Abstract
Climate change is an issue which elicits low engagement, even among concerned segments of the public. While research suggests that the presentation of factual information (e.g., scientific consensus) can be persuasive to some audiences, there is also empirical evidence indicating that it may also increase resistance in others. In this research, we investigate whether climate change narratives structured as stories are better than informational narratives at promoting pro-environmental behavior in diverse audiences. We propose that narratives structured as stories facilitate experiential processing, heightening affective engagement and emotional arousal, which serve as an impetus for action-taking. Across three studies, we manipulate the structure of climate change communications to investigate how this influences narrative transportation, measures of autonomic reactivity indicative of emotional arousal, and pro-environmental behavior. We find that stories are more effective than informational narratives at promoting pro-environmental behavior (studies 1 and 3) and self-reported narrative transportation (study 2), particularly those with negatively valenced endings (study 3). The results of study 3 indicate that embedding information in story structure influences cardiac activity, and subsequently, pro-environmental behavior. These findings connect works from the fields of psychology, neuroscience, narratology, and climate change communication, advancing our understanding of how narrative structure influences engagement with climate change through emotional arousal, which likely incites pro-environmental behavior as the brain’s way of optimizing bodily budgets.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Recent research finds a consistent ideological divide on belief and engagement with climate change across a range of countries, though none to the extent observed in the USA, Canada, or Australia (Dryzek et al. 2011; Tranter and Booth 2015). In the USA, approximately 28% of the population neither believes in anthropogenic climate change nor accepts the global scientific consensus. Of even greater concern, individual engagement with climate change is also low among those who profess to being concerned and alarmed by it (Leiserowitz et al. 2013). In line with Lorenzoni et al. (2007), we define climate change “engagement” as a personal state of connection, “an individual state of involvement…at cognitive, affective and behavioral levels” (p. 476), focusing primarily on the two latter aspects, emotional engagement and behavior. The information deficit approach to science communication (Brown 2009; Dickson 2005), and climate change communication more specifically, evinces the belief that giving people (more) peer-reviewed scientific evidence will reduce skepticism, bolster public opinion, and mobilize action. Yet mounting evidence suggests that fact-based narratives are only minimally effective at motivating behavioral change (e.g., Whitmarsh et al. 2013), and there is little to no relationship between public understanding of climate science and risk perception (Kahan 2015). In this research, we argue that the deficit approach to communication underestimates not only the critical role of affect and emotion in rationality (Peters and Slovic 2000; Weber 2006a) but also the formidable force of motivated cognition. In some countries, an individual’s stance on the issue of climate change has become a marker of identity and a potential threat to social affiliation. As Kahan points out (Klein 2014), although it may seem irrational to ignore scientific evidence, the high social and neurological cost of updating beliefs is likely to eclipse the benefits of cognitive flexibility and factual accuracy.
Effectively communicating climate change to diverse, non-scientific audiences requires alternative approaches, and a few scholars have even suggested that stories might be part of this solution (e.g., Dahlstrom 2014; Martinez-Conde and Macknik 2017). A growing body of research suggests that engagement with emotional stories and their characters (i.e., Hoeken et al. 2016; Loewenstein 2010) more effectively motivate pro-social behavior (Barraza et al. 2015; Lin et al. 2013; Small and Loewenstein 2003) than informational frameworks (Small and Loewenstein 2003). Through a state known as narrative transportation, stories facilitate experiential rather than analytical processing (Green 1996; Green and Brock 2000), heightening emotional arousal (Zak 2015), and reducing counter-arguing (Green and Brock 2000). There is a vast literature in the humanities and arts discussing the rhetorical use of storytelling in environmental narratives (e.g., Cronon 1992; McComas and Shanahan 1999; Sakakibara 2008) and growing interest in how they might function as forms of evidence and communication within energy and climate change research (Moezzi et al. 2017). However, to our knowledge, there is little research about how narrative structure influences pro-environmental behavior in the context of climate change. In this article, we build on prior research investigating the persuasive powers of stories as well as the underpinnings of affect, emotion, and end valence (i.e., the positive or negative emotional charge at the end of a stimulus) to explicate how they influence behavior. Using three experiments, we investigate whether climate change messages structured as stories are better than analytical narratives at motivating pro-environmental behavior.
2 Homo narrans: humans and stories
According to the Narrative Paradigm (W. Fisher 1987), humans are “homo narrans”—storytelling animals who are persuaded to make decisions based on the coherence and fidelity of stories. Coherence deals with the internal consistency of a story’s characters and context, while fidelity relates to external consistency and “fit” with the listener’s values. Stories have dominated human interaction for millennia, and their efficacy as a form of communication seems to be related to how the human brain processes, imposes structure on, and interprets, information (Bransford et al. 2000; Pinker 2003). Research from diverse fields suggests that story structure matches human neural maps and how we make sense of the world from birth (Donald 1991; Nelson 2003; Pinker 2003; Plotkin 1982): we process and communicate in story structure (Gopnik et al. 1999). Bruner (1986) posits that neural story maps are a form of the heuristic used to process and decode narrative and experiential information. Schank (1990) goes so far as to assert that humans automatically select among accumulated story scripts rather than engaging in “thinking.”
We adopt Haven’s (2007) definition of story: “a detailed, character-based narration of a character’s struggles to overcome obstacles and reach an important goal … a framework and way of structuring information” (Haven 2007, p. 79). The terms narrative and story are often used interchangeably but our frame of reference is that stories are a specific subset within the category of narratives: all stories are narratives, but not all narratives are effective stories (Dalkir and Wiseman 2004). Stories are often automatically associated with fiction but are actually a way of structuring information (Haven 2007). Here, we define narrative structure as the degree to which a narrative tells a story and contains essential features including an identifiable character, plot (temporal dimension, goal), and setting. The higher the narrative structure, the more story-like the narrative.
2.1 How stories engage
The phenomenon of being “lost in a story” (Nell 1988) is known as “narrative transportation” and can be defined as the degree to which a plot activates the story receiver’s imagination through an empathic connection with the characters (Bagozzi and Moore 1994; Fisher et al. 2008; Lin et al. 2013), causing them to temporarily experience a sense of being suspended from reality (vanLaer et al. 2014). Narrative transportation is a convergent process (Green and Brock 2000) involving experiential processing through immersion into a story. This is distinctly different from the divergent process of cognitive elaboration (Petty and Cacioppo 1986), which entails analytical attention and scrutiny to major points of an argument. Under conditions of high cognitive elaboration, a person can still access pre-existing schemas, prior knowledge, experience, and opinions. Instead, through the process of narrative transportation, the mind becomes focused on the events of the story, and the aforementioned aspects of “reality” may fade into the background. Indeed, Green and Brock (2000) find reduced counter-arguing, resistance, and reactance in highly transported story receivers compared with less transported receivers—irrespective of whether narratives were labeled as “fact” or “fiction.” Stories can become proxies for the vivid personal experience (Cron 2012) shown to be an effective way of learning (Hertwig et al. 2004; Weber et al. 2004).
These findings have important implications for the information deficit hypothesis because numerous experiments have shown only a weak association between public understanding of climate science and risk perception (Kahan 2017; Kahan et al. 2012). Scientific literacy and numeracy can actually increase cultural polarization (Kahan et al. 2011). When confronted with the same scientific evidence about climate change, those already predisposed to believe become more concerned but those predisposed to be dismissive became even more dismissive (Kahan et al. 2011). In contrast, individuals who report being narratively transported into a story, experience higher empathy and are more likely to exhibit story-consistent beliefs and pro-social behavior in real life, even when controlling for individual dispositions toward empathy and transportability (Green and Brock 2000) (Johnson 2012). More, in a study where participants were exposed to an emotional narrative (Barraza et al. 2015), Barraza, Alexander, Beavin, Terris, and Zak found that changes in measures of autonomic reactivity and emotional arousal were associated with self-reported narrative transportation, empathic concern for characters in a story, and reliably predicted pro-social behavior. Non-invasive measures of sympathetic and parasympathetic reactivity in the autonomic nervous system are used to identify potential physiologic mechanisms underlying narrative persuasion; fluctuations in heart rate and skin conductance have been associated with attentional allocation (Potter and Bolls 2012) and emotional engagement (Mitkidis et al. 2015). In order to understand how autonomic reactivity influences behavior, it is important to establish how emotion is constructed through affective engagement.
2.2 Emotion, the impetus for action-taking
The psychophysiological state of affect is a perpetual stream of information used by the body as evidence about the world (Barrett 2017). Affect is a critical component of rationality, and analytical processing cannot be effective without it (Damasio 2003). Valence, an important dimension of affect, influences attention allocation based on how the brain predicts external stimuli will impact bodily budgets (Barrett 2017). It is the inherently positive or negative charge of an emotion (Russell and Barrett 1999) indicating the value or expected consequence of a specific piece of information (Barrett 2006). Although people might prefer to experience the pleasure of positive emotional valence, it appears that emotions associated with negative valence, such as worry, drive risk management and are better at actually getting us out of our proverbial chairs to do something about a problem (Peters and Slovic 2000). In the context of climate change, negatively valenced emotions conceptualized as fear and anxiety serve as early indicators, which compel urgency and action (Weber 2006b). For the purposes of this research, we focus on how end valence influences behavior because the valence of most narratives naturally waxes and wanes throughout its duration.
3 Conceptual model and overview of studies
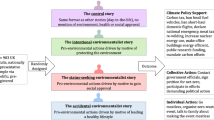
The central proposition of this research is that climate change narratives structured as stories will facilitate higher levels of pro-environmental behavior than their analytical counterparts. Specifically, we seek to understand the psychological processes underlying the influence of narrative structure on pro-environmental behavior. We posit that, through narrative transportation, stories influence autonomic reactivity indicative of affective engagement, enabling the construction of emotion, which compels the brain to execute orders for action-taking. Using three studies (two laboratory works and one online survey), we test the assumption that autonomic reactivity indicative of narrative transportation and emotional arousal will mediate the relationship between narrative structure and pro-environmental behavior, moderated by the end valence of the stimuli. Figure 1 provides an overview of the conceptual model summarizing our propositions and studies.
4 Study 1
In study 1, we examine whether the narrative structure influences pro-environmental behavior using controlled, written stimuli in a lab setting.
4.1 Materials and methods
In a single factor design, 158 participants (53% female) were recruited via email from a participant recruiting pool (ages 18–24 (51.9%), 25–34 (44.9%), 35–44 (1.9%), 55–64 (1.3%)). The sample size was determined with the goal of having at least 40 participants in each condition (Simmons et al. 2011). All sessions were conducted at a lab in a Danish university, and participants were compensated with DKK 150 (approximately $28). An ethics advisory group approved this study.
After completing demographic questions, the participants were randomly assigned to one of three conditions where they were asked to read a text containing identical pro-environmental content and number of words, structured either as a story (n = 53) or informational narrative (n = 52) (Appendix A). The control group (n = 53) was asked to read a neutral article about the construction of a university. Following the reading of the article, the participants were asked to answer a series of questions assessing evaluations of the article and to complete a short task listing post-stimulus thoughts. In the second part of the study, the participants were taken to a different lab room where they were offered a drink (with the option of choosing a glass or plastic cup) and completed the final survey which included state/trait measures (Appendix B). Measures of pro-environmental behavior were recorded throughout the experiment and included the following: (i) number of papers used in a task/whether both sides were used, (ii) whether participants cleaned off their desk (as instructed in the survey), (iii) recycled, (iv) subscribed to the Greenpeace newsletter, (v) donated a portion of their participant compensation as a charitable gift, (vi*) turned off the light/computer, (vii*) used a plastic or glass cup if taking a drink, and (viii) responded to a follow-up survey 6 weeks later. Measures denoted with an “*” were poor or contained significant noise (e.g., had no variation or were culturally confounding), and therefore not included in the analysis (see Appendix D).
We computed the log odds ratio and Cohen’s d between the independent variable (narrative structure) and the dependent variables (pro-environmental behaviors; Appendix C), using R Studio (Team 2012). Effect sizes for continuous outcome variables were computed directly from the observed data, dividing the mean differences by the pooled standard deviation \( \sqrt{\frac{\left({n}_1-1\right){s}_1^2+\left({n}_2-1\right)\ {s}_2^2\ }{n_1+{n}_2-2}\ } \), where sj and nj refer to the standard deviation and sample size of conditions to be compared. Effect sizes for binary outcome variables were calculated using log odds ratios (Appendix C).
4.2 Results
Effect size calculations revealed that narrative structure influenced most of the post-stimuli pro-environmental behaviors we measured, with the exception of the number of papers used, or whether or not the participants turned off the light or computer when exiting the lab room. Figure 2 shows the log odds ratios between the variables (as described above). A bar that represents “story/control,” for example, marks the difference in probabilities that a given pro-environmental behavior will occur in the story versus control conditions.
As can be seen in Appendix D, Table D1, the greatest observed difference in donation amount was between story and control groups, Cohen’s d = 0.26 (95% CI [− 0.13, 0.64]), story and information groups, d = 0.21 (95% CI [− 0.18, 0.59]), with the smallest observed difference between information, and control group, d = 0.08 (95% CI [− 0.31, 0.46]). The participants in the story condition were 2.00 times more likely to subscribe to the Greenpeace newsletter, and 1.72 times more likely to respond to the follow-up survey (with no additional payment or incentive) than those presented with information. Across all three conditions, the odds of a person recycling were 1.95 times higher in the story condition than that in the information condition and 2.83 times higher than that in the control group. The participants in the story condition were 1.82 times more likely to clean off their desk than those in the information condition, 1.88 times more likely than the control group, and approximately equal likelihood between information and control groups. No treatment effect was found for the number of papers used or whether or not the participants turned off the overhead light upon leaving.
4.3 Discussion
Results from this first study provide support for our expectations that narratives structured as stories are better vehicles of persuasion than informational narratives. We found that the participants in the story condition were consistently more likely to exhibit pro-environmental behavior than those in the information condition. Moreover, it appears that this treatment effect persisted 6 weeks after the initial experiment: as can be seen from Fig. 2, the participants in the story condition were far more likely to respond to a follow-up survey, without additional remuneration. Even more striking is the finding that the participants treated with informational narratives performed fewer pro-environmental behaviors (e.g., response to a follow-up survey; willingness to subscribe to a newsletter) compared with the control group. Participants were, after all, being exposed to messaging with the not-so-subtle theme of environmental degradation. This result serves to further undermine the credibility of the information deficit hypothesis developed by social scientists in the 1980s (Brown 2009; Dickson 2005). Indeed, it is thought-provoking that more than half of the carbon ever emitted into the air through fossil fuel combustion was released just in the past 25 years (IPCC 2018); this in the face of unequivocal data and widespread knowledge about the deleterious effects of CO2 emissions.
For some measures, no treatment difference was observed, such as whether or not participants turned off the overhead light when leaving the lab room or the number of papers they used in a recall task. While the results of this first study suggest an association between narrative structure and pro-environmental behavior in the context of climate change, we had no evidence for the mechanisms underlying this relationship. Moreover, the sample for this study was drawn from a participant pool consists mainly of university students, and caution should be exercised in extrapolating from the heavily skewed age distribution. Study 2, a survey experiment, builds on the findings of study 1 by investigating how narrative structure impacts self-reported narrative transportation and pro-environmental behavior, with added external validity derived from the use of naturalistic stimuli.
5 Study 2
Given the importance of public engagement with climate change and the implications of our findings for practitioners, in this second study, we employ videos produced by climate change communicators (e.g., the Royal Society, World Bank, NASA).
5.1 Methods and materials
In a single factor between-subjects online experiment, 315 US residents (53% female; ages 18–24 (7%), 25–34 (47%), 35–44 (22.2%), 45–54 (16.2%), 55–64 (6.7%), 65–74 (1%)) were recruited through MTurk. In accordance with guidelines by Simmons et al. (2011), the sample size was determined beforehand with the goal of ensuring that each video was viewed by between 50 and 60 people.
As stimuli preparation for study 2, a set of 91 videos produced by numerous climate change communicators was compiled from YouTube, rated by trained, independent coders who assessed their narrative structure and residual emotional valence. The videos were given a narrative structure score based on whether or not they possessed essential story features such as an identifiable character, plot (temporal dimension, goal), and setting (Escalas 1996; Escalas and Stern 2007). The higher (lower) the score, the more (less) story-like the narrative. The videos were also coded on end valence. For each narrative structure item, the mode was taken to create an index model of narrative structure for each video (Appendix E). To arrive at the final stimuli set, the following elimination criteria were used: (1) video duration should be no longer than 240 s, (2) no producer should have more than one video in the final set so as to preclude the possibility of repetition, and (3) no pop-up advertisements embedded in the video. Next, the 22 videos (Appendix F) with the highest/lowest narrative structure index scores ranging from 0.40 to 1.64 were selected. There were high consistency and inter-rater reliability with a percentage of agreement ranging from 72.5 to 93.4%, calculated based on Krippendorff’s Alpha (Appendix G).
All participants gave written informed consent and were compensated at fair market wages in the MTurk setting. Those accurately answering all attention checks were compensated with USD 4.90; participants who failed attention checks were paid USD 0.20, and their data was not analyzed. After answering demographic questions, the participants were randomly assigned to view four of the 22 videos in either high (n = 157) or low narrative structure condition (n = 158). After viewing each video, the participants answered a 5-item self-reported measure of narrative transportation adopted by Appel et al. (Appel et al. 2015) (Appendix H). Once all four videos were viewed, the subjects were given the opportunity to donate between 1 and 7 min of time to help further climate change research (e.g., testing an online carbon footprint calculator) when the survey was over. Following the time donation question, the participants completed additional trait measures (see Appendix I). Attention check accuracy was 98%.
In order to test the relationship between the independent variable, narrative structure, and the dependent variable, narrative transportation, we ran a series of models performing linear mixed effects analysis using R Studio (Team 2012) and lme4 (Bates et al. 2015). The ∆BIC (Bayesian Information Criterion) scores were generated for all models, and the model with the lowest ∆BIC was selected as the most predictive.
5.2 Results
The model most predictive of narrative transportation included “narrative structure” (story/info) with a fixed effect (β = 4.30; SE = 0.69) and the random intercept (participant ID) with a BIC score 26.91 points lower than the second most predictive model, which included the random intercept (participant ID) alone. Model coefficients are given in Appendix J. The model indicates that participants in the high narrative structure condition scored considerably higher on self-reported narrative transportation, Cohen’s d = 0.64 than those in the low narrative structure condition, yet this had no observed effect on their willingness to donate time to furthering climate change research in a time donation task.
5.3 Discussion
The results of this study support our proposition that the narrative structure of climate change videos has a direct influence on the self-reported subjective experience of narrative transportation. However, these findings do not provide evidence for an association with subsequent pro-environmental behavior, as operationalized by the time donation task. One probable explanation is the online setting in which the study was conducted. A high percentage of MTurk workers are professional survey takers (Stewart et al. 2015) and likely to be cynical about requests for participation outside the MTurk environment. Moreover, we remain uncertain that an immersive psychological experience such as narrative transportation can be reliably measured via self-report. To explore these issues in greater depth, we designed a third study using autonomic measures of emotional arousal previously identified as indicative of narrative transportation.
6 Study 3
Study 3 investigates whether autonomic reactivity and self-reported narrative transportation mediate the effect of narrative structure on pro-environmental behavior as well as how this relationship might be moderated by the end valence of the stimuli.
In this study, we test the expectation that narrative structure impacts pro-environmental behavior by influencing autonomic reactivity and heightened emotional arousal associated with the subjective experience of narrative transportation. To strengthen the robustness of our findings, we triangulate self-report measures of narrative transportation with measures of autonomic reactivity using a further reduced set of naturalistic stimuli from study 2. We predict that the influence of narrative structure on behavior is mediated by physiology, which is in turn moderated by the emotional valence of a video’s ending and narrative transportation.
6.1 Methods and materials
In a within-subjects, repeated-measures design, we pared down the stimuli list to six videos (Appendix K), selecting those with three highest and lowest mean narrative transportation scores as well as the following elimination criteria: (1) all videos should be produced by non-profit organizations; (2) no producer should have more than one video in the final stimuli set so as to preclude the possibility of repetition; (3) videos should not specifically mention localities outside of the USA; (4) video duration was limited to a maximum 195 s so as to limit noise attributable to attentional variation between individual stimuli and to accommodate attentional constraints in an experimental setting.
Sessions were conducted at the lab of an American university, and 87 participants were recruited (53% female) from the surrounding community through mass e-mails and an existing online recruitment pool (ages 18–24 (55.8%), 25–34 (32.5%), 35–44 (7%), 45–54 (3.5%), 55–64 (1.2%)). The sample size was determined beforehand in line with recommendations by Simmons et al. (2011) and Quintana (Quintana 2017). An Institutional Review Board approved this study. Immediately after consent, the participants responded to a pre-treatment questionnaire containing demographic items and trait measures (Appendix L). Upon completion, the participants were fitted with sensors, escorted to a private lab room, and seated in front of a laptop computer outfitted with headphones. All proceeding tasks, including the donation task, were presented in Psychopy (Peirce 2009). A research assistant was seated on the opposite side of a privacy curtain throughout the duration of the study.
To gauge affective engagement and emotional arousal, we employ non-invasive measures of reactivity in the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Inter-beat (RR) intervals measure the number of milliseconds between R peaks in the QRS complex of the ECG wave. Closely associated with RR intervals, high-frequency heart rate variability (HF-HRV) is calculated with the RR interval over a period of time using an algorithm known as the fast Fourier transform. Because the heart is dully innervated, cardiac measures such as HF-HRV and RR intervals generally indicate both sympathetic and parasympathetic reactivity with HF-HRV reflecting greater parasympathetic control of the heart (Potter and Bolls 2012). Electrodermal activity (EDA) measures changes in skin conductance and tends to be a more “pure” measure of SNS activation.
After a 5-minute baseline acquisition period for ANS measures of cardiac activity and skin conductance (see Appendix M for more detail), the participants viewed all videos presented in a random order. Autonomic activity was recorded continuously throughout the entire session. The participants were given a base compensation fee of USD 29 and the opportunity to earn an additional USD 1 per video. These additional dollars were our dependent variable in a donation task similar to that designed by Xygalatas et al. (Xygalatas et al. 2016). Additional earnings were given to participants in the form of 100 pennies in a clear plastic container labeled “earnings,” and placed next to an empty, but otherwise identical, container labeled “donations.” Post-video stimulus, the participants could voluntarily donate a portion of this dollar to the producer of the climate change video they had just viewed. The participants were instructed to pour the amount they wished to donate from the “earnings” cup to the “donations” cup without touching the coins or counting.
Upon the completion of the task, the participants notified the research assistant who removed both containers, privately weighing and recording donations out of the participant’s purview. The participants were then asked to answer five items designed to assess self-reported narrative transportation (Appel et al. 2015), and two items to gauge narrative familiarity and attention. This process was repeated for each of the six stimuli, after which time all sensors were removed, and participants were escorted to another room where they completed a final questionnaire containing additional demographic, state, and trait measures. After finishing the last survey, the participants were privately paid their earnings, minus any donations, and dismissed. The donations were sent to the video producers at the conclusion of the study.
To examine the relationships between narrative structure and pro-environmental behavior, including mediators of autonomic reactivity (EDA, HF-HRV, and RR intervals), moderated by residual valence, and the unmoderated mediator of self-reported narrative transportation, we performed a conditional process and linear mixed effects analyses, using R Studio (Team 2012) and lme4 (Bates et al. 2015). Six participants were considered outliers or excluded from analysis for one or more of the following reasons: skin conductance levels ≥ 3 SD from the mean (Sokol-Hessner et al. 2009), cardiac activity ≥ 4 SD from the mean (Potter and Bolls 2012), or missing data, leaving a total of 81 participants for final analysis. The ∆BIC scores were generated for all models, and the model with the lowest ∆BIC was selected as the most predictive. In cases where the ∆BIC of models was ≤ 2, the most parsimonious model was selected.
6.2 Results
As can be seen from Table 1, we observed a direct effect of narrative structure on one measure of cardiac activity, RR intervals (a3 = 0.031). There was a conditional indirect effect of narrative structure on pro-environmental donation behavior, mediated by a 3.1% increase in inter-beat intervals (RR), compared with baseline, moderated by negative residual valence, Cohen’s d = 0.021 (b8 = − 79.723). The results presented in Table 1 are conveyed in a more intuitive way in Fig. 3. This diagram depicts the statistical representation of the conceptual model showing expected paths, together with the coefficients. Our final model provides no evidence that narrative structure predicts behavior through self-reported narrative transportation or alterations in the other autonomic measures, electrodermal activity (EDA), or heart rate variability (HF-HRV).
Although our primary aim with this study is not to investigate a direct relationship between narrative structure and donations, we include the path in our conditional process analyses, as recommended by Hayes (2013). Subsequent analysis revealed no direct effect between narrative structure and pro-environmental behavior, nor do we find self-reported narrative transportation results to be predictive of donation behavior. The results of the analysis using the pruned model (Appendix N) following the Hayes (2013) method serve as a robustness check and can be seen in Appendix O.
6.3 Discussion
Study 3 provides empirical support for our proposition that climate change narratives structured as stories stand a better chance than analytical narratives at influencing pro-environmental behavior through heightened emotional arousal. Indeed, climate change stories with negatively valenced endings influenced pro-environmental behavior by increasing inter-beat (RR) intervals. Inferences about psychophysiology should always be made with caution, and RR intervals are one of the more difficult autonomic measures to interpret because the cardiac activity is influenced by both the sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic (PNS) branches of the autonomic nervous system. These systems are comprised of motor neurons that control the organs and glands, and can be coactive (Berntson et al. 1993) or decoupled (Potter and Bolls 2012). The SNS facilitates energy expenditure and, when activated, prepares the body for fight, flight, and procreation. It prepares to mobilize the body to confront threats through physiologic changes such as an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. The PNS facilitates recovery and energy storage through rest, repair, and digestion. SNS and PNS reactivity can operate independently or orthogonally, and both are indicative of attention and affective engagement (Barraza et al. 2015). Although our measure is likely under the influence of multiple patterns of ANS activity, it is clear that negatively valenced stories resulted in cardiac deceleration, which in turn predicted behavior.
Fluctuations in cardiac activity have been associated with attentional allocation (Potter and Bolls 2012) and emotional arousal (Mitkidis et al. 2015), and key determinants of empathic and sympathetic responses (Dickert and Slovic 2009). Stereotypical threat states and emotional arousal generally result in acceleration in heart rate and decrease in RR intervals, as a result of SNS reactivity (Potter and Bolls 2012). Climate change, however, lacks a number of salient characteristics which typically trigger our cerebral alarms in the face of danger. Because the danger does not feel immediate or proximal, it provokes a different type of reactivity compared with threats which activate sympathetic arousal. Given that we observed no effect in the “purer” measure of sympathetic activation (EDA), the finding that cardiac deceleration predicts behavior suggests predominantly PNS reactivity. PNS activation has been associated with the orienting reflex (Graham and Clifton 1966), increased the allocation of cognitive resources in the form of attention and interest (Potter and Bolls 2012), and the encoding of information into working memory (Potter and Bolls 2012).
Our finding is in line with the information intake-rejection hypothesis, which posits that parasympathetic activation improves response effectiveness by enhancing the ability to encode meaningful information from an individual’s environment into working memory (Lacey and Lacey 1974). These results may indicate a bodily state of “vigilant readiness,” a preparatory response pattern akin to a predator stalking its prey (Lang and Bradley 2010): attentive and observant, weighing the options. This aligns with a prior work proposing a relationship between negative emotional valence and heart rate deceleration (Bolls et al. 2001; Lang et al. 1996) as well as increased autonomic arousal (Potter and Bolls 2012). Negative valence has been shown to have a more enduring effect on heart rate response compared with positive emotion (Brosschot and Thayer 2003), which may help explain why participants who experienced cardiac deceleration also exhibited increased pro-environmental behavior.
Although it is difficult to disentangle emotional arousal and cognitive processing, our finding that heart rate deceleration leads to increased pro-environmental behavior likely reflects emotional arousal in tandem with cognitive processing, culminating in a calculated form of autonomic response to a distal threat. It is noteworthy that analytical narratives did not evoke this same autonomic response. We posit that, unlike stories, these informational narratives do not effectively aid the construction of emotion which, in complement, signals the brain to take action to optimize bodily budgets.
7 Conclusion and discussion
Based on the findings of this research, we echo the concerns of those who question the sufficiency of the information deficit approach to climate change communication. The primary goal of climate change communication campaigns is to persuade lay audiences as to the (a) severity of the problem and (b) need for action. While information and awareness are certainly not without value (van der Linden et al. 2014, 2015), our findings suggest that the structure in which information is embedded is of great consequence for eliciting pro-environmental behavior. It is always crucial to tailor messages to the needs of a specific audience, but this is especially true for a psychologically distant threat and politically polarized issue.
It appears that climate change communications designed to motivate diverse audiences will benefit from being structured as stories. Across three experiments, we found that narratives framed as stories consistently outperformed factual narratives for encouraging action-taking in all audiences. We suggest that this is because they more effectively trigger autonomic reactivity and emotional arousal. The results of this research also propose a key role for end valence as a moderator of the relationship between physiology and action. Studies by Bradley et al. (1996) as well as Shoemaker (1996) provide evidence that humans allocate more attentional resources to negative messages as an adaptive survival response. In order to maintain “allostasis,” most of the brain’s activity is dedicated to the intrinsic activity of prediction. Using past experience and the Bayesian logic (Deneve 2008), it continuously runs predictive models, and select among competing simulations, thereafter implementing an associated plan of action (Barrett 2016). External stimuli do not easily interrupt this process (Barrett 2017). Interoceptive predictions about internal bodily sensations produce affective feelings, which are the “brain’s best guess about the state of [bodily] budgets” (Barrett 2017). These interoceptive predictions monitor potential threats to allostasis and determine the “affective niche”—what an individual is affectively engaged with at a particular moment in time (Barrett 2017). However, on its own, affect lacks meaning. For the brain to order action, it must perceive the need and construct an instance of emotion, which is then expressed through involuntary changes in the autonomic nervous system (ANS) (Barrett 2017). Our results suggest that negative end valence plays a key role in facilitating affective engagement and the perceived need for action. At the same time, having a sense of efficacy is extremely important for motivation to act in the face of a threat (Bandura 1986). Feeling overwhelmed by the enormity of a problem can cause paralysis. To what extent and under what conditions is negative valence more motivational than positive valence? These issues should be explored in greater depth.
Although we observed a clear association between narrative structure and self-reported narrative transportation, this did not translate into pro-environmental behavior in either of the studies where this was measured. Instead, we found autonomic reactivity to be a better indicator of emotional arousal and cognitive processing as well as a predictor of pro-environmental behavior. Self-report has limitations when it comes to providing insights into a highly complex, immersive, largely sub-conscious, psychological process. Nevertheless, given the fact that our findings did not replicate prior work on this subject (vanLaer et al. 2014), future research should consider triangulating self-report with more objective measures of affective engagement and emotional arousal to gain a better understanding of how these correlate with the construct of narrative transportation. More, the behavioral measures used in the controlled settings of these studies were necessarily operationalizations of engagement with climate change (e.g., recycling, newsletter subscription, charitable donations to organizations fighting climate change); proxies, inferior to direct measures which might be included in field studies (e.g., decreased air and automotive travel, reduction in meat consumption).
To accommodate the variation inherent in naturalistic stimuli, an intentionally broad definition of the narrative structure was applied in these studies. Future research could contribute to a greater understanding of how essential story elements such as character identification, goals, and motivations influence risk perception in climate change narratives. Given the important implications for practitioners, further studies could benefit by investigating all of these questions using controlled stimuli in a real-world setting. Finally, as the issue of climate change is characterized by extreme ideological polarization with important implications for identity and social affiliation (Kahan 2015), future work should consider how these influence risk perception and bodily response to climate change stories (Kahan et al. 2007; Slovic 1999).
This research advances our understanding of how narrative structure influences engagement with climate change through emotional arousal, which likely incites pro-environmental behavior as the brain’s way of optimizing bodily budgets. These findings have important implications for science communication scholars and practitioners alike. In a twist of irony, structuring narratives as factual presentations ignore what science tells us about the important role of affective and emotional engagement for optimizing communication and decision-making. To maximize the likelihood of action-taking, our results suggest that science communicators should consider enrobing the presentation of information in story structure instead.
References
Appel M, Gnambs T, Richter T, Green MC (2015) The transportation scale-short form (Ts-Sf). Media Psychol 18(2):243–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2014.987400
Bagozzi RP, Moore DJ (1994) Public service advertisements: emotions and empathy guide prosocial behavior. J Mark 58(1):56–70
Bandura A (1986) Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, US
Barraza JA, Alexander V, Beavin LE, Terris ET, Zak PJ (2015) The heart of the story: peripheral physiology during narrative exposure predicts charitable giving. Biol Psychol 105:138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.01.008
Barrett LF (2006) Valence is a basic building block of emotional life. J Res Pers 40(1):35–55
Barrett LF (2016) The theory of constructed emotion: an active inference account of interoception and categorization. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci:nsw154. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsw154
Barrett LF (2017) How emotions are made. Houghton-Mifflin-Harcourt, New York, NY
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Eigen and S4. J Stat Softw 67(1):1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Berntson GG, Cacioppo JT, Quigley KS (1993) Cardiac psychophysiology and autonomic space in humans: empirical perspectives and conceptual implications. Psychol Bull 114(2):296–322
Bolls PD, Lang A, Potter RF (2001) The effects of message valence and listener arousal on attention, memory, and facial muscular responses to radio advertisements. Commun Res 28(5):627–651. https://doi.org/10.1177/009365001028005003
Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN, Lang PJ (1996) Picture media and emotion: effects of a sustained affective context. Psychophysiology 33(6):662–670
Bransford JD, Brown A, Cocking R (2000) How people learn (expanded Ed.). National Academy, Washington, DC
Brosschot JF, Thayer JF (2003) Heart rate response is longer after negative emotions than after positive emotions. Int J Psychophysiol 50(3):181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8760(03)00146-6
Brown S (2009) The new deficit model. Nat Nanotechnol 4(10):609
Bruner J (1986) Actual minds, possible worlds. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass
Cron, L. (2012). Wired for story: the writer’s guide to using brain science to hook readers from the very first sentence: Ten Speed Press
Cronon W (1992) A place for stories: nature, history, and narrative. J Am Hist 78(4):1347–1376
Dahlstrom MF (2014) Using narratives and storytelling to communicate science with nonexpert audiences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(Supplement 4):13614–13620. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320645111
Dalkir K, Wiseman E (2004) Organizational storytelling and knowledge management: a survey. Storytelling Self Soc 1:57–73
Damasio AR (2003) Descartes’ error : emotion, reason, and the human brain, Repr edn. Quill, New York
Deneve S (2008) Bayesian spiking neurons I: inference. Neural Comput 20(1):91–117
van der Linden SL, Leiserowitz AA, Feinberg GD, & Maibach EW (2014). How to communicate the scientific consensus on climate change: plain facts, pie charts or metaphors? An Interdisciplinary, International Journal Devoted to the Description, Causes and Implications of Climatic Change, 126(1), 255–262. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1190-4
van der Linden SL, Leiserowitz AA, Feinberg GD, Maibach EW (2015) The scientific consensus on climate change as a gateway belief: experimental evidence. PLoS One 10(2):e0118489
Dickert S, Slovic P (2009) Attentional mechanisms in the generation of sympathy. Judgm Decis Mak 4(4):297–306
Dickson D (2005). The case for a ‘deficit model’ of science communication. SciDev net 27
Donald M (1991). Origins of the modern mind: three stages in the evolution of culture and cognition: Harvard University Press
Dryzek JS, Norgaard RB, Schlosberg D (2011) The Oxford handbook of climate change and society. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Escalas JAE (1996). Narrative processing: building connections between brands and the self: ProQuest Dissertations Publishing
Escalas JAE, Stern B (2007) Narrative structure: plot and emotional responses. L. Erlbaum, Mahwah, N.J.
Fisher W (1987) Human communication as narration: toward a philosophy of reason, value, and action. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, SC
Fisher RJ, Vandenbosch M, Antia KD (2008) An empathy-helping perspective on consumers’ responses to fund-raising appeals. J Consum Res 35(3):519–531
Gopnik A, Meltzoff AN, & Kuhl PK (1999). The scientist in the crib: minds, brains, and how children learn: William Morrow & Co.
Graham FK, Clifton RK (1966) Heart-rate change as a component of the orienting response. Psychol Bull 65(5):305
Green MC (1996). Mechanisms of narrative-based belief change. The Ohio State University. Retrieved from http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1235579429. Accessed 11 Nov 2015
Green MC, Brock TC (2000) The role of transportation in the persuasiveness of public narratives. J Pers Soc Psychol 79(5):701–721. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.79.5.701
Haven KF (2007) Story proof: the science behind the startling power of story. Libraries Unlimited, Westport, CT
Hayes AF (2013) Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: a regression-based approach. Guilford Press, New York, NY
Hertwig R, Barron G, Weber EU, Erev I (2004) Decisions from experience and the effect of rare events in risky choice. Psychol Sci 15(8):534–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0956-7976.2004.00715.x
Hoeken H, Kolthoff M, José S (2016) Story perspective and character similarity as drivers of identification and narrative persuasion. Hum Commun Res 42(2):292–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/hcre.12076
IPCC. (2018). Summary for policymakers of IPCC special report on global warming of 1.5°C Approved by Governments. Retrieved from https://www.ipcc.ch/2018/10/08/summary-for-policymakers-of-ipcc-special-report-on-global-warming-of-1-5c-approved-by-governments/. Accessed 30 Oct 2018
Johnson DR (2012) Transportation into a story increases empathy, prosocial behavior, and perceptual Bias toward fearful expressions. Personal Individ Differ 52(2):150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2011.10.005
Kahan DM (2015) Climate-science communication and the measurement problem. Polit Psychol 36(S1):1–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/pops.12244
Kahan DM (2017) ‘Ordinary science intelligence’: a science-comprehension measure for study of risk and science communication, with notes on evolution and climate change. Journal of Risk Research 20(8):995–1016. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2016.1148067
Kahan DM, Braman D, Slovic P, Gastil J, & Cohen GL (2007). The second national risk and culture study: making sense of-and making progress in-the American culture war of fact
Kahan DM, Wittlin M, Peters E, Slovic P, Ouellette LL, Braman D, & Mandel, G. N. (2011). The tragedy of the risk-perception commons: culture conflict, rationality conflict, and climate change Temple University Legal Studies Research Paper No. 2011–26; Cultural Cognition Project Working Paper No. 89; Yale Law & Economics Research Paper No. 435; Yale Law School, Public Law Working Paper No. 230
Kahan DM, Peters E, Wittlin M, Slovic P, Ouellette LL, Braman D, Mandel G (2012) The polarizing impact of science literacy and numeracy on perceived climate change risks. Nat Clim Chang 2(10):732–735
Klein E (2014). How politics make us stupid. Vox
Lacey JI, Lacey BC (1974) On heart rate responses and behavior: a reply to Elliott. J Pers Soc Psychol 30(1):1–18
vanLaer T, Ruyter K d, Visconti LM, Wetzels M (2014) The extended transportation-imagery model: a meta-analysis of the antecedents and consequences of consumers’ narrative transportation. J Consum Res 40(5):797–817. https://doi.org/10.1086/673383
Lang PJ, Bradley MM (2010) Emotion and the motivational brain. Biol Psychol 84(3):437–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.10.007
Lang A, Newhagen J, Reeves B (1996) Negative video as structure: emotion, attention, capacity, and memory. J Broadcast Electron Media 40(4):460–477
Leiserowitz A, Maibach E, Roser-Renouf C, Feinberg G, Howe P (2013) Global warming’s six Americas, September 2012. Yale University and George Mason University. Yale Project on Climate Change Communication, New Haven, CT
Lin PY, Grewal NS, Morin C, Johnson WD, Zak PJ (2013) Oxytocin increases the influence of public service advertisements. PLoS One 8(2):e56934. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056934
Loewenstein G (2010) Insufficient emotion: soul-searching by a former indicter of strong emotions. Emot Rev 2(3):234–239. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073910362598
Lorenzoni I, Nicholson-Cole S, Whitmarsh L (2007) Barriers perceived to engaging with climate change among the UK public and their policy implications. Glob Environ Chang 17(3–4):445–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2007.01.004
Martinez-Conde S, Macknik SL (2017) Opinion: finding the plot in science storytelling in hopes of enhancing science communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(31):8127–8129
McComas K, Shanahan J (1999) Telling stories about global climate change: measuring the impact of narratives on issue cycles. Commun Res 26(1):30–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/009365099026001003
Mitkidis P, McGraw JJ, Roepstorff A, Wallot S (2015) Building trust: heart rate synchrony and arousal during joint action increased by public goods game. Physiol Behav 149:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.05.033
Moezzi M, Janda KB, Rotmann S (2017) Using stories, narratives, and storytelling in energy and climate change research. Energy Res Soc Sci 31:1–10
Nell V (1988) The psychology of reading for pleasure: needs and gratifications. Read Res Q 23(1):6–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/747903
Nelson K (2003) Narratives and the emergence of a consciousness of self. In: Fireman GDM, Ted E, Flanagan OJ (eds) Narrative and consciousness: literature, psychology and the brain. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, pp 17–36
Peirce JW (2009) Generating stimuli for neuroscience using psychopy. Frontiers in neuroinformatics 2:10
Peters E, Slovic P (2000) The springs of action: affective and analytical information processing in choice. Personal Soc Psychol Bull 26(12):1465–1475. https://doi.org/10.1177/01461672002612002
Petty RE, Cacioppo JT (1986) The elaboration likelihood model of persuasion. Adv Exp Soc Psychol 19:123–205
Pinker S (2003). The language instinct: how the mind creates language: Penguin UK
Plotkin HC (1982). Learning, development, and culture: essays in evolutionary epistemology: John Wiley & Sons
Potter RF, & Bolls P (2012). Psychophysiological measurement and meaning: cognitive and emotional processing of media: Routledge
Quintana DS (2017) Statistical considerations for reporting and planning heart rate variability case-control studies. Psychophysiology 54(3):344–349
Russell JA, Barrett LF (1999) Core affect, prototypical emotional episodes, and other things called emotion: dissecting the elephant. J Pers Soc Psychol 76(5):805
Sakakibara C (2008) “Our home is drowning”: Inupiat storytelling and climate change in Point Hope, Alaska. Geogr Rev [HW Wilson - SSA] 98(4):456
Schank RC (1990) Tell me a story: a new look at real and artificial memory. Scribner, New York
Shoemaker PJ (1996) Hardwired for news: using biological and cultural evolution to explain the surveillance function. J Commun 46(3):32–47
Simmons JP, Nelson LD, Simonsohn U (2011) False-positive psychology: undisclosed flexibility in data collection and analysis allows presenting anything as significant. Psychol Sci 22(11):1359–1366
Slovic P (1999) Trust, emotion, sex, politics, and science: surveying the risk-assessment battlefield. Risk Anal 19(4):689–701
Small DA, Loewenstein G (2003) Helping a victim or helping the victim: altruism and identifiability. J Risk Uncertain 26(1):5–16. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022299422219
Sokol-Hessner P, Hsu M, Curley NG, Delgado MR, Camerer CF, Phelps EA (2009) Thinking like a trader selectively reduces individuals’ loss aversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(13):5035–5040
Stewart N, Ungemach C, Harris AJ, Bartels DM, Newell BR, Paolacci G, Chandler J (2015) The average laboratory samples a population of 7,300 Amazon mechanical Turk workers. Judgm Decis Mak 10(5):479
Team RS (2012) RStudio: integrated development environment for R. In: RStudio Inc. Boston, Massachusetts
Tranter B, Booth K (2015) Scepticism in a changing climate: a cross-national study. Glob Environ Chang 33:154–164
Weber EU (2006a) Experience-based and description-based perceptions of long-term risk: why global warming does not scare us (yet). An Interdisciplinary, International Journal Devoted to the Description, Causes and Implications of. Clim Chang 77(1):103–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9060-3
Weber EU (2006b) Experience-based and description-based perceptions of long-term risk: why global warming does not scare us (yet). Clim Chang 77(1):103–120
Weber EU, Shafir S, Blais A-R (2004) Predicting risk sensitivity in humans and lower animals: risk as variance or coefficient of variation. Psychol Rev 111(2):430–445. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.111.2.430
Whitmarsh L, O'Neill S, Lorenzoni I (2013) Public engagement with climate change: what do we know and where do we go from here? Int J Media Cultural Polit 9(1):7–25. https://doi.org/10.1386/macp.9.1.7_1
Xygalatas D, Klocová EK, Cigán J, Kundt R, Maňo P, Kotherová S, ... Kanovsky M (2016). Location, location, location: effects of cross-religious primes on prosocial behavior. Int J Psychol Relig, 26(4), 304–319. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/10508619.2015.1097287
Zak PJ (2015) Why inspiring stories make us react: the neuroscience of narrative. Cerebrum : the Dana forum on brain science 2015:2
Acknowledgements
We thank the entire lab team at the Center for Neuroeconomic Studies, especially Elizabeth Terris and Collin Binder for their diligence in the cleaning of physiological data from study 3. We thank Sue Campbell for her help with stimuli development in study 1 and John Thøgersen for his comments on this study’s design. Finally, we thank Ekaterina Salnikova and Michael J. Morris for their comments.
Funding
This research has been supported by seed funding from the Interacting Minds Centre, Aarhus University, as well as the Aarhus University Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.S.M, P.C., P.M., J.O., J.B., and P.Z. designed the research; B.S.M. and J.B. performed the research; B.S.M., P.C., P.M., J.C., and J.O. analyzed the data; B.S.M. wrote the initial draft; and all co-authors contributed with edits.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The work was carried out in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration, taking every precaution to protect the privacy and interests of research participants, all of whom gave written, informed consent. Laboratory studies were approved by an ethics advisory group and Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 7208 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Morris, B.S., Chrysochou, P., Christensen, J.D. et al. Stories vs. facts: triggering emotion and action-taking on climate change. Climatic Change 154, 19–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-019-02425-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-019-02425-6