Abstract
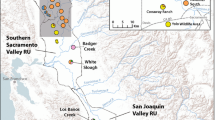
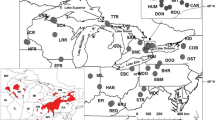
The giant garter snake, Thamnophis gigas, is a threatened species endemic to California’s Central Valley. We tested the hypothesis that current watershed boundaries have caused genetic differentiation among populations of T. gigas. We sampled 14 populations throughout the current geographic range of T. gigas and amplified 859 bp from the mitochondrial gene ND4 and one nuclear microsatellite locus. DNA sequence variation from the mitochondrial gene indicates there is some genetic structuring of the populations, with high FST values and unique haplotypes occurring at high frequency in several populations. We found that clustering populations by watershed boundary results in significant between-region genetic variance for mtDNA. However, analysis of allele frequencies at the microsatellite locus NSU3 reveals very low FST values and little between-region variation in allele frequencies. The discordance found between mitochondrial and microsatellite data may be explained by aspects of molecular evolution and/or T. gigas life history characteristics. Differences in effective population size between mitochondrial and nuclear DNA, or male-biased gene flow, result in a lower migration rate of mitochondrial haplotypes relative to nuclear alleles. However, we cannot exclude homoplasy as one explanation for homogeneity found for the single microsatellite locus. The mitochondrial nucleotide sequence data supports conservation practices that identify separate management units for T. gigas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwater BF (1979) Ancient Processes at the Site of Southern San Francisco Bay: Movement of the Crust and Changes in Sea Level. In: San Francisco Bay: The Urbanized Estuary. (eds. Conomos TJ, Leviton AE, Berson M), pp. 31–45, Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Pacific Division of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, San Francisco, CA.
BF Atwater BE Ross JF Wehmiller (1981) ArticleTitleStratigraphy of late Quaternary estuarine deposits and amino acid stereochemistry of oyster shells beneath San Francisco Bay, California Quat. Res. 16 181–200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXlvFSgt7Y%3D
E Arevalo JW Sites SuffixJr. (1994) ArticleTitleMitochondrial DNA sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships among eight chromosome races of the Sceloporus grammicus complex (Phrynosomatidae) in Central Mexico Syst. Biol. 43 387–418
JC Avise (1992) ArticleTitleMolecular population structure and the biogeographic history of a regional fauna: A case history with lessons for conservation biology Oikos 63 62–76 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XisFansbw%3D
JC Avise (1995) ArticleTitleMitochondrial DNA polymorphism and a connection between genetics and demography of relevance to conservation Conserv. Biol. 9 686–690 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.09030686.x
CW Birky SuffixJr. P Fuerst T Maruyama (1989) ArticleTitleOrganelle gene diversity under migration, mutation, and drift: Equilibrium expectations, approach to equilibrium, effects of heteroplasmic cells, and comparison to nuclear genes Genetics 121 613–627 Occurrence Handle2714640
Brode JM (1988) Natural history of the giant garter snake (Thamnophis couchii gigas). In: Proceedings of the conference on California herpetology (eds. De Lisle HF, Brown DB, Kaufman B, McGurty BM), pp. 25–28, vol. 4, Southwestern Herpetological Society.
California Department of Fish and Game Commission (1971) California Code of Regulations: Animals of California declared to be endangered or threatened Title 14, sect. 670.5. Available at: http//www.calregs.com.
B Charlesworth (1998) ArticleTitleMeasures of divergence between populations and the effect of forces that reduce variability Mol. Biol. Evol. 15 538–543 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXislens7g%3D Occurrence Handle9580982
Dennis NB, Marcus ML, Hill H (1984) Status and trends of California wetlands. Report prepared for The California Assembly Resources Subcommittee on Status and Trends.
A Estoup JM Cornuet (1999) Microsatellite evolution: inferences from population data DB Goldstein C Schlotterer (Eds) Microsatellites Evolution and Applications Oxford University Press Inc. New York 49–65
L Excoffier PE Smouse JM Quattro (1992) ArticleTitleAnalysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data Genetics 131 479–491 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlsVCntro%3D Occurrence Handle1644282
HS Fitch (1940) ArticleTitleA biogeographical study of the ordinoides artenkreis of garter snakes (genus Thamnophis) Univ. Calif. Pub. Zool. 44 1–150
NN Fitzsimmons CJ Limpus JA Norman AR Goldizen JD Miller C Moritz (1997) ArticleTitlePhilopatry of male marine turtles inferred from mitochondrial DNA markers Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94 8912–8917 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.94.16.8912 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXltlWhtLg%3D Occurrence Handle9238077
NB Ford (1986) The role of pheromone trails in the sociobiology of snakes D Duvall D Muller-Schwarze RM Silverstein (Eds) Chemical Signals in Vertebrates NumberInSeries4 Plenum Press New York 261–278
Fredrickson LH (1991) Strategies for water level manipulations in moist-soil systems. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Leaflet 13.4.6, pp 1–8.
Hansen GE (1988) Review of the status of the giant garter snake (Thamnophis gigas) and its supporting habitat during 1986–1987. California Department of Fish and Game Draft Report, C-2060, pp.31.
Hansen GE, Brode JM (1980) Status of the giant garter snake, Thamnophis couchii gigas. Inland Fisheries Endangered Species Program special publication, 80–5, 1–14.
PW Hedrick (1999) ArticleTitlePerspective: Highly variable loci and their interpretation in evolution and conservation Evolution 53 313–318
DM Hillis BK Mable A Larson SK Davis EA Zimmer (1996) Nucleic Acids IV: Sequencing and Cloning DM Hillis C Moritz BK Mable (Eds) Molecular Systematics EditionNumber2 Sinauer Associates Inc. Massachusetts 342–343
AD Howard (1979) Geologic History of Middle California University of California Press Berkeley, CA.
SA Karl BW Bowen JC Avise (1992) ArticleTitleGlobal population genetic structure and male-mediated gene flow in the Green turtle (Chelonia mydas): RFLP analyses of anonymous nuclear loci Genetics 131 163–173 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVCqu74%3D Occurrence Handle1350555
Y Kumazawa H Pta M Nishida T Ozawa (1998) ArticleTitleThe complete nucleotide sequence of a snake (Dinodon semicarinatus) mitochondrial genome with two identical control regions. Genbank accession No. NC001945 Genetics 150 313–329 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmtFKgsL8%3D Occurrence Handle9725849
R Lawson HC Dessauer (1979) ArticleTitleBiochemical genetics and systematics of garter snakes of the Thamnophis elegans-couchii-ordinoides complex Occ. Pap. Mus. Zool. Louisiana St. Univ. 56 1–23
JE Maldonado C Vila RK Wayne (2001) ArticleTitleTripartite genetic subdivisions in theornate shrew (Sorex ornatus) Mol. Ecol. 10 127–147 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01178.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjs1ejtLY%3D Occurrence Handle11251793
JR Macey Y Wang NB Ananjeva A Larson TJ Papenfuss (1999) ArticleTitleVicariant patterns of fragmentation among gekkonid lizards of the genus Teratoscincus produced by the Indian collision: A molecular phylogenetic perspective and an area cladogram for Central Asia Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 12 320–332 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksVOisrk%3D Occurrence Handle10413626
JR Macey JL Strasburg JA Brisson VT Vredenburg M Jennings A Larson (2001) ArticleTitleMolecular phylogenetics of western North American frogs of the Rana boylii species group Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 19 131–143 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitlOjtbo%3D Occurrence Handle11286498
GF McCracken GM Burghardt SE Houts (1999) ArticleTitleMicrosatellite markers and multiple paternity in the garter snake Thamnophis sirtalis Mol. Ecol. 8 1475–1479 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-294x.1999.00720.x Occurrence Handle10564453
DJ Melnick GA Hoelzer (1992) ArticleTitleDifferences in male and female macaque dispersal lead to contrasting distributions of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA variation Int. J. Primatol. 13 379–393
WS Moore (1995) ArticleTitleInferring phylogenies from mtDNA variation: mitochondrial-gene trees versus nuclear-gene trees Evolution 49 718–726
C Moritz (1994) ArticleTitleDefining ‘Evolutionarily Significant Units’ for conservation Trends Ecol. Evolut. 9 373–375
InstitutionalAuthorNameNational Research Council (1989) Irrigation-Induced Water Quality Problems: What Can Be Learned from the San Joaquin Valley Experience. Committee on Irrigation-Induced Water Quality Problems National Academy Press Washington, DC
MR Prosser HL Gibbs PJ Weatherhead (1999) ArticleTitleMicrogeographic population genetic structure in the northern water snake, Nerodia sipedon sipedon, detected using microsatellite DNA loci Mol. Ecol. 8 329–333 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-294X.1999.00530.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjtVOgu7c%3D Occurrence Handle10065548
HK Reinert LM Bushar (1991) ArticleTitleA safe and simple method of blood collection from rattlesnakes Herpetol. Rev. 22 51–52
DA Rossman NB Ford RA Seigel (1996) The Garter Snakes: Evolution and Ecology University of Oklahoma Press Oklahoma
S Schneider D Roessli L Excoffier (2000) Arlequin version 2000. A Software for Population Genetics Data Analysis Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, Department of Anthropology and Ecology, University of Geneva Geneva, Switzerland
M Slatkin (1995) ArticleTitleA measure of population subdivision based on microsatelliteallele frequencies Genetics 139 457–462 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB38%2FmvVE%3D Occurrence Handle7705646
AM Tan DB Wake (1995) ArticleTitleMtDNA phylogeography of the California newt, Taricha torosa (Caudata, Salamandridae) Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 4 383–394 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtF2isLs%3D Occurrence Handle8747295
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1989) Wetlands of the California Central Valley: Status and Trends 1939 to mid-1980s. Eds. Frayer WE, Peters DD, Pywell HR, pp. 25.
InstitutionalAuthorNameU.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1993) ArticleTitleEndangered and threatened wildlife and plants: Determination of threatened status for the giant garter snake Federal Register 58 54053–54066
DB Wake (1997) ArticleTitleIncipient species formation in salamanders of the Ensatina complex Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94 7761–7767 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.94.15.7761 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksl2nsb8%3D Occurrence Handle9223261
BS Weir CC Cockerham (1984) ArticleTitleEstimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure Evolution 38 1358–1370
S Wright (1969) Evolution and the Genetics of Populations, Vol. 2 The Theory of Gene Frequencies University of Chicago Press Chicago
Yanev KP (1980) Biogeography and distribution of three parapatric salamander species in coastal and borderland California (ed. Power DM), pp. 531–550. Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History, California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paquin, M.M., Wylie, G.D. & Routman, E.J. Population Structure of the Giant Garter Snake, Thamnophis gigas. Conserv Genet 7, 25–36 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-005-7439-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-005-7439-8