Abstract
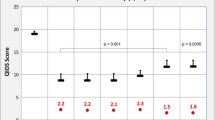
In this study, we use the Colorado Symptom Index, a measure of psychiatric symptomatology, to identify vulnerable subgroups within the severely mentally ill population at elevated risk for HIV infection. Baseline data on 228 HIV positive and 281 HIV negative participants from two clinical trials were used. With years to HIV diagnosis as our primary endpoint, Kaplan–Meier estimates were calculated to find a CSI cut-off score, and a Cox proportional hazards model was used to obtain relative risks of infection for the two CSI categories created by the cut point. We found that a CSI score ≥ 30 was associated with a 47% increased risk for HIV infection (P < 0.01). While this study establishes the foundation for using CSI scores to identify a vulnerable subgroup within the SMI community, further studies should develop effective approaches to mitigate psychiatric symptomatology in order to examine the impact on HIV transmission risky behaviors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blank, M. B., Mandell, D. S., Aiken, L., & Hadley, T. R. (2002). Co-occurrence of HIV and serious mental illness among medicaid recipients. Psychiatric Services (Washington, D.C.), 53(7), 868–873.
Blank, M. B., Metzger, D. S., Wingood, G. M., & DiClemente, R. J. (2008). The first national scientific meeting of the social and behavioral science research network. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes (1999), 47(1), S1-4.
Boothroyd, R. A., & Chen, H. J. (2008). The psychometric properties of the colorado symptom index. Administration and Policy In Mental Health, 35(5), 370–378.
Brooner, R. K., Greenfield, L., Schmidt, C. W., & Bigelow, G. E. (1993). Antisocial personality disorder and HIV infection among intravenous drug abusers. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 150(1), 53–58.
Brunette, M. F., Mercer, C. C., Carlson, C. L., Rosenberg, S. D., & Lewis, B. F. (2000). HIV-related services for persons with severe mental illness: Policy and practice in new hampshire community mental health. The Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research, 27(3), 347–353.
Carey, M. P., Carey, K. B., Maisto, S. A., Schroder, K. E., Vanable, P. A., & Gordon, C. M. (2004). HIV risk behavior among psychiatric outpatients: Association with psychiatric disorder, substance use disorder, and gender. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 192(4), 289–296.
Carey, M. P., Weinhardt, L. S., & Carey, K. B. (1995). Prevalence of infection with HIV among the seriously mentally ill: Review of the research and implications for practice. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice., 26, 262–268.
Ciarlo, J., & Edwards, D. (1981). The assessment of client/patient outcome: techniques for use in mental health programs. Washington: National Institute of Mental Health.
Conrad, K. J., Yagelka, J. R., Matters, M. D., Rich, A. R., Williams, V., & Buchanan, M. (2001). Reliability and validity of a modified colorado symptom index in a national homeless sample. Mental Health Services Research, 3(3), 141–153.
Cournos, F., & McKinnon, K. (1997). HIV seroprevalence among people with severe mental illness in the United States: A critical review. Clinical Psychology Review, 17(3), 259–269.
Coverdale, J. H., & Turbott, S. H. (2000). Sexual and physical abuse of chronically ill psychiatric outpatients compared with a matched sample of medical outpatients. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 188(7), 440–445.
Dickey, B., Normand, S. L., Weiss, R. D., Drake, R. E., & Azeni, H. (2002). Medical morbidity, mental illness, and substance use disorders. Psychiatric Services (Washington, D.C.), 53(7), 861–867.
Dixon, L., Postrado, L., Delahanty, J., Fischer, P. J., & Lehman, A. (1999). The association of medical comorbidity in schizophrenia with poor physical and mental health. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 187(8), 496–502.
Grassi, L. (1996). Risk of HIV infection in psychiatrically ill patients. AIDS Care, 8(1), 103–116.
Green, R. S., & Gracely, E. J. (1987). Selecting a rating scale for evaluating services to the chronically mentally ill. Community Mental Health Journal, 23(2), 91–102.
Himelhoch, S., Josephs, J. S., Chander, G., Korthuis, P. T., Gebo, K. A., & HIV Research Network. (2009). Use of outpatient mental health services and psychotropic medications among HIV-infected patients in a multisite, multistate study. General Hospital Psychiatry, 31(6), 538–545.
Kalichman, S. C., Kelly, J. A., Johnson, J. R., & Bulto, M. (1994). Factors associated with risk for HIV infection among chronic mentally ill adults. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 151(2), 221–227.
Lawless, J. F., & Louis A. (Duhring Fund). (2003). Statistical models and methods for lifetime data (2nd ed.). Hoboken, N.J: Wiley-Interscience.
McKinnon, K., & Cournos, F. (1998). HIV infection linked to substance use among hospitalized patients with severe mental illness. Psychiatric Services (Washington, D.C.), 49(10), 1269.
McLellan, A. T., Kushner, H., Metzger, D., Peters, R., Smith, I., Grissom, G., et al. (1992). The fifth edition of the addiction severity index. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 9(3), 199–213.
Metzger, D. S., Woody, G. E., McLellan, A. T., O’Brien, C. P., Druley, P., Navaline, H., et al. (1993). Human immunodeficiency virus seroconversion among intravenous drug users in- and out-of-treatment: An 18-month prospective follow-up. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 6(9), 1049–1056.
Rosenberg, S. D., Trumbetta, S. L., Mueser, K. T., Goodman, L. A., Osher, F. C., Vidaver, R. M., et al. (2001). Determinants of risk behavior for human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in people with severe mental illness. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 42(4), 263–271.
Rothbard, A. B., Lee, S., & Blank, M. B. (2009). Cost of treating seriously mentally ill persons with HIV following highly active retroviral therapy (HAART). The Journal of Mental Health Policy and Economics, 12(4), 187–194.
Sikkema, K. J., Watt, M. H., Drabkin, A. S., Meade, C. S., Hansen, N. B., & Pence, B. W. (2010). Mental health treatment to reduce HIV transmission risk behavior: A positive prevention model. AIDS and Behavior, 14(2), 252–262.
Walkup, J., Blank, M. B., Gonzalez, J. S., Safren, S., Schwartz, R., Brown, L., et al. (2008). The impact of mental health and substance abuse factors on HIV prevention and treatment. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes (1999), 47 (1), S15–S19.
Woody, G. E., Metzger, D., Navaline, H., McLellan, T., & O’Brien, C. P. (1997). Psychiatric symptoms, risky behavior, and HIV infection. NIDA Research Monograph, 172, 156–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, E.S., Rothbard, A. & Blank, M.B. Using Psychiatric Symptomatology to Assess Risk for HIV Infection in Individuals with Severe Mental Illness. Community Ment Health J 47, 672–678 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-011-9402-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-011-9402-0