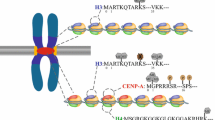
Abstract
Centromeres are sites of chromosomal spindle attachment during mitosis and meiosis. Centromeres are defined, in part, by a distinct chromatin landscape in which histone H3 is replaced by the conserved histone H3 variant, CENP-A. Sequences competent for centromere formation and function vary among organisms and are typically composed of repetitive DNA. It is unclear how such diverse genomic signals are integrated with the epigenetic mechanisms that govern CENP-A incorporation at a single locus on each chromosome. Recent work highlights the intriguing possibility that the transcriptional properties of centromeric core DNA contribute to centromere identity and maintenance through cell division. Moreover, core-derived noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) have emerged as active participants in the regulation and control of centromere activity in plants and mammals. This paper reviews the transcriptional properties of eukaryotic centromeres and discusses the known roles of core-derived ncRNAs in chromatin integrity, kinetochore assembly, and centromere activity.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCAN:
-
Constitutive centromere-associated network
- CENP:
-
Centromere protein
- CHD:
-
Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein
- CPC:
-
Chromosomal passenger complex
- HAC:
-
Human artificial chromosome
- HJURP:
-
Holliday junction recognition protein
- FACT:
-
Facilitates in chromatin transcription
- ncRNA:
-
Noncoding RNA
- RNAPII:
-
RNA polymerase II
- RNAPIII:
-
RNA polymerase III
- tDNA:
-
tRNA gene
- TFIIIC:
-
Transcription factor III C
References
Ananiev EV, Wu C, Chamberlin MA, Svitashev S, Schwartz C, Gordon-Kamm W, Tingey S (2009) Artificial chromosome formation in maize (Zea mays L.). Chromosoma 118:157–177
Barnhart MC, Kuich PH, Stellfox ME, Ward JA, Bassett EA, Black BE, Foltz DR (2011) HJURP is a CENP-A chromatin assembly factor sufficient to form a functional de novo kinetochore. J Cell Biol 194:229–243
Bergmann JH, Jakubsche JN, Martins NM, Kagansky A, Nakano M, Kimura H, Kelly DA, Turner BM, Masumoto H, Larionov V et al (2012a) Epigenetic engineering: histone H3K9 acetylation is compatible with kinetochore structure and function. J Cell Sci 125:411–421
Bergmann JH, Martins NM, Larionov V, Masumoto H, Earnshaw WC (2012b) HACking the centromere chromatin code: insights from human artificial chromosomes. Chromosom Res 20:505–519
Bouzinba-Segard H, Guais A, Francastel C (2006) Accumulation of small murine minor satellite transcripts leads to impaired centromeric architecture and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8709–8714
Cam HP, Sugiyama T, Chen ES, Chen X, FitzGerald PC, Grewal SI (2005) Comprehensive analysis of heterochromatin- and RNAi-mediated epigenetic control of the fission yeast genome. Nat Genet 37:809–819
Cardinale S, Bergmann JH, Kelly D, Nakano M, Valdivia MM, Kimura H, Masumoto H, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC (2009) Hierarchical inactivation of a synthetic human kinetochore by a chromatin modifier. Mol Biol Cell 20:4194–4204
Carone DM, Longo MS, Ferreri GC, Hall L, Harris M, Shook N, Bulazel KV, Carone BR, Obergfell C, O’Neill MJ et al (2009) A new class of retroviral and satellite encoded small RNAs emanates from mammalian centromeres. Chromosoma 118:113–125
Carone DM, Zhang C, Hall LE, Obergfell C, Carone BR, O’Neill MJ, O’Neill RJ (2013) Hypermorphic expression of centromeric retroelement-encoded small RNAs impairs CENP-A loading. Chromosom Res 21:49–62
Chan FL, Marshall OJ, Saffery R, Kim BW, Earle E, Choo KH, Wong LH (2012) Active transcription and essential role of RNA polymerase II at the centromere during mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:1979–1984
Chen ES, Zhang K, Nicolas E, Cam HP, Zofall M, Grewal SI (2008) Cell cycle control of centromeric repeat transcription and heterochromatin assembly. Nature 451:734–737
Choi ES, Stralfors A, Castillo AG, Durand-Dubief M, Ekwall K, Allshire RC (2011) Identification of noncoding transcripts from within CENP-A chromatin at fission yeast centromeres. J Biol Chem 286:23600–23607
Choi ES, Stralfors A, Catania S, Castillo AG, Svensson JP, Pidoux AL, Ekwall K, Allshire RC (2012) Factors that promote H3 chromatin integrity during transcription prevent promiscuous deposition of CENP-A(Cnp1) in fission yeast. PLoS Genet 8:e1002985
Chueh AC, Northrop EL, Brettingham-Moore KH, Choo KH, Wong LH (2009) LINE retrotransposon RNA is an essential structural and functional epigenetic component of a core neocentromeric chromatin. PLoS Genet 5:e1000354
Clapier CR, Cairns BR (2009) The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem 78:273–304
Du Y, Topp CN, Dawe RK (2010) DNA binding of centromere protein C (CENPC) is stabilized by single-stranded RNA. PLoS Genet 6:e1000835
Dunleavy EM, Roche D, Tagami H, Lacoste N, Ray-Gallet D, Nakamura Y, Daigo Y, Nakatani Y, Almouzni-Pettinotti G (2009) HJURP is a cell-cycle-dependent maintenance and deposition factor of CENP-A at centromeres. Cell 137:485–497
Earnshaw WC, Allshire RC, Black BE, Bloom K, Brinkley BR, Brown W, Cheeseman IM, Choo KH, Copenhaver GP, Deluca JG et al (2013) Esperanto for histones: CENP-A, not CenH3, is the centromeric histone H3 variant. Chromosom Res 21:101–106
Ebersole T, Kim JH, Samoshkin A, Kouprina N, Pavlicek A, White RJ, Larionov V (2011) tRNA genes protect a reporter gene from epigenetic silencing in mouse cells. Cell Cycle 10:2779–2791
Ferri F, Bouzinba-Segard H, Velasco G, Hube F, Francastel C (2009) Non-coding murine centromeric transcripts associate with and potentiate Aurora B kinase. Nucleic Acids Res 37:5071–5080
Foltz DR, Jansen LE, Black BE, Bailey AO, Yates JR 3rd, Cleveland DW (2006) The human CENP-A centromeric nucleosome-associated complex. Nat Cell Biol 8:458–469
Gassmann R, Rechtsteiner A, Yuen KW, Muroyama A, Egelhofer T, Gaydos L, Barron F, Maddox P, Essex A, Monen J et al (2012) An inverse relationship to germline transcription defines centromeric chromatin in C. elegans. Nature 484:534–537
Hall LE, Mitchell SE, O’Neill RJ (2012) Pericentric and centromeric transcription: a perfect balance required. Chromosom Res 20:535–546
Hayden KE (2012) Human centromere genomics: now it’s personal. Chromosom Res 20:621–633
Ishii K, Ogiyama Y, Chikashige Y, Soejima S, Masuda F, Kakuma T, Hiraoka Y, Takahashi K (2008) Heterochromatin integrity affects chromosome reorganization after centromere dysfunction. Science 321:1088–1091
Izuta H, Ikeno M, Suzuki N, Tomonaga T, Nozaki N, Obuse C, Kisu Y, Goshima N, Nomura F, Nomura N et al (2006) Comprehensive analysis of the ICEN (Interphase Centromere Complex) components enriched in the CENP-A chromatin of human cells. Genes Cells 11:673–684
Jolly C, Metz A, Govin J, Vigneron M, Turner BM, Khochbin S, Vourc’h C (2004) Stress-induced transcription of satellite III repeats. J Cell Biol 164:25–33
Ketel C, Wang HS, McClellan M, Bouchonville K, Selmecki A, Lahav T, Gerami-Nejad M, Berman J (2009) Neocentromeres form efficiently at multiple possible loci in Candida albicans. PLoS Genet 5:e1000400
Kirkland JG, Raab JR, Kamakaka RT (2013) TFIIIC bound DNA elements in nuclear organization and insulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1829:418–424
Krasikova A, Fukagawa T, Zlotina A (2012) High-resolution mapping and transcriptional activity analysis of chicken centromere sequences on giant lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosom Res 20:995–1008
Lam AL, Boivin CD, Bonney CF, Rudd MK, Sullivan BA (2006) Human centromeric chromatin is a dynamic chromosomal domain that can spread over noncentromeric DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4186–4191
Lampson MA, Cheeseman IM (2011) Sensing centromere tension: Aurora B and the regulation of kinetochore function. Trends Cell Biol 21:133–140
Lunyak VV, Prefontaine GG, Nunez E, Cramer T, Ju BG, Ohgi KA, Hutt K, Roy R, Garcia-Diaz A, Zhu X et al (2007) Developmentally regulated activation of a SINE B2 repeat as a domain boundary in organogenesis. Science 317:248–251
Maggert KA, Karpen GH (2001) The activation of a neocentromere in Drosophila requires proximity to an endogenous centromere. Genetics 158:1615–1628
Masumoto H, Nakano M, Ohzeki J (2004) The role of CENP-B and alpha-satellite DNA: de novo assembly and epigenetic maintenance of human centromeres. Chromosom Res 12:543–556
Mellone BG, Grive KJ, Shteyn V, Bowers SR, Oderberg I, Karpen GH (2011) Assembly of Drosophila centromeric chromatin proteins during mitosis. PLoS Genet 7:e1002068
Nakano M, Cardinale S, Noskov VN, Gassmann R, Vagnarelli P, Kandels-Lewis S, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC, Masumoto H (2008) Inactivation of a human kinetochore by specific targeting of chromatin modifiers. Dev Cell 14:507–522
Ochs RL, Press RI (1992) Centromere autoantigens are associated with the nucleolus. Exp Cell Res 200:339–350
Ohkuni K, Kitagawa K (2011) Endogenous transcription at the centromere facilitates centromere activity in budding yeast. Curr Biol 21:1695–1703
Okada M, Okawa K, Isobe T, Fukagawa T (2009) CENP-H-containing complex facilitates centromere deposition of CENP-A in cooperation with FACT and CHD1. Mol Biol Cell 20:3986–3995
Palmer DK, O’Day K, Trong HL, Charbonneau H, Margolis RL (1991) Purification of the centromere-specific protein CENP-A and demonstration that it is a distinctive histone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:3734–3738
Partridge JF, Borgstrom B, Allshire RC (2000) Distinct protein interaction domains and protein spreading in a complex centromere. Genes Dev 14:783–791
Perpelescu M, Fukagawa T (2011) The ABCs of CENPs. Chromosoma 120:425–446
Podhraski V, Campo-Fernandez B, Worle H, Piatti P, Niederegger H, Bock G, Fyodorov DV, Lusser A (2010) CenH3/CID incorporation is not dependent on the chromatin assembly factor CHD1 in Drosophila. PLoS One 5:e10120
Raab JR, Chiu J, Zhu J, Katzman S, Kurukuti S, Wade PA, Haussler D, Kamakaka RT (2012) Human tRNA genes function as chromatin insulators. EMBO J 31:330–350
Ruchaud S, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC (2007) Chromosomal passengers: conducting cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:798–812
Rudd MK, Willard HF (2004) Analysis of the centromeric regions of the human genome assembly. Trends Genet 20:529–533
Saffery R, Sumer H, Hassan S, Wong LH, Craig JM, Todokoro K, Anderson M, Stafford A, Choo KH (2003) Transcription within a functional human centromere. Mol Cell 12:509–516
Scott K, Merrett S, Willard H (2006) A heterochromatin barrier partitions the fission yeast centromere into discrete chromatin domains. Curr Biol 16:119–129
Scott KC, White CV, Willard H (2007) An RNA polymerase III-dependent heterochromatin barrier at fission yeast centromere 1. PLoS ONE 2:e1099
Shang WH, Hori T, Martins NM, Toyoda A, Misu S, Monma N, Hiratani I, Maeshima K, Ikeo K, Fujiyama A et al (2013) Chromosome engineering allows the efficient isolation of vertebrate neocentromeres. Dev Cell 24:635–648
Shelby RD, Monier K, Sullivan KF (2000) Chromatin assembly at kinetochores is uncoupled from DNA replication. J Cell Biol 151:1113–1118
Sims RJ 3rd, Belotserkovskaya R, Reinberg D (2004) Elongation by RNA polymerase II: the short and long of it. Genes Dev 18:2437–2468
Slee RB, Steiner CM, Herbert BS, Vance GH, Hickey RJ, Schwarz T, Christan S, Radovich M, Schneider BP, Schindelhauer D et al (2012) Cancer-associated alteration of pericentromeric heterochromatin may contribute to chromosome instability. Oncogene 31:3244–3253
Stimpson KM, Sullivan BA (2010) Epigenomics of centromere assembly and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:772–780
Stoler S, Rogers K, Weitze S, Morey L, Fitzgerald-Hayes M, Baker RE (2007) Scm3, an essential Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere protein required for G2/M progression and Cse4 localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:10571–10576
Sullivan BA (2002) Centromere round-up at the heterochromatin corral. Trends Biotechnol 20:89–92
Sullivan B, Karpen G (2001) Centromere identity in Drosophila is not determined in vivo by replication timing. J Cell Biol 154:683–690
Sullivan BA, Karpen GH (2004) Centromeric chromatin exhibits a histone modification pattern that is distinct from both euchromatin and heterochromatin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:1076–1083
Sullivan KF, Hechenberger M, Masri K (1994) Human CENP-A contains a histone H3 related histone fold domain that is required for targeting to the centromere. J Cell Biol 127:581–592
Sullivan LL, Boivin CD, Mravinac B, Song IY, Sullivan BA (2011) Genomic size of CENP-A domain is proportional to total alpha satellite array size at human centromeres and expands in cancer cells. Chromosom Res 19:457–470
Takahashi K, Murakami S, Chikashige Y, Niwa O, Yanagida M (1991) A large number of tRNA genes are symmetrically located in fission yeast centromeres. J Mol Biol 218:13–17
Telenius H, Szeles A, Kereso J, Csonka E, Praznovszky T, Imreh S, Maxwell A, Perez CF, Drayer JI, Hadlaczky G (1999) Stability of a functional murine satellite DNA-based artificial chromosome across mammalian species. Chromosom Res 7:3–7
Thakur J, Sanyal K (2013) Efficient neocentromere formation is suppressed by gene conversion to maintain centromere function at native physical chromosomal loci in Candida albicans. Genome Res 23:638–652
Thiry M, Lafontaine DL (2005) Birth of a nucleolus: the evolution of nucleolar compartments. Trends Cell Biol 15:194–199
Ting DT, Lipson D, Paul S, Brannigan BW, Akhavanfard S, Coffman EJ, Contino G, Deshpande V, Iafrate AJ, Letovsky S et al (2011) Aberrant overexpression of satellite repeats in pancreatic and other epithelial cancers. Science 331:593–596
Topp CN, Zhong CX, Dawe RK (2004) Centromere-encoded RNAs are integral components of the maize kinetochore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15986–15991
Verdaasdonk JS, Bloom K (2011) Centromeres: unique chromatin structures that drive chromosome segregation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:320–332
Volpe T, Schramke V, Hamilton GL, White SA, Teng G, Martienssen RA, Allshire RC (2003) RNA interference is required for normal centromere function in fission yeast. Chromosom Res 11:137–146
Walfridsson J, Bjerling P, Thalen M, Yoo EJ, Park SD, Ekwall K (2005) The CHD remodeling factor Hrp1 stimulates CENP-A loading to centromeres. Nucleic Acids Res 33:2868–2879
Weimer R, Haaf T, Kruger J, Poot M, Schmid M (1992) Characterization of centromere arrangements and test for random distribution in G0, G1, S, G2, G1, and early S′ phase in human lymphocytes. Hum Genet 88:673–682
Westhorpe FG, Straight AF (2013) Functions of the centromere and kinetochore in chromosome segregation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 25:334–340
Wong LH, Brettingham-Moore KH, Chan L, Quach JM, Anderson MA, Northrop EL, Hannan R, Saffery R, Shaw ML, Williams E et al (2007) Centromere RNA is a key component for the assembly of nucleoproteins at the nucleolus and centromere. Genome Res 17:1146–1160
Yan H, Jin W, Nagaki K, Tian S, Ouyang S, Buell CR, Talbert PB, Henikoff S, Jiang J (2005) Transcription and histone modifications in the recombination-free region spanning a rice centromere. Plant Cell 17:3227–3238
Yan H, Ito H, Nobuta K, Ouyang S, Jin W, Tian S, Lu C, Venu RC, Wang GL, Green PJ et al (2006) Genomic and genetic characterization of rice Cen3 reveals extensive transcription and evolutionary implications of a complex centromere. Plant Cell 18:2123–2133
Acknowledgments
The author apologizes to all her colleagues whose work on centromeres and transcription could not be acknowledged due to space constraints. In addition, Karen Hayden Miga and Rachel O’Neill are thanked for editorial comments and critical reading of the manuscript. The Scott lab is supported by the Duke Institute for Genome Sciences and Policy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editors: Brian P. Chadwick, Kristin C. Scott, and Beth A. Sullivan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, K.C. Transcription and ncRNAs: at the cent(rome)re of kinetochore assembly and maintenance. Chromosome Res 21, 643–651 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-013-9387-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-013-9387-3