Abstract
Memory bias modification (MBM) is a relatively new approach at targeting biased processing—a central cognitive factor causing and maintaining depression. In this pilot study we aimed to develop a smartphone-based autobiographical memory training, a novel form of MBM. A total of 153 unselected participants were randomly allocated to one of three experimental training conditions (positive, negative or sham memory training) conducted over a period of three days. Autobiographical memory bias and depressive scores were assessed pre- and post-training, whilst recent event recall and explicit self-referent memory bias were assessed post-training. Positive memory bias significantly increased in the positive training condition, however memory bias did not significantly differ post-training between the three conditions. Participants who received positive training recalled a positive autobiographical event more frequently compared to the other conditions. No significant difference between conditions was found in the other outcomes, including symptoms. The novel smartphone-based MBM intervention seems apt to affect autobiographical memory of emotional material. Future research should explore its possible (therapeutic) application.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Antidepressant medication and cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) are first-line treatment options for major depressive disorder (MDD), one of the most prevalent mental disorders in the world (Mathers and Loncar 2006; DeRubeis et al. 2005; Kessler et al. 2005). Both therapies have shortcomings with regard to accessibility, latency periods, effectiveness, time investment and costs. Latency periods of antidepressants are known to last several weeks (Machado-Vieira et al. 2010) and a full CBT treatment regime typically requires at least 12 weekly sessions, considered as time-consuming by most patients (DeRubeis et al. 2005; Newman et al. 2011; 2000). Furthermore, CBT is deemed particularly costly and is terminated once an individual has reached remission. Beside this, CBT is not always readily available for currently depressed or remitted individuals. It is therefore imperative that new low-threshold therapeutic options for depression are developed.
eHealth (add-on) treatments are a novel therapeutic candidate category (Bhui 2017; Yuen et al. 2012) and can potentially fill the aforementioned gaps in the current treatment provision. Some digitalized treatment options have been developed based on cognitive risk factors for depression. The cognitive theory of depression states that latent dysfunctional schemas and biased cognitive processing are mechanisms involved in the onset and persistence of depressive symptoms (Beck 2008; Disner et al. 2011; Gethin et al. 2017; LeMoult et al. 2017; LeMoult and Gotlib 2018). Underlying dysfunctional schemas seem to drive biased information processing, thus filtering and over-representing internal, external or incoming information. This selective processing causes preferential retrieval of negative, mood-congruent information (i.e. memory bias), resulting in sustained negative affect (Johnson et al. 2007; Gotlib and Joormann 2010; Joormann and Quinn 2014). Research shows ample evidence for this negative memory bias as a cognitive factor causing and maintaining depression (Matt et al. 1992; Ridout et al. 2009; Gaddy and Ingram 2014; LeMoult and Gotlib 2018). In contrast, non-depressed individuals tend to have a bias towards positively valenced information (Mathews and MacLeod 2005; Gaddy and Ingram 2014).
Cognitive bias modification (CBM) is a technique aimed to attenuate anxiety or depressive symptoms by computerised training (MacLeod et al. 2002). CBM is designed to directly target emotional processes by modifying cognitive routes known to contribute to the aetiology and maintenance of affective symptoms (Becker et al. 2015). Because CBM can be flexibly self-administered, it holds promise as an e-health treatment and recurrence prevention tool. However, most CBM studies have thus far used a lab-based application. CBM has been reported to rapidly influence emotional symptoms found in anxiety and depression (Hallion and Ruscio 2011), and to extend time to recurrence in addiction (Rinck and Becker 2007; Eberl et al. 2013). However, negative findings have also been frequently reported (Cristea et al. 2015; Jones and Sharpe 2017).
Several distinct subtypes of CBM have been developed, each targeting different cognitive domains such as attention (Attention bias modification/ABM; MacLeod et al. 2002), interpretation (Interpretation Bias Modification/CBM-I; Yiend et al. 2005), approach-avoidance (Approach-avoidance training/AAT; Rinck and Becker 2007) and memory (Memory bias modification/MBM; Vrijsen et al. 2016; Hertel et al. 2017; Vrijsen et al. 2018). Initial lab-based MBM studies in unselected samples have shown promising results (Vrijsen et al. 2016; Hertel et al. 2017; Arditte Hall et al. 2018). Recently, a lab-based MBM study performed by Vrijsen et al. (2018) in high-ruminating and dysphoric participants to memorise and recall positive, neutral and negative Swahili words (non-personalised verbal stimuli) paired with their translations in a single lab session. The study had overall null findings, however the positive training session in dysphoric individuals with a pre-existing positive memory bias resulted in an increased positive autobiographical bias. Due to depression being characterised by pervasive explicit conceptual processing (Disner et al. 2011; LeMoult and Gotlib 2018), it may require a more frequently applied (Roediger et al. 2011) and more self-referential training protocol in order to change memory bias. It is also conceivable that the potency of MBM sessions can be increased by offering the training in the subject’s natural environment. For example, most cognitive behavioural therapy protocols include positive diary keeping which is somewhat similar in concept to MBM. With this, we expect that administering multiple more personalised MBM sessions at home will result in a higher likelihood of transfer to daily life cognitive processing.
In this pilot study we set out to test a novel smartphone-based MBM-training in an unselected sample. This training is designed to habituate the process of autobiographical information retrieval with either a positive, neutral or negative emotional valence in an ecologically valid setting. To facilitate transfer to daily life memory, retrieval of autobiographical events was repeatedly prompted via an application on a mobile phone for three consecutive days. Participants in the positive condition were prompted to retrieve, evaluate and describe recent positive events whilst participants in the negative condition were instructed to do the same with negative events. In the sham training (the active control condition), participants were prompted to think of study- or work-related events—assuming this would also be specific categorical retrieval involving neutral and perhaps occasional positive or negative recall. In depression, spontaneously recalled memories are often more negative than positive or neutral, e.g. negative memory bias—a core cognitive depression process. With the positive training we thus aim to directly antagonise negative memory bias with repetitive positive memory training. Conversely, with the negative training we intended to simulate ruminative retrieval of negative information. In fact, repeated retrieval of information results in long-term memory retention (Karpicke and Roediger 2008), making retrieval-based learning a strong training approach.
Our primary aim was to test the effect of the training on the emotional valence and strength of spontaneous autobiographical memories—our Manipulation check. This was assessed using the experience sampling method (ESM), which is a valid and reliable method for monitoring psychological dimensions of experience, such as memories (Csikszentmihalyi and Larson 2014). It was expected that the positive condition would induce a more positive memory bias after training, whilst negative memory bias was expected to increase in the negative condition as seen in depression. This could be reflected as the number of recalled positive or negative memories and/or the strength of the recalled positive or negative memories. Memory bias was expected to remain stable in the sham condition. Short-term autobiographical memory recall valence after the training was assessed as a measure of near transfer. This was our primary outcome measure. We also explored whether the modification of memory bias would transfer further to self-referential but non-autobiographical explicit memory bias using the self-referential encoding task (SRET; Derry and Kuiper 1981; Hammen and Zupan 1984). The SRET is a wide-used memory bias task and was included in many previous memory bias (modification) studies (e.g., Gotlib et al. 2004; van Oostrom et al. 2012; Vogel et al. 2014; Vrijsen et al. 2018). To explore the reach of the training effect and to include clinically relevant measures, symptoms of depression including state and trait rumination and negative affect were assessed pre and post training. Here we theoretically expected a decrease of symptoms in the positive training condition and an increase in the negative training condition, although a floor effect could also be expected given the relatively healthy sample.
With this study, we aim to support the future development of at-home e-health approaches of CBM, with the broader aim to improve the treatment options for depression.
Materials and Methods
Participants
This study initially included 155 participants (mean age: 22.8 ± 6.4, 76% female), who were acquired via the Research Participation System (SONA) of the Radboud University in Nijmegen Social Sciences faculty, The Netherlands. No sample size calculation was performed because a new technique was used in this pilot study. Participants, who had to be fluent in Dutch, were selected based on age (18–70). They were kept oblivious of the study’s exact aim and were only informed that they would receive memory training using a smartphone. Participants received either course credit or financial compensation for their participation. All participants provided informed consent.
Two participants were excluded from the analyses because they responded to less than 80% of the training prompts, leaving 153 individuals for further analyses. Note that sample sizes differ slightly between analyses due to participants not responding consistently to all study components. Participants were randomly assigned to one of three conditions: positive, negative or sham memory training (see Fig. 1 for an overview of the study design).
Study design. Memory bias was measured twice before and twice after the CBM training using questions integrated in the smartphone application. BDI-II beck depression inventory second edition, MRSI momentary ruminative self-focus inventory, RRS Rumination Response Scale, PANAS NA positive and negative affect schedule negative affect scale, MBM memory bias modification training, life event autobiographical memory test, SRET self-referential encoding task
The Memory Bias Modification intervention
The participants received a Samsung Galaxy Y (2011) smartphone containing either a positive, negative or sham version of the MBM application (via the MovisensXS application; xs.movisens.com). All training cycles occurred over a period of three days and invariably began on a Tuesday and ended on a Thursday.
Subjects were prompted a total of ten times per day. They could be prompted to perform either an MBM task with a filler task or only a filler task. A total of four MBM-specific tasks were given per day during active hours (08:00–23:00) with a total of twelve MBM prompts within three days. In the positive condition, participants were asked to think of a recent positive event i.e. the most pleasant event that happened since the last prompt. Adherence to the MBM protocol was maintained by requesting participants to briefly describe the event using three keywords and by evaluating the event using a 100-point slider ranging from “extremely unpleasant” (− 50) to “extremely pleasant” (+ 50). The three versions of the training differed only in content of the MBM prompts that were given (see Table 1): unpleasant event recall in the negative condition and study- or work-related event recall in the sham condition. The three-worded answers given during the training were manually analysed post training to check for obvious unreliable adherence to the MBM training protocol. Failure to adhere to the protocol was defined as: systematically providing no answer to the questions (leaving the forms empty or typing in random letters) or repeatedly typing in the same memory.
In order to obscure the study’s aim, filler tasks were performed ten times per day either alone or alongside the MBM tasks. The filler questions are based on other experience sampling method studies (Wichers et al. 2007; Palmier-Claus et al. 2011) and were answered by adjusting a slider between “completely agree” and “completely disagree” (see Table 1).
Additional questionnaires were included for answering a different research question: Positive Mental Health Scale, International Physical Activity Questionnaire, and the Autobiographical Memory Test.
Measurements
Memory Bias Assessment (Manipulation Check)
Memory bias was assessed twice at the start and twice at the end of the three-day smartphone-based MBM training using the experience sampling method (ESM; Hektner et al. 2007; Csikszentmihalyi and Larson 2014) (Fig. 1). ESM is a systematic, non-intrusive, reliable and (ecologically) valid method to monitor biases during psychological research in real-time (Csikszentmihalyi and Larson 2014; Trull and Ebner-Priemer 2009). Memory bias assessment was done by asking participants to spontaneously recall the most important event since the previous prompt, to try to relive it vividly and to provide a three-word description of this event on their smartphone (Table 1). Examples of recalls were: “missed my bus” (negative) and “completed my homework” (positive). Participants were also asked to evaluate the event using a 100-point slider ranging from “extremely unpleasant” (− 50) to “extremely pleasant” (+ 50), thus assessing the emotional strength of the memories as well as the valence (+ or −). The slider position was pre-set at 0 (neutral) before the participants adjusted it to rate their memory. Participants’ mean ratings of their retrieved events pre and post training were used to analyse change in emotional strength of autobiographical memories, measured within the training paradigm.
In order to analyse whether the valence of the MBM training transferred to the emotional valence of the memories, the retrieved events ratings were dichotomised: at the cut-off rating of 0 or above, memories were classified as mainly ‘positive’. The rationale for the choice of dichotomized scores was due to the fact that the types of training we offered were also dichotomous in nature: either positive or negative. Furthermore, the autobiographical recall in the laboratory was also based on dichotomous data which made it possible to compare these outcomes. Below a rating of 0, memories were classified as mainly ‘negative’. Subsequently, the first two and the last two memory bias scores were grouped together per participant creating individual scores. Thus, a single person could be scored as having either two mainly positive memories, mixed memories, or two mainly negative memories, both pre- and post-training.
Autobiographical Recall (Near Transfer)
After the MBM training, participants returned to the lab. The participants were asked to “think of an event that took place in the previous week and that made an impression and/or evoked an emotional response”. These personal events were scored as being a positive or negative event by two independent raters blinded to the participants’ training conditions. Discrepancies were resolved by a third blinded rater. By doing so, it was possible to determine whether the training influenced the valence of autobiographical long-term memory.
Self-Referential Encoding Task (Far Transfer)
In order to explore the far transfer effects of the training, participants performed the Self-Referential Encoding Task (SRET; Derry and Kuiper 1981; Hammen and Zupan 1984) at the lab after the MBM training. The SRET assesses explicit memory bias for self-referential but non-autobiographical material. During the incidental learning phase, twelve positive and twelve negative potentially self-describing adjectives (e.g., “social” or “depressed”) were consecutively presented in a fixed randomised order. Participants were instructed to evaluate if the presented word was self-descriptive and either endorse or renounce it. This procedure was followed by a paper-based distraction task to keep participants naïve as to the task’s purpose. Next, participants were asked to recall all the words of the previous task. The positive recall bias score was calculated by dividing the number of endorsed and correctly recalled positive adjectives by the total number of endorsed and recalled adjectives (in line with Gotlib et al. 2004). Thus, a positive bias score of 0.80 would indicate that 80% of the words the participant endorsed and recalled were positive and consequently 20% would be negative emotional content.
Depressive Symptoms (Far Transfer)
Prior to (day 1) and after (day 5) the MBM training, participants were asked to fill out four validated questionnaires in Dutch:
The Beck Depression Inventory—second edition (BDI-II; Beck et al. 1996) is a depression severity questionnaire which has been validated in Dutch (Van der Does 2002). The BDI-II contains 21 items that can be scored between 0 to 3 and the total score can be categorised as minimal- (0–13), mild- (14–19), moderate- (20–28) or severe depressive symptoms (≥ 29). The BDI-II asks about symptoms that occurred over the previous 2 week period. The BDI-II instructions were altered for the post-training assessment: participants were asked to respond to the questions, looking back at the last week during the training.
The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) is a 20-item questionnaire that has a 10-item negative affect sub-scale (PANAS NA; Watson and Clark 1999). These items can be scored 1 to 5 with the total sub-scale illustrating the negative state of an individual.
The Momentary Ruminative Self-focus Inventory (MRSI) is a brief 6-item questionnaire that can be scored between 0 and 5 (Mor et al. 2013). It describes state ruminative responses to a depressed mood.
The Rumination Response Scale (RRS) consists of 22 items that can be scored between 1 and 4, and describes trait ruminative responses to a depressed mood (Treynor et al. 2003).
Awareness of Study Aim
At the end of the study, participants filled out an awareness check. They were asked what they believed the study aim was and whether they noticed any effects on how they felt or behaved. This made it possible to investigate whether sufficient blinding of the study’s goal had taken place.
Statistical Analyses
Parametric data was analysed with the use of repeated measures ANOVA’s with a within subjects factor of time (before MBM, after MBM) and a between subjects factor for the training condition (positive, negative, or sham MBM). Effect sizes for these parametric data were reported as partial eta-squared. Non-linear parametric data was log-transformed in order to fit linear assumptions. Non-parametric data was compared with the use of a Chi-square test of independence and effect sizes of the non-parametric data were expressed where possible as odds ratios. A Fisher’s exact test was conducted instead of a chi-square test if less than 80% of the cells had an expected count less than 5. Correlation analyses were expressed using Pearson’s r. The significance level for all analyses was set at a conventional 5%.
Results
Sample Characteristics
The three groups did not differ significantly with regard to age, self-identified gender, ethnicity, medication use and native language. Most importantly there were also no significant baseline differences in depressive characteristic ratings including the BDI-II, RRS, PANAS NA and MRSI total scores (Table 2). The mean BDI-II score was 7.7 ± 7.7 (range 0–49). At baseline, 13.7% (n = 21) of all participants scored ≥ 14 on the BDI-II indicating a mild depression or higher, there was no significant difference between groups χ2(2, n = 153) = 2.083, p = 0.353. The mean MRSI was 23.3 ± 6.6 (range 8–39), the total mean RRS score was 40.1 ± 11.0 (range 22–75) and the mean PANAS negative affect score was 13.84 ± 4.3 (range 10–29).
Smartphone-Based Memory Bias Assessments
First, we investigated whether the MBM training influenced the evaluation (strength) of the recalled memories measured at the beginning and end of the training using the smartphone application. Two participants from the positive MBM condition did not complete the smartphone-based memory bias assessment; their data was therefore excluded from this analysis.
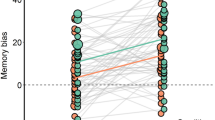
No significant time-by-condition effect was found, F (2, 149) = 0.06, p = 0.938, ηp2 = 0.001 analysing the self-evaluated memory strength scores. There was however a significant main effect of time F (2, 149) = 19.36, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.116, indicating that the memory evaluations increased significantly irrespective of the training condition. There was a general tendency to positively evaluate the memories in all groups with gross average memory strength scores of + 12.46 (± 7.95) before and + 20.19 (± 8.77) after the training (Fig. 2). This generally positive bias might represent the healthy status of our unselected sample.
Subsequently, the ratings of the recent events were dichotomised as either generally positive or generally negative based on the cut-off rating of 0 in order to examine the training effect on memory valence: these are non-parametric data. As there were two memory bias prompts at the beginning and two at the end of the training, we combined the dichotomised scores as follows: both positive, both negative and mixed memory. The three conditions did not differ at baseline, χ2(n = 151) = 2.371, p = 0.668 (Fig. 3).
There was a significant effect within the positive MBM condition on positive recall valence, p = 0.031 in a two-tailed 3 (valence) × 2 (time) Fisher’s exact test. No significant valence by time interaction effects were obtained in the negative MBM condition p = 0.281 and sham MBM condition p = 0.554. When the proportions were compared in the positive MBM condition pre and post training, it was found that there was a significant change in the proportion of positive memories as a result of a decline in the proportion of mixed memory (χ2(n = 48) = 6.561, p = 0.010, OR: 4.000). Positive versus negative memory and negative memory versus mixed memory showed no significant interaction: p = 0.999, OR 0.938 and p = 0.165, OR 0.234, respectively for the pre- and post-training comparison. It thus seems that the difference (before versus after) seen in the positive MBM condition can be attributed to a significant decline in mixed valenced memory proportion as a result of an increase in positive recall. However, the conditions post training (positive versus negative versus sham) did not differ significantly from each other in memory valence proportions, χ2(n = 151) = 1.384, p = 0.847.
Assessment of Autobiographical Recall After Training
After the MBM, participants were asked to recall an event that occurred in the last week that evoked an emotional response. Six participants refrained from adequately participating in this component of the study: two from the negative training condition and four from the sham training condition. This difference in dropout rate per training group was statistically not significant (p = 0.145). In the positive MBM training condition, 80% (41 out of 51) of the recalled events were rated as positive, in the negative condition 50% (24 out of 48), and in the sham condition 58% (28 out of 48). This difference in positive recalled event frequency between the conditions was statistically significant, χ2(2, n = 147) = 10.57, p = 0.005. Participants who were in the positive MBM condition recalled significantly more positive autobiographical events compared to participants who received the negative (p = 0.002, OR 0.244) and sham (p = 0.008, OR 0.348) MBM training. The sham and negative MBM conditions did not differ significantly in proportion of positive autobiographical recall (p = 0.413).
Depressive Symptoms
No significant time-by-condition interaction was found for the BDI-II score,2Footnote 1 F (2, 151) = 1.635, p = 0.198, ηp2 = 0.021. Nor were there significant time-by-condition interaction effects for the MRSI, F (2, 151) = 0.960, p = 0.385, ηp2 = 0.013, the PANAS NA, F (2, 151) = 0.041, p = 0.960, ηp2 = 0.001, or the RRS scores, F (2, 151) = 0.922, p = 0.400, ηp2 = 0.012. There were significant time effects on BDI-II and MRSI, irrespective of training condition: F (2, 151) = 27.587, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.155. and F (2, 151) = 32.582, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.178, respectively. Depressive symptom scores decreased significantly in all conditions, see Fig. 4.
Overview of the BDI-II, MRSI, RRS and PANAS NA scores before (grey) and after (white) the three CBM memory recall training conditions; positive (n = 51), negative (n = 50) and sham training (n = 52). Error bars depict the 95% confidence intervals. *p < .05. *BDI-II with modified instructions referring to symptoms during the past week including today
Self-Referential Encoding Task
Three participants did not complete the Self-Referential Encoding Task. Positive recall bias at the end of the study was 0.748 (± 0.090). Split per training condition this was 0.746 (± 0.076) in the positive group, 0.765 (± 0.086) in the negative group and 0.733 (± 0.105) in the sham group. An ANOVA of the positive recall bias scores between conditions showed no significant difference after the training between the three types of MBM, F (2, 141) = 1.483, p = 0.230, ηp2 = 0.021.
Memory Bias Correlation Analyses
Pearson correlation analyses were performed to assess the relationship between memory bias (both valence and strength) with depressive symptom scoring methods (BDI-II, RRS, MRSI, PANAS NA) and other assessments of memory bias (SRET). There was a significant inverse correlation between the BDI-II and the memory valence and strength at baseline; r = −.265, n = 153, p = 0.001 and r = −.186, n = 153, p = 0.021 respectively. When the memory bias valence and strength were compared to the RRS at baseline it was found that it was inversely correlated with memory bias valence r = −.178, n = 153, p = 0.028. This however was not the case when compared to the memory bias strengths r = − .081, n = 153, p = 0.320. Conversely, the MRSI scores at baseline revealed a significant inverse correlation with the memory bias strength r = − .185, n = 153, p = 0.022, but not valence r = -− .157, n = 153, p = 0.052. Finally, there was a significant inverse correlation of the memory bias valence r = − .189, n = 153, p = 0.019 and memory bias strength r = -− .166, n = 153, p = 0.040 with the PANAS NA at baseline. There was no correlation found between the SRET score post-training and the autobiographical memory ratings post-training, r = .121, n = 142, p = 0.152, likely indicating that these two tasks may assess different types of memory bias.
Participants’ Awareness of the Study Aims and Adherence to the MBM Protocol
On the last day of the study participants were asked what they thought the main study aim was. 95% of the study participants (n = 145) provided answers to the awareness questions. Of the respondents, 18% guessed that the study had something to do with emotions and memory. None of the participants correctly guessed the exact aim of the study. When participants were asked whether they noticed any effect of the training, 15.5% responded affirmatively (n = 148): 22% in the positive condition, 18% in the negative condition and 6% in the sham training condition; these differences were not significant χ2 (2, n = 148) = 4.87, p = 0.088. In the negative condition five participants reported that they had difficulties recalling negative events. These participants reported that this made them more aware of their positive mood during training.
The twelve three-worded memory answers given per participant of the training were manually analysed at the end of the training to detect obvious lack of adherence to the training protocol. No systematic failures to adhere to the training protocol were detected in the participants included in the study analyses.
Discussion
This pilot study provides a first attempt to modulate memory bias using a smartphone with participants residing in their own environment. Participants’ emotional autobiographical memory was trained four times a day over the course of three days. With the positive training we repeatedly requested participants to recall recent positive events. By doing so, we intended to strengthen their positive cognitive schemas relatively to their negative schema’s (Beck 2008). According to Beck’s theory of depression, strengthening these positive schemas should protect against future schematic re-activation of negative bias (near transfer of the training) and thus depression (far transfer). Protection against (re)activation of negative schemas is particularly important in depression due to the “kindling” phenomenon whereby negative information processing becomes more rigorous the more often they are activated (Crick and Dodge 1994). In fact, the MBM intervention holds some similarities to (positive) diary keeping, a technique often used in cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT). Both techniques prompt recall of positive events specifically. Smartphone-based MBM is specifically designed to increase the change of spontaneous positive retrieval by repeatedly promoting positive event recall. CBT diary keeping also included techniques such as reading back reported events and discussed this with the therapist.
It was investigated whether positive MBM resulted in more positive memory bias and if negative MBM would conversely result in more negative memory bias. Furthermore, it was explored whether these changes in memory bias would transfer to a corresponding change in depressive scores. The results demonstrated that only our positive smartphone-based MBM could alter the valence of positive (but not negative) event recall in daily life (Fig. 3). We were unsuccessful in evoking a negative memory bias in the negative training group. Furthermore, the positive training did not seem to influence the emotional strength (mean evaluation) of the recalled memories (Fig. 2). The training effect on memory valence, only seen in the positive group, also seemed to transfer to autobiographical memory assessed a day after the 3 days of training. The effects in the positive training did not seem to transfer to a different type of memory bias, i.e. bias for self-referential non-autobiographical verbal material – a far transfer outcome measure. Somewhat contrary to our initial predictions, no transfer of training effect was observed on depressive symptomatology measured with the BDI-II, MRSI, RRS and PANAS. Our correlation analyses comparing memory bias valence and strength to depressive symptoms indicated that there was a weak relationship between these outcome measures. Causal effects of a change in memory bias to a change in depressive symptoms remains to be investigated in future studies. Given our baseline sample characteristics (mostly euthymic with 13.7% displaying mild to severe depressive symptoms) the lack of positive memory bias transfer to other biases and symptoms may relate to a possible floor effect. Another possibility is that three days of training do not provide a sufficient dose for transfer to different types of memory bias or symptoms. An alternative explanation, especially applicable to more clinical populations, comes from studies in pharmacology. These studies observe that changes in bias after antidepressants precede clinical effects (Harmer et al. 2009). Therefore, we advise in new MBM-studies to investigate this possibility with a longer follow-up. Given that our target manipulation was engaged (autobiographical memory), we propose to study transfer of positive smartphone-based MBM using a longer training protocol including follow-up measures in a subclinically depressed sample or patients whom are in remission. The finding that the BDI-II and MRSI scores decreased over time in all training conditions might represent regression to the mean. This could also have been a side-effect of the filler-tasks, which might have resulted in increased emotional self-awareness, in turn modulating affective characteristics (Morris et al. 2010).
Previously, Vrijsen et al. (2016) also found that the positive condition yielded change in bias, while no change was found in the negative MBM condition. It seems that our population of generally healthy individuals are resilient against developing negative memory bias, at least with the current MBM dose. This is corroborated by in the awareness check data, where some subjects reported that they felt better as a result of their difficulty recalling negative events. This is also in line with earlier findings by Vrijsen et al. (2018), where only dysphoric individuals with an initial positive processing style showed more positive autobiographical memory bias after positive MBM, suggesting that it may be more difficult to revert a pre-existing negative memory bias as seen in depression.
Noticeable strengths of this study are that we provided an at-home CBM training using personal material, while administering the training at multiple time points over multiple days. A limitation of the study is the reliability of the sham condition as a ‘neutral’ active control training. We saw a non-significant difference in depressive symptom scores between the sham condition and the positive training condition, thus the sham training may have acted as a ‘lower-dosed’ version of the positive training. Participants with the sham training were prompted to recall specific events of unspecified emotional valence. Future studies should therefore consider including a non-active control condition. Another limitation of this study was the rather homogenously young sample population of 23 ± 6.37 years. Future research should investigate the acceptability and impact of our smartphone-based MBM intervention in in a sample with a wider age group. Furthermore, the statistically significant outcome measures of this study were solely made up of non-parametric data (our manipulation check and longer-term autobiographical recall valence frequencies). Non-parametric data have their specific disadvantages when compared to parametric data (Nahm 2016). A main critique is that the entirety of the original data is not completely utilised and therefore the information and conclusions drawn from these non-parametric methods is limited. Another limitation of this study is that the psychometric properties of the ESM method used in our manipulation check have not yet been formally reported. Furthermore, the choice of questionnaires to monitor changes in depressive symptoms (for example: BDI-II, RRS) may not have been apt enough to detect fast changes in DSM-based depressive symptoms. On the other hand, this may explain why we could not find a transfer to these outcome measures. A final limitation is that, due to the intrinsic nature of the MBM training, it is not possible to fully ensure the legitimacy of the recalled memories during the training. Three-worded memory recollections revealed no obvious discrepancies, however consistent truthful answers could not be guaranteed.
Conclusions
In light of the postulates mentioned in recent review by Grafton et al. (2017), our positive MBM training influences its primary target mechanism (i.e. autobiographical memory bias) and this modification seems to transfer to longer-term memories. However, further transfer to other depressive symptoms was not seen. Our negative MBM training failed to evoke negative memory bias and no significant effect on depressive symptoms were seen. This study represents a novel direction of CBM research, in which current versions are becoming more specified/personalized and hence more valid for their target population. In potential, our intervention could hold promise as a new CBM approach for (individuals recovering from) depression as relapse prevention. Currently, the value of our MBM intervention remains speculative, future research ought to investigate the clinical applicability as well as dose–response effects of smartphone-based MBM.
Notes
Log-transformed data used to apply linear model.
References
Arditte Hall, K. A., De Raedt, R., Timpano, K. R., & Joormann, J. (2018). Positive memory enhancement training for individuals with major depressive disorder. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy,47(2), 155–168.
Beck, A. T. (2008). The evolution of the cognitive model of depression and its neurobiological correlates. American Journal of Psychiatry,165(8), 969–977.
Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A., & Brown, G. K. (1996). Beck depression inventory-II. San Antonio,78(2), 490–498.
Becker, E. S., Vanderhasselt, M. A., & Vrijsen, J. N. (2015). Memory training in depression. Current Opinion in Psychology,4, 48–52.
Bhui, K. (2017). eHealth adventures in psychiatric therapeutics. The British Journal of Psychiatry,210(4), 309–310.
Crick, N. R., & Dodge, K. A. (1994). A review and reformulation of social information-processing mechanisms in children's social adjustment. Psychological Bulletin,115(1), 74.
Cristea, I. A., Kok, R. N., & Cuijpers, P. (2015). Efficacy of cognitive bias modification interventions in anxiety and depression: Meta-analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry,206(1), 7–16.
Csikszentmihalyi, M., & Larson, R. (2014). Validity and reliability of the experience-sampling method (pp. 35–54). Dordrecht: Flow and the foundations of positive psychology. Springer.
Derry, P. A., & Kuiper, N. A. (1981). Schematic processing and self-reference in clinical depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,90(4), 286.
DeRubeis, R. J., Hollon, S. D., Amsterdam, J. D., Shelton, R. C., Young, P. R., Salomon, R. M., et al. (2005). Cognitive therapy vs medications in the treatment of moderate to severe depression. Archives of General Psychiatry,62(4), 409–416.
Disner, S. G., Beevers, C. G., Haigh, E. A., & Beck, A. T. (2011). Neural mechanisms of the cognitive model of depression. Nature Reviews Neuroscience,12(8), 467.
Eberl, C., Wiers, R. W., Pawelczack, S., Rinck, M., Becker, E. S., & Lindenmeyer, J. (2013). Approach bias modification in alcohol dependence: do clinical effects replicate and for whom does it work best? Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience,4, 38–51.
Gaddy, M. A., & Ingram, R. E. (2014). A meta-analytic review of mood-congruent implicit memory in depressed mood. Clinical Psychology Review,34(5), 402–416.
Gethin, J. A., Lythe, K. E., Workman, C. I., Mayes, A., Moll, J., & Zahn, R. (2017). Early life stress explains reduced positive memory biases in remitted depression. European Psychiatry,45, 59–64.
Gotlib, I. H., & Joormann, J. (2010). Cognition and depression: Current status and future directions. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology,6, 285–312.
Gotlib, I. H., Kasch, K. L., Traill, S., Joormann, J., Arnow, B. A., & Johnson, S. L. (2004). Coherence and specificity of information-processing biases in depression and social phobia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,113(3), 386.
Grafton, B., MacLeod, C., Rudaizky, D., Holmes, E. A., Salemink, E., Fox, E., et al. (2017). Confusing procedures with process when appraising the impact of cognitive bias modification on emotional vulnerability. The British Journal of Psychiatry,211(5), 266–271.
Hammen, C., & Zupan, B. A. (1984). Self-schemas, depression, and the processing of personal information in children. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology,37(3), 598–608.
Harmer, D., Phil, C. J., O’Sullivan, U., Favaron, E., Massey-Chase, R., Ayres, R., et al. (2009). Effect of acute antidepressant administration on negative affective bias in depressed patients. American Journal of Psychiatry,166(10), 1178–1184.
Hektner, J. M., Schmidt, J. A., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2007). Experience sampling method: Measuring the quality of everyday life. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Hertel, P. T., Maydon, A., Cottle, J., & Vrijsen, J. N. (2017). Cognitive Bias Modification: Retrieval practice to simulate and oppose ruminative memory biases. Clinical Psychological Science,5(1), 122–130.
Hallion, L. S., & Ruscio, A. M. (2011). A meta-analysis of the effect of cognitive bias modification on anxiety and depression. Psychological Bulletin,137(6), 940.
Johnson, S. L., Joormann, J., & Gotlib, I. H. (2007). Does processing of emotional stimuli predict symptomatic improvement and diagnostic recovery from major depression? Emotion,7(1), 201.
Jones, E. B., & Sharpe, L. (2017). Cognitive bias modification: A review of meta-analyses. Journal of Affective Disorders,223, 175–183.
Joormann, J., & Quinn, M. E. (2014). Cognitive processes and emotion regulation in depression. Depression and Anxiety,31(4), 308–315.
Karpicke, J. D., & Roediger, H. L. (2008). The critical importance of retrieval for learning. Science,319(5865), 966–968.
Kessler, R. C., Berglund, P., Demler, O., Jin, R., Merikangas, K. R., & Walters, E. E. (2005). Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry,62(6), 593–602.
LeMoult, J., & Gotlib, I. H. (2018). Depression: A cognitive perspective. Clinical Psychology Review,69, 51–66.
LeMoult, J., Kircanski, K., Prasad, G., & Gotlib, I. H. (2017). Negative self-referential processing predicts the recurrence of major depressive episodes. Clinical Psychological Science,5(1), 174–181.
Machado-Vieira, R., Baumann, J., Wheeler-Castillo, C., Latov, D., Henter, I. D., Salvadore, G., et al. (2010). The timing of antidepressant effects: A comparison of diverse pharmacological and somatic treatments. Pharmaceuticals,3(1), 19–41.
MacLeod, C., Rutherford, E., Campbell, L., Ebsworthy, G., & Holker, L. (2002). Selective attention and emotional vulnerability: Assessing the causal basis of their association through the experimental manipulation of attentional bias. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,111(1), 107.
Mathers, C. D., & Loncar, D. (2006). Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Medicine,3(11), e442.
Mathews, A., & MacLeod, C. (2005). Cognitive vulnerability to emotional disorders. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol.,1, 167–195.
Matt, G. E., Vázquez, C., & Campbell, W. K. (1992). Mood-congruent recall of affectively toned stimuli: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review,12(2), 227–255.
Mor N, Marchetti I, Koster EHW (2013) The momentary ruminative self-focus inventory (MRSI): Validation and psychometric evaluation. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Morris, M. E., Kathawala, Q., Leen, T. K., Gorenstein, E. E., Guilak, F., Labhard, M., et al. (2010). Mobile therapy: Case study evaluations of a cell phone application for emotional self-awareness. Journal of Medical Internet Research,12(2), e10.
Nahm, F. S. (2016). Nonparametric statistical tests for the continuous data: The basic concept and the practical use. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology,69(1), 8.
Newman, M. G. (2000). Recommendations for a cost-offset model of psychotherapy allocation using generalized anxiety disorder as an example. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology,68(4), 549.
Newman, M. G., Szkodny, L. E., Llera, S. J., & Przeworski, A. (2011). A review of technology-assisted self-help and minimal contact therapies for anxiety and depression: Is human contact necessary for therapeutic efficacy? Clinical Psychology Review,31(1), 89–103.
Palmier-Claus, J. E., Myin-Germeys, I., Barkus, E., Bentley, L., Udachina, A., Delespaul, P. A. E. G., et al. (2011). Experience sampling research in individuals with mental illness: Reflections and guidance. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica,123(1), 12–20.
Ridout, N., Noreen, A., & Johal, J. (2009). Memory for emotional faces in naturally occurring dysphoria and induced sadness. Behaviour Research and Therapy,47(10), 851–860.
Rinck, M., & Becker, E. S. (2007). Approach and avoidance in fear of spiders. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry,38(2), 105–120.
Roediger, H. L., III, & Butler, A. C. (2011). The critical role of retrieval practice in long-term retention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences,15(1), 20–27.
Treynor, W., Gonzalez, R., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2003). Rumination reconsidered: A psychometric analysis. Cognitive Therapy and Research,27(3), 247–259.
Trull, T. J., & Ebner-Priemer, U. W. (2009). Using experience sampling methods/ecological momentary assessment (ESM/EMA) in clinical assessment and clinical research: Introduction to the special section. Psychological Assessment,21(4), 457–462.
Van der Does, A. J. W. (2002). Manual of the Dutch version of the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II-NL). Amsterdam: Harcourt.
Van Oostrom, I., Franke, B., Rijpkema, M., Gerritsen, L., Arias-Vásquez, A., Fernández, G., et al. (2012). Interaction between BDNF Val66Met and childhood stressful life events is associated to affective memory bias in men but not women. Biological Psychology,89(1), 214–219.
Vogel, S., Gerritsen, L., van Oostrom, I., Arias-Vásquez, A., Rijpkema, M., Joëls, M., et al. (2014). Linking genetic variants of the mineralocorticoid receptor and negative memory bias: Interaction with prior life adversity. Psychoneuroendocrinology,40, 181–190.
Vrijsen, J. N., Hertel, P. T., & Becker, E. S. (2016). Practicing emotionally biased retrieval affects mood and establishes biased recall a week later. Cognitive Therapy and Research,40(6), 764–773.
Vrijsen, J. N., Dainer-Best, J., Witcraft, S. M., Papini, S., Hertel, P., Beevers, C. G., et al. (2018). Effect of cognitive bias modification-memory on depressive symptoms and autobiographical memory bias: Two independent studies in high-ruminating and dysphoric samples. Cognition and Emotion,33(2), 288–304.
Watson D, Clark LA (1999) The PANAS-X: Manual for the positive and negative affect schedule-expanded form.
Wichers, M., Myin-Germeys, I., Jacobs, N., Peeters, F., Kenis, G., Derom, C., et al. (2007). Genetic risk of depression and stress-induced negative affect in daily life. The British Journal of Psychiatry,191(3), 218–223.
Yiend, J., Mackintosh, B., & Mathews, A. (2005). Enduring consequences of experimentally induced biases in interpretation. Behaviour Research and Therapy,43(6), 779–797.
Yuen, E. K., Goetter, E. M., Herbert, J. D., & Forman, E. M. (2012). Challenges and opportunities in internet-mediated telemental health. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice,43(1), 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Damian A. Visser, Indira Tendolkar, Aart H. Schene, Livia van de Kraats, Henricus G. Ruhe, Janna N. Vrijsen declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research Involving Animal Rights
No animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Research Transparency Statement
We report on all conditions, data exclusions and measures.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Visser, D.A., Tendolkar, I., Schene, A.H. et al. A Pilot Study of Smartphone-Based Memory Bias Modification and Its Effect on Memory Bias and Depressive symptoms in an Unselected Population. Cogn Ther Res 44, 61–72 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-019-10042-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-019-10042-x