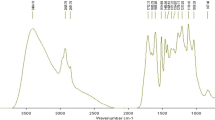
Steam-exploded lignin (SEL) was separated from cornstalk residue, which came from steam-exploded cornstalk after enzymatic hydrolysis. There are two methods to acquire SEL, the alkali solution and the organic solvent method. SEL was analyzed with respect to the elementary composition, molecular weight, IR spectrum, and 13C NMR spectra. The C9-formula of SEL was calculated from the experiment data. According to 13C NMR, SEL can be classified as a “GSH” type of lignin, and it is composed mainly of β-O-4 ether bonds together with β-5 and β-1 carbon-carbon linkages between the lignin structural units.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Xu, Q. Yong, G. Shan, and S. Y. Yu, J. Chem. Ind. Forest Prod., 33, 15 (1999).
X. S. Cheng, Abstract of First Asian-Oceanian Conference on Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Tokyo, Japan, 3, 136 (2007).
N. Nishimura, A. Izumi, and K. S. Kuroda, Ind. Crops Prod., 15, 115 (2002).
A. M. A. Nada, H. El-Saied, M. Fadl, and M. Nassar, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 43, 55 (1994).
A. M. A. Nada, M. El-Sakhawy, and S. Kamel, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 60, 247 (1998).
D. Z. Huang, J. Guangxi University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition) [in Chinese], 4, 32 (1998).
K. Freudenberg, The Constitution and Biosynthesis of Lignin, New York: Springer verlag, 1968.
O. Faix, Holzforschung, 45 (suppl), 21 (1991).
G. Vazquez, G. Gonzalez, J. Antorrena, and S. Freire, Holzforschung, 51, 158 (1975).
B. Scholze and D. Meier, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 60, 41 (2001).
J. Lawther, Mark, R. C. Sun, and W. B. Banks, Ind. Crops Prod., 5, 97 (1996).
B. Xiao, X. F. Sun, and R. C. Sun, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 74, 307 (2001).
R. C. Sun, J. Tomkinson, and X. F. Sun, Polymer, 41, 8409 (2000)
R. C. Sun, X. F. Sun, P. Fowler, and J. Tomkinson, Eur. Polym. J., 38, 1399 (2002).
J. X. Xu, X. S. Cheng, Y. P. Chen, and C. Y. Lin, Spec. Purp. Rubber Prod., 5, 1 (2004).
Acknowledgment
The author thanks the Key Laboratory of Cellulose and Lignocellulosics Chemistry, Guangzhou Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences for financial support (LCLC-2004-158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 5, pp. 582–584, September–October, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y.P., Cheng, X.S. Separation and characteristic analysis of steam-exploded lignin from cornstalk residue. Chem Nat Compd 45, 693–696 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-009-9429-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-009-9429-4