalow K, Jons T, Vieth M, Schlag PM, Kemmner W, Wiedenmann B, Cramer T, Hocker M (2009) HIF-1alpha determines the metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer 100:772–781. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604919
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sanchez-Tillo E, de Barrios O, Siles L, Amendola PG, Darling DS, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A, Postigo A (2013) ZEB1 promotes invasiveness of colorectal carcinoma cells through the opposing regulation of uPA and PAI-1. Clin Cancer Res 19:1071–1082. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-12-2675
Santos MA, Faryabi RB, Ergen AV, Day AM, Malhowski A, Canela A, Onozawa M, Lee JE, Callen E, Gutierrez-Martinez P, Chen HT, Wong N, Finkel N, Deshpande A, Sharrow S, Rossi DJ, Ito K, Ge K, Aplan PD, Armstrong SA, Nussenzweig A (2014) DNA-damage-induced differentiation of leukaemic cells as an anti-cancer barrier. Nature 514:107–111. doi:10.1038/nature13483
Scudiero DA, Meyer SA, Clatterbuck BE, Mattern MR, Ziolkowski CH, Day RS 3rd (1984) Relationship of DNA repair phenotypes of human fibroblast and tumor strains to killing by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Cancer Res 44:961–966
Seelan RS, Khalyfa A, Lakshmanan J, Casanova MF, Parthasarathy RN (2008) Deciphering the lithium transcriptome: microarray profiling of lithium-modulated gene expression in human neuronal cells. Neuroscience 151:1184–1197. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.10.045
Sherman MH, Bassing CH, Teitell MA (2011) Regulation of cell differentiation by the DNA damage response. Trends Cell Biol 21:312–319. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2011.01.004
Shetty P, Velusamy T, Bhandary YP, Shetty RS, Liu MC, Shetty S (2008a) Urokinase expression by tumor suppressor protein p53: a novel role in mRNA turnover. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 39:364–372. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2007-0406OC
Shetty S, Shetty P, Idell S, Velusamy T, Bhandary YP, Shetty RS (2008b) Regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by tumor suppressor protein p53. J Biol Chem 283:19570–19580. doi:10.1074/jbc.M710268200
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Vidal B, Parra M, Jardi M, Saito S, Appella E, Munoz-Canoves P (2005) The alkylating carcinogen N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine activates the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene through sequential phosphorylation of p53 by ATM and ATR kinases. Thromb Haemost 93:584–591
von der Ahe D, Pearson D, Nakagawa J, Rajput B, Nagamine Y (1988) Multiple nuclear factors interact with promoter sequences of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene. Nucleic Acids Res 16:7527–7544
Wang X, Ohnishi K, Takahashi A, Ohnishi T (1998) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is required for p53-dependent signal transduction induced by radiation. Oncogene 17:2819–2825. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202216
Whitley BR, Beaulieu LM, Carter JC, Church FC (2007) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt regulates the balance between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and urokinase to promote migration of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 104:470–479
Yang L, Huang K, Li X, Du M, Kang X, Luo X, Gao L, Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Tong Q, Zhang F, Huang D (2013) Identification of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 as a cell cycle regulator through modulating Sp1 mediated transcription in human hepatoma cells. PLoS One 8:e82872. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082872
Zavizion B, White JH, Bramley AJ (1998) Cell cycle-dependent fluctuation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its receptor, and inhibitors in cultured bovine mammary epithelial and myoepithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1403:141–150
Zhang R, Banik NL, Ray SK (2008) Combination of all-trans retinoic acid and interferon-gamma upregulated p27(kip1) and down regulated CDK2 to cause cell cycle arrest leading to differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma LN18 (PTEN-proficient) and U87MG (PTEN-deficient) cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:407–416. doi:10.1007/s00280-007-0619-0
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Sc. Valerie Schreiber for generously providing pEGFP-hPARP-1 plasmid and Dr. Sc. Janet E. Mertz for expression plasmid pcDNA4hismaxCZEB1. We would also like to thank Mr. Mladen Paradžik, Dr. Sc. Branko Brdar, and especially the members of the Laboratory for cellular and molecular biology of the Rudjer Boskovic Institute. We would also like to thank Dr. Sc. Anamarija Brozovic and Dr. Sc. Andreja Ambriović Ristov for phospho-JNK antibody, as well as Dr. Sc. Ivana Ivančić-Baće for helpful suggestions. This work was supported by Ministry of Science, Technology and Sport of the Republic of Croatia through Grant Nos. 098-0982913-2332 and 119-0000000-3172.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madunić, J., Antica, M., Cvjetko, P. et al. Modulation of urokinase plasminogen activator system by poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 inhibition. Cytotechnology 68, 783–794 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9829-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9829-6