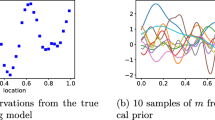
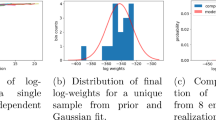
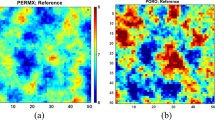
Abstract
This paper examines the properties of the Iterated Ensemble Smoother (IES) and the Multiple Data Assimilation Ensemble Smoother (ES–MDA) for solving the history matching problem. The iterative methods are compared with the standard Ensemble Smoother (ES) to improve the understanding of the similarities and differences between them. We derive the three smoothers from Bayes’ theorem for a scalar case which allows us to compare the equations solved by the three methods, and we can better understand which assumptions are applied and their consequences. When working with a scalar model, it is possible to use a vast ensemble size, and we can construct the sample distributions for both priors and posteriors, as well as intermediate iterates. For a linear model, all three methods give the same result. For a nonlinear model, the iterative methods improve on the ES result, but the two iterative methods converge to different solutions, and it is not clear which should be the preferred choice. It is clear that the ensemble of cost functions used to define the IES solution does not represent an exact sampling of the posterior-Bayes’ probability density function. Also, the use of an ensemble representation for the gradient in IES introduces an additional approximation compared to using an exact analytic gradient. For ES–MDA, the convergence, as a function of increasing number of uniform update steps, is studied for a huge ensemble size. We illustrate that ES–MDA converges to a solution that differs from the Bayesian posterior. The convergence is also examined using a realistic sample size to study the impact of the number of realizations relative to the number of update steps. We have run multiple ES–MDA experiments to examine the impact of using different schemes for choosing the lengths of the update steps, and we have tried to understand which properties of the inverse problem imply that a non-uniform update step length is beneficial. Finally, we have examined the smoother methods with a highly nonlinear model to examine their properties and limitations in more extreme situations.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Aanonsen, S.I., Naevdal, G., Oliver, D.S., Reynolds, A., Valles, B.: Ensemble Kalman filter in reservoir engineering – A review. SPE J. 14(3), 393–412 (2009). https://doi.org/10.21188/117274-PA. SPE-117274-PA
Bocquet, M., Sakov, P.: An iterative ensemble Kalman smoother. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140, 1521–1535 (2014)
Burgers, G., van Leeuwen, P.J., Evensen, G.: Analysis scheme in the ensemble Kalman filter. Mon. Weather. Rev. 126, 1719–1724 (1998)
Chen, Y., Oliver, D.S.: Ensemble randomized maximum likelihood method as an iterative ensemble smoother. Math. Geosci. 44, 1–26 (2012)
Chen, Y., Oliver, D.S.: Levenberg-Marquardt forms of the iterative ensemble smoother for efficient history matching and uncertainty quantification. Comput. Geosci. 17, 689–703 (2013)
Emerick, A.A.: Analysis of performance of ensemble-based assimilation of production and seismic data. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 139, 219–239 (2016)
Emerick, A.A., Reynolds, A.C.: History matching time-lapse seismic data using the ensemble Kalman filter with multiple data assimilations. Comput. Geosci. 16(3), 639–659 (2012)
Emerick, A.A., Reynolds, A.C.: Ensemble Smoother with multiple data assimilation. Comput. Geosci. 55, 3–15 (2013)
Evensen, G.: Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. J. Geophys. Res. 99(C5), 10,143–10,162 (1994)
Evensen, G.: Sampling strategies and square root analysis schemes for the EnKF. Ocean Dyn. 54, 539–560 (2004)
Evensen, G.: Data Assimilation: the Ensemble Kalman Filter, 2ed. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Evensen, G.: The ensemble Kalman filter for combined state and parameter estimation. IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 29(3), 83–104 (2009)
Evensen, G., van Leeuwen, P.J.: An ensemble Kalman smoother for nonlinear dynamics. Mon. Weather. Rev. 128, 1852–1867 (2000)
Iglesias, M.A.: Iterative regularization for ensemble data assimilation in reservoir models. Comput. Geosci. 19(1), 177–212 (2015)
Iglesias, M.A.: A regularizing iterative ensemble Kalman method for PDE-constrained inverse problems. Inverse Prob. 32(2), (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/32/2/025002
Kitanidis, P.K.: Quasi-linear geostatistical therory for inversing. Water Resour. Res. 31(10), 2411–2419 (1995)
Le, D.H., Emerick, A.A., Reynolds, A.C.: An adaptive ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation for assisted history matching. SPE Journal, SPE-173214-PA 21(6), 2195–2207 (2016)
Luo, X., Stordal, A.S., Lorentzen, R.J., Nævdal, G.: Iterative Ensemble Smoother as an approximate solution to a regularized minimum-average-cost problem: Theory and applications. SPE Journal, SPE-176023-PA 20 (5), 962–982 (2015)
Nævdal, G., Johnsen, L.M., Aanonsen, S.I., Vefring, E.: Reservoir monitoring and continuous model updating using the ensemble Kalman filter. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition (SPE 84372) (2003)
Neal, R.M.: Sampling from multimodal distributions using tempered transitions. Stat. Comput. 6(4), 353–366 (1996)
Oliver, D.S., He, N., Reynolds, A.C.: Conditioning Permeability Fields to Pressure Data. In: ECMOR – 5th European Conference on the Mathematics of Oil Recovery (1996)
Rafiee, J., Reynolds, A.C.: Theoretical and efficient practical procedures for the generation of inflation factors for ES–MDA. Inverse Problems 33(11), 115003 (2017)
Sakov, P., Oliver, D.S., Bertino, L.: An iterative EnKF for strongly nonlinear systems. Mon. Weather. Rev. 140, 1988– 2004 (2012)
Skjervheim, J.A., Evensen, G., Hove, J., Vabø, J.: An ensemble smoother for assisted history matching. SPE 141929 (2011)
Stordal, A., Elsheikh, A.H.: Iterative ensemble smoothers in the annealed importance sampling framework. Adv. Water Resour. 86, 231–239 (2015)
van Leeuwen, P.J., Evensen, G.: Data assimilation and inverse methods in terms of a probabilistic formulation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 124, 2898–2913 (1996)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research project funded by Statoil and has benefited from the interaction and collaborations with the Nordforsk Nordic center of excellence in data assimilation, EMBLA. The author is grateful for constructive comments by three anonymous reviewers that improved the readability of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Evensen, G. Analysis of iterative ensemble smoothers for solving inverse problems. Comput Geosci 22, 885–908 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-018-9731-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-018-9731-y