Abstract
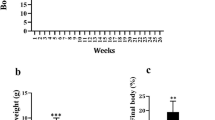
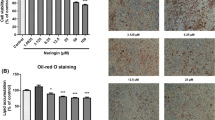
α-Linolenic acid (ALA), a major fatty acid in flaxseed oil, has multiple functionalities such as anti-cardiovascular and anti-hypertensive activities. In this study, we investigated the effects of ALA on lipid metabolism and studied the possible mechanisms of its action in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes using DNA microarray analysis. From a total of 34,325 genes in the DNA chip, 87 genes were down-regulated and 185 genes were up-regulated at least twofold in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells treated with 300 μM ALA for a week, 5–12 days after induction of cell differentiation, compared to ALA-untreated 3T3-L1 adipocytes (control). From the Reactome analysis results, eight lipid metabolism-related genes involved in cholesterol and triacylglycerol biosynthesis pathway and lipid transport were significantly down-regulated by ALA treatment. Furthermore, ALA significantly decreased the mRNA expressions of sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)-2, SREBP-1a, SREBP-1c and fatty acid synthase (FAS) in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells. On the other hand, the average levels of the gene expressions of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT-1a) and leptin in 300 μM ALA treatment were increased by 1.7- and 2.9-fold, respectively, followed by an increase in the intracellular ATP content. These results show that ALA is likely to inhibit cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis pathway by suppressing the expression of transcriptional factor SREBPs. Furthermore, ALA promotes fatty acid oxidation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, thereby increasing its health benefits.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALA:
-
α-Linolenic acid
- CPT-1a:
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a
- PUFAs:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- SREBP:
-
Sterol regulatory element binding protein
- FAS:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- SRE:
-
Sterol regulatory element
References
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2005) The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet 366:1059–1062
Annuzzi G, Rivellese A, Capaldo B, Di Marino L, Iovine C, Marotta G, Riccardi G (1991) A controlled study on the effects of n-3 fatty acids on lipid and glucose metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 87:65–73
Bennati AM, Castelli M, Della Fazia MA, Beccari T, Caruso D, Servillo G, Roberti R (2006) Sterol dependent regulation of human TM7SF2 gene expression: role of the encoded 3beta-hydroxysterol Delta14-reductase in human cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1761:677–685
Bu SY, Mashek MT, Mashek DG (2009) Suppression of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase 3 decreases hepatic de novo fatty acid synthesis through decreased transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 284:30474–30483
Burdge GC (2006) Metabolism of alpha-linolenic acid in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 75:161–168
Clarke SD, Gasperikova D, Nelson C, Lapillonne A, Heird WC (2002) Fatty acid regulation of gene expression: a genomic explanation for the benefits of the mediterranean diet. Ann N Y Acad Sci 967:283–298
Croft D, O’Kelly G, Wu G, Haw R, Gillespie M, Matthews L, Caudy M, Garapati P, Gopinath G, Jassal B, Jupe S, Kalatskaya I, Mahajan S, May B, Ndegwa N, Schmidt E, Shamovsky V, Yung C, Birney E, Hermjakob H, D’Eustachio P, Stein L (2011) Reactome: a database of reactions, pathways and biological processes. Nucl Acids Res 39 (Database issue):D691–D697
Cunnane SC, Ganguli S, Menard C, Liede AC, Hamadeh MJ, Chen ZY, Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ (1993) High alpha-linolenic acid flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum): some nutritional properties in humans. Br J Nutr 69:443–453
Djousse L, Hunt SC, Arnett DK, Province MA, Eckfeldt JH, Ellison RC (2003) Dietary linolenic acid is inversely associated with plasma triacylglycerol: the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Heart Study. Am J Clin Nutr 78:1098–1102
Ferno J, Skrede S, Vik-Mo AO, Havik B, Steen VM (2006) Drug-induced activation of SREBP-controlled lipogenic gene expression in CNS-related cell lines: marked differences between various antipsychotic drugs. BMC Neurosci 7:69
Fukumitsu S, Aida K, Ueno N, Ozawa S, Takahashi Y, Kobori M (2008) Flaxseed lignan attenuates high-fat diet-induced fat accumulation and induces adiponectin expression in mice. Br J Nutr 100:669–676
Gemma S, Vichi S, Testai E (2006) Individual susceptibility and alcohol effects: biochemical and genetic aspects. Ann I Super Sanita 42:8–16
Green H, Meuth M (1974) An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 3:127–133
Harmon AW, Harp JB (2001) Differential effects of flavonoids on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and lipolysis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C807–C813
Hirsch-Reinshagen V, Zhou S, Burgess BL, Bernier L, McIsaac SA, Chan JY, Tansley GH, Cohn JS, Hayden MR, Wellington CL (2004) Deficiency of ABCA1 impairs apolipoprotein E metabolism in brain. J Biol Chem 279:41197–41207
Horton JD, Shimomura I, Brown MS, Hammer RE, Goldstein JL, Shimano H (1998) Activation of cholesterol synthesis in preference to fatty acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of transgenic mice overproducing sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. J Clin Invest 101:2331–2339
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Luong A, Hannah VC, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2000) Molecular characterization of human acetyl-CoA synthetase, an enzyme regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 275:26458–26466
Madsen L, Petersen RK, Kristiansen K (2005) Regulation of adipocyte differentiation and function by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1740:266–286
Nagai M, Sakakibara J, Nakamura Y, Gejyo F, Ono T (2002) SREBP-2 and NF-Y are involved in the transcriptional regulation of squalene epoxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:74–80
Nishimura K, Hatano Y, Setoyama T, Tsumagari H, Miyashita K, Lu S, Jisaka M, Nagaya T, Yokota K (2004) Control of life cycle of mouse adipogenic 3T3-L1 cells by dietary lipids and metabolic factors. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 118:97–114
Nissen E, Pauli G, Vollenbroich D (1997) WST-1 assay—a simple colorimetric method for virus titration. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:28–29
Pai JT, Guryev O, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1998) Differential stimulation of cholesterol and unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis in cells expressing individual nuclear sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 273:26138–26148
Roche HM, Gibney MJ (2000) Effect of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on fasting and postprandial triacylglycerol metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 71:232S–237S
Romans JR, Johnson RC, Wulf DM, Libal GW, Costello WJ (1995) Effects of ground flaxseed in swine diets on pig performance and on physical and sensory characteristics and omega-3 fatty acid content of pork: I. Dietary level of flaxseed. J Anim Sci 73:1982–1986
Ronnett GV, Kleman AM, Kim EK, Landree LE, Tu Y (2006) Fatty acid metabolism, the central nervous system, and feeding. Obes (Silver Spring) 14:201S–207S
Rosen ED, Sarraf P, Troy AE, Bradwin G, Moore K, Milstone DS, Spiegelman BM, Mortensen RM (1999) PPAR gamma is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell 4:611–617
Rozman D (2000) Lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51)—a cholesterol biosynthetic enzyme involved in production of meiosis activating sterols in oocytes and testis—a minireview. Pflugers Arch 439:R56–R57
Rozman D, Waterman MR (1998) Lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51) and spermatogenesis. Drug Metab Dispos 26:1199–1201
Schiavoni G, Bennati AM, Castelli M, Fazia MA, Beccari T, Servillo G, Roberti R (2010) Activation of TM7SF2 promoter by SREBP-2 depends on a new sterol regulatory element, a GC-box, and an inverted CCAAT-box. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:587–592. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.01.013
Sekine S, Sasanuki S, Aoyama T, Takeuchi H (2007) Lowering systolic blood pressure and increases in vasodilator levels in SHR with oral alpha-linolenic acid administration. J Oleo Sci 56:341–345
Senggunprai L, Yoshinari K, Yamazoe Y (2009) Inhibitory effects of kynurenic acid, a tryptophan metabolite, and its derivatives on cytosolic sulfotransferases. Biochem J 422:455–462
Sessler AM, Kaur N, Palta JP, Ntambi JM (1996) Regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 mRNA stability by polyunsaturated fatty acids in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 271:29854–29858
Shimano H (2001) Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): transcriptional regulators of lipid synthetic genes. Prog Lipid Res 40:439–452
Shimano H (2002) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein family as global regulators of lipid synthetic genes in energy metabolism. Vitam Horm 65:167–194
Shimano H, Horton JD, Hammer RE, Shimomura I, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1996) Overproduction of cholesterol and fatty acids causes massive liver enlargement in transgenic mice expressing truncated SREBP-1a. J Clin Invest 98:1575–1584
Shimano H, Horton JD, Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) Isoform 1c of sterol regulatory element binding protein is less active than isoform 1a in livers of transgenic mice and in cultured cells. J Clin Invest 99:846–854
Shimano H, Yahagi N, Amemiya-Kudo M, Hasty AH, Osuga J, Tamura Y, Shionoiri F, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Harada K, Gotoda T, Ishibashi S, Yamada N (1999) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 as a key transcription factor for nutritional induction of lipogenic enzyme genes. J Biol Chem 274:35832–35839
Singh MS, Michael M (2009) Role of xenobiotic metabolic enzymes in cancer epidemiology. Methods Mol Biol 472:243–264
Sugawara T, Fujimoto Y, Ishibashi T (2001) Molecular cloning and structural analysis of human sterol C5 desaturase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1533:277–284
Takeuchi H, Sakurai C, Noda R, Sekine S, Murano Y, Wanaka K, Kasai M, Watanabe S, Aoyama T, Kondo K (2007) Antihypertensive effect and safety of dietary alpha-linolenic acid in subjects with high-normal blood pressure and mild hypertension. J Oleo Sci 56:347–360
Tsuruoka N, Kidokoro A, Matsumoto I, Abe K, Kiso Y (2005) Modulating effect of sesamin, a functional lignan in sesame seeds, on the transcription levels of lipid- and alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in rat liver: a DNA microarray study. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:179–188
Van Epps-Fung M, Williford J, Wells A, Hardy RW (1997) Fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes. Endocrinology 138:4338–4345
Vastrik I, D’Eustachio P, Schmidt E, Gopinath G, Croft D, de Bono B, Gillespie M, Jassal B, Lewis S, Matthews L, Wu G, Birney E, Stein L (2007) Reactome: a knowledge base of biologic pathways and processes. Genome Biol 8:R39
Vijaimohan K, Jainu M, Sabitha KE, Subramaniyam S, Anandhan C, Shyamala Devi CS (2006) Beneficial effects of alpha linolenic acid rich flaxseed oil on growth performance and hepatic cholesterol metabolism in high fat diet fed rats. Life Sci 79:448–454
Wang MY, Lee Y, Unger RH (1999) Novel form of lipolysis induced by leptin. J Biol Chem 274:17541–17544
Yi P, Lu FE, Xu LJ, Chen G, Dong H, Wang KF (2008) Berberine reverses free-fatty-acid-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through targeting IKKbeta. World J Gastroenterol 14:876–883
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the members of the Isoda Laboratory (University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan) and Central Laboratory (Nippon Flour Mills Co., Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan) for their scientific input and contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukumitsu, S., Villareal, M.O., Onaga, S. et al. α-Linolenic acid suppresses cholesterol and triacylglycerol biosynthesis pathway by suppressing SREBP-2, SREBP-1a and -1c expression. Cytotechnology 65, 899–907 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9510-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9510-x