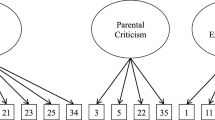
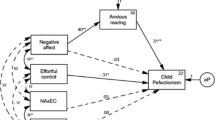
Abstract
Previous research has shown that perfectionism predicts for increased worry in children. Theoretically, children with high levels of perfectionism may show a decreased ability to control their emotions during times of perceived failure. Children may then worry as a maladaptive attempt to cope with intense emotions. The current study sought to test the mediating role of emotional control on the relation between perfectionism dimensions and worry in children. Participants were 66 parent–child dyads. Children were 7–13 years (50 % male; 77.3 % Caucasian, 9.1 % African American). Overall the model fit the data well. Results indicated that perfectionism domains predicted for emotional control deficits and increased worry. Emotional control also partially mediated the relation between perfectionism dimensions and worry. These results suggest that emotional control may be one mechanism through which perfectionism exerts its effect on worry and perfectionistic children may worry due to difficulty controlling their emotional responses.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weems CF, Silverman WK, La Greca AM (2000) What do youth referred for anxiety problems worry about? Worry and its relation to anxiety and anxiety disorders in children and adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol 28:63–72
Alfano CA, Ginsburg GS, Kingery JN (2007) Sleep-related problems among children and adolescents with anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:224–232
Ginsburg GS, Riddle MA, Davies M (2006) Somatic symptoms in children and adolescents with anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 45:1179–1187
Chang EC, Zumberg KM, Sanna LJ, Girz LP, Kade AM, Shair SR, Hermann NB, Srivastava K (2007) Relationship between perfectionism and domains of worry in a college student population: considering the role of BIS/BAS motives. Pers Individ Dif 43:925–936
Flett GL, Coulter LM, Hewitt PL, Nepon T (2011) Perfectionism, rumination, worry, and depressive symptoms in early adolescents. Can J Sch Psychol 26:159–176
Short MM, Mazmanian D (2013) Perfectionism and negative repetitive thoughts: examining a multiple mediator model in relation to mindfulness. Pers Individ Dif 55:716–721
Gramszlo C, Woodruff-Borden J (2015) Emotional reactivity and executive control: a pathway of risk for the development of childhood worry. J Anxiety Disord 35:35–41
Mandel T, Dunkley DM, Moroz M (2015) Self-critical perfectionism and depressive and anxious symptoms over 4 years: the mediating role of daily stress reactivity. J Couns Psychol 62:703–717
Flett GL, Hewitt PL, Oliver JM, Macdonald S (2002) Perfectionism in children and their parents: a developmental analysis. In: Flett GL, Hewitt PL (eds) Perfectionism: theory, research, and treatment. American Psychological Association, Washington, pp 89–132
Hewitt PL, Flett GL (1991) Perfectionism in the self and social contexts: conceptualization, assessment, and association with psychopathology. J Pers Soc Psychol 60:456–470
Stoeber J, Otto K (2006) Positive conceptions of perfectionism: approaches, evidence, challenges. Pers Soc Psychol Rev 10:295–319
Flett G, Hewitt P, Boucher D, Davidson L, Munro Y (1997) The child adolescent perfectionism scale: development, validation, and association with adjustment. Unpublished Manuscript
Bieling PJ, Israeli A, Smith J, Antony MM (2003) Making the grade: the behavioural consequences of perfectionism in the classroom. Pers Individ Dif 35:163–178
Herman KC, Wang K, Trotter R, Reinke WM, Ialongo N (2013) Developmental trajectories of maladaptive perfectionism among African American adolescents. Child Dev 84:1633–1650
McCreary BT, Joiner TE, Schmidt NB, Ialongo NS (2004) The structure and correlates of perfectionism in African American children. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 33:313–324
Santanello AW, Gardner FL (2007) The role of experiential avoidance in the relationship between maladaptive perfectionism and worry. Cognit Ther Res 31:319–332
Stöber J, Joormann J (2001) Worry, procrastination, and perfectionism: differentiating amount of worry, pathological worry, anxiety, and depression. Cognit Ther Res 25:49–60
Handley AK, Egan SJ, Kane RT, Rees CS (2014) The relationships between perfectionism, pathological worry and generalised anxiety disorder. BMC Psychiatry 14:1–8
Affrunti NW, Woodruff-Borden J (2015) Negative affect and child internalizing symptoms: the mediating role of perfectionism. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 47:358–368
Affrunti NW, Woodruff-Borden J (2014) Perfectionism in pediatric anxiety and depressive disorders. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 17:299–317
Gioia GA, Isquith PK, Guy SC, Kenworthy L (2000) Test review behavior rating inventory of executive function. Child Neuropsychol 6:235–238
Richardson CM, Rice KG, Devine DP (2014) Perfectionism, emotion regulation, and the cortisol stress response. J Couns Psychol 61:110–118
Wirtz PH, Elsenbruch S, Emini L, Rüdisüli K, Groessbauer S, Ehlert U (2007) Perfectionism and the cortisol response to psychosocial stress in men. Psychosom Med 69:249–255
Aldea MA, Rice KG (2006) The role of emotional dysregulation in perfectionism and psychological distress. J Couns Psychol 53:498–510
Rudolph SG, Flett GL, Hewitt PL (2007) Perfectionism and deficits in cognitive emotion regulation. J Ration-Emot Cogn-Behav Ther 25:343–357
McRae K, Gross JJ, Weber J, Robertson ER, Sokol-Hessner P, Ray RD, Gabrieli JD, Ochsner KN (2012) The development of emotion regulation: an fMRI study of cognitive reappraisal in children, adolescents and young adults. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 7:11–22
Borkovec TD, Alcaine O, Behar E (2004) Avoidance theory of worry and generalized anxiety disorder. In: Heimberg RG, Turk CL, Mennin DS (eds) Generalized anxiety disorder: advances in research and practice. Guilford Press, New York, pp 77–108
Llera SJ, Newman MG (2014) Rethinking the role of worry in generalized anxiety disorder: evidence supporting a model of emotional contrast avoidance. Behav Ther 45:283–299
Mennin DS, Heimberg RG, Turk CL, Fresco DM (2005) Preliminary evidence for an emotion dysregulation model of generalized anxiety disorder. Behav Res Ther 43:1281–1310
Salters-Pedneault K, Roemer L, Tull MT, Rucker L, Mennin DS (2006) Evidence of broad deficits in emotion regulation associated with chronic worry and generalized anxiety disorder. Cognit Ther Res 30:469–480
Decker ML, Turk CL, Hess B, Murray CE (2008) Emotion regulation among individuals classified with and without generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord 22:485–494
Blanchard-Fields F, Coats AH (2008) The experience of anger and sadness in everyday problems impacts age differences in emotion regulation. Dev Psychol 44:1547–1556
Newman MG, Llera SJ (2011) A novel theory of experiential avoidance in generalized anxiety disorder: a review and synthesis of research supporting a contrast avoidance model of worry. Clin Psychol Rev 31:371–382
O’Connor RC, Rasmussen S, Hawton K (2010) Predicting depression, anxiety and self-harm in adolescents: the role of perfectionism and acute life stress. Behav Res Ther 48:52–59
Donders J, DenBraber D, Vos L (2010) Construct and criterion validity of the Behaviour Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF) in children referred for neuropsychological assessment after paediatric traumatic brain injury. J Neuropsychol 4:197–209
Isquith PK, Gioia GA, Espy KA (2004) Executive function in preschool children: examination through everyday behavior. Dev Neuropsychol 26:403–422
Toplak ME, Bucciarelli SM, Jain U, Tannock R (2008) Executive functions: performance-based measures and the behavior rating inventory of executive function (BRIEF) in adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Child Neuropsychol 15:53–72
Chorpita BF, Tracey SA, Brown TA, Collica TJ, Barlow DH (1997) Assessment of worry in children and adolescents: an adaptation of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire. Behav Res Ther 35:569–581
Pestle SL, Chorpita BF, Schiffman J (2008) Psychometric properties of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire for children in a large clinical sample. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 37:465–471
Hu L, Bentler PM (1999) Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J 6:1–55
Zhao X, Lynch JG, Chen Q (2010) Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: myths and truths about mediation analysis. J Consum Res 37:197–206
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF (2008) Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 40:879–891
MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Hoffman JM, West SG, Sheets V (2002) A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychol Methods 7:83–104
Geronimi EM, Patterson HL, Woodruff-Borden J (2015) Relating worry and executive functioning during childhood: the moderating role of age. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 47:430–439
Muris P, Meesters C, Merckelbach H, Hülsenbeck P (2000) Worry in children is related to perceived parental rearing and attachment. Behav Res Ther 38:487–497
Newman MG, Llera SJ, Erickson TM, Przeworski A, Castonguay LG (2013) Worry and generalized anxiety disorder: a review and theoretical synthesis of evidence on nature, etiology, mechanisms, and treatment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 9:275–297
Gentes EL, Ruscio AM (2014) Perceptions of functioning in worry and generalized anxiety disorder. Cognit Ther Res 38:518–529
Flett GL, Nepon T, Hewitt PL (2016) Perfectionism, worry, and rumination in health and mental health: a review and a conceptual framework for a cognitive theory of perfectionism. In: Sirois F, Molnar DS (eds) Perfectionism, health, and well-being. Springer International Publishing, New York, pp 121–155
Sullivan PJ, Keller M, Paternostro J, Friedberg RD (2015) Treating emotionally dysregulated and perfectionistic youth with transdiagnostic cognitive behavioral procedures. J Contemp Psychother 45:151–158
Herman KC, Trotter R, Reinke WM, Ialongo N (2011) Developmental origins of perfectionism among African American youth. J Couns Psychol 58:321–334
Egan SJ, Wade TD, Shafran R (2011) Perfectionism as a transdiagnostic process: a clinical review. Clin Psychol Rev 31:203–212
Werner K, Gross JJ (2010) Emotion regulation and psychopathology: a conceptual framework. In: Kring AM, Sloan DM (eds) Emotion and psychopathology: a transdiagnostic approach to etiology and treatment. Guilford Press, New York, pp 13–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Affrunti, N.W., Woodruff-Borden, J. Emotional Control Mediates the Association Between Dimensions of Perfectionism and Worry in Children. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 48, 73–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-016-0654-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-016-0654-3