Abstract
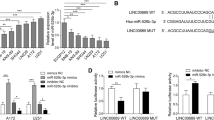
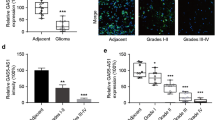
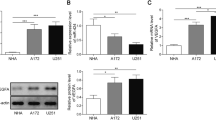
Glioma is the most common malignant brain tumor and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been reported to play an important role in the growth and angiogenesis of glioma. However, the potential mechanisms of lncRNA H19 in glioma remain unclear. In the present study, the effects of lncRNA H19 on glioma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis were evaluated. The expression levels of H19, miR-342, and Wnt5a in glioma tissues and cells were detected by RT-qPCR or Western blotting. Dual luciferase reporter assay confirmed the interaction between H19, miR-342, and Wnt5a. Cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis were analyzed by colony formation, transwell, and tube formation assays, respectively. IHC was performed to test the angiogenesis-related factor CD31. H19 and Wnt5a expression were remarkably upregulated in glioma tissues and cells, whereas miR-342 expression was downregulated. Moreover, functional analysis confirmed that knockdown of H19 or overexpression of miR-342 suppressed glioma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. Besides, H19 was found to directly target miR-342 to promote Wnt5a expression and activate β-catenin pathway in glioma cells. Moreover, suppression of miR-342 or overexpression of Wnt5a reversed the inhibitory effect of sh-H19 on glioma growth and metastasis. Additionally, we verified that H19 promoted glioma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis via miR-342/Wnt5a/β-catenin axis in vivo. H19 regulates glioma cell growth and metastasis through miR-342 to mediate Wnt5a/β-catenin signaling pathway, which provides new therapeutic targets for glioma treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- NHA:
-
Normal human astrocytes
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
References
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS (2017) Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res 77(15):3965–3981. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-16-2634
Binda E, Visioli A, Giani F, Trivieri N, Palumbo O, Restelli S, Dezi F, Mazza T, Fusilli C, Legnani F, Carella M, Di Meco F, Duggal R, Vescovi AL (2017) Wnt5a drives an invasive phenotype in human glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cancer Res 77(4):996–1007. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-16-1693
Carneiro I, Quintela-Vieira F, Lobo J, Moreira-Barbosa C, Menezes FD, Martins AT, Oliveira J, Silva R, Jerónimo C, Henrique R (2019) Expression of EMT-related genes CAMK2N1 and WNT5A is increased in locally invasive and metastatic prostate cancer. J Cancer 10(24):5915–5925. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.34564
Chen R, Smith-Cohn M, Cohen AL, Colman H (2017) Glioma subclassifications and their clinical significance. Neurother J Am Soc Exp NeuroTher 14(2):284–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0519-x
Chen L, Wang Y, He J, Zhang C, Chen J, Shi D (2018) Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes proliferation and invasion in human glioma cells by downregulating miR-152. Oncol Res. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504018x15178768577951
Chen D, Li D, Xu XB, Qiu S, Luo S, Qiu E, Rong Z, Zhang J, Zheng D (2019) Galangin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by downregulating CD44 in glioma. J Cancer 10(19):4499–4508. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.31487
Cheng Z, Li Z, Ma K, Li X, Tian N, Duan J, Xiao X, Wang Y (2017) Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes glioma tumorigenicity and angiogenesis by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-429. J Cancer 8(19):4106–4116. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.21024
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 9:287–314. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104715
Dijksterhuis JP, Arthofer E, Marinescu VD, Nelander S, Uhlén M, Pontén F, Mulder J, Schulte G (2015) High levels of WNT-5A in human glioma correlate with increased presence of tumor-associated microglia/monocytes. Exp Cell Res 339(2):280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.10.022
Gandía-González ML, Cerdán S, Barrios L, López-Larrubia P, Feijoó PG, Palpan A Jr, Roda JM, Solivera J (2019) Assessment of overall survival in glioma patients as predicted by metabolomic criteria. Front Oncol 9:328. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00328
Guan N, Wang R, Guo WS, Lai YJ, Zhang YD, Cheng YY (2019) Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates the development of gliomas through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(10):4243–4253. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201905_17929
Huang Y, Chi C (2019) Glioma cell proliferation is inhibited by miR-342-3p, miR-377/E2F1 signaling pathway. Neoplasma 66(4):524–531. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2018_180805N574
Jia P, Cai H, Liu X, Chen J, Ma J, Wang P, Liu Y, Zheng J, Xue Y (2016) Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a. Cancer Lett 381(2):359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.009
Jia L, Tian Y, Chen Y, Zhang G (2018) The silencing of LncRNA-H19 decreases chemoresistance of human glioma cells to temozolomide by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. OncoTargets Ther 11:313–321. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s154339
Jiang X, Yan Y, Hu M, Chen X, Wang Y, Dai Y, Wu D, Wang Y, Zhuang Z, Xia H (2016) Increased level of H19 long noncoding RNA promotes invasion, angiogenesis, and stemness of glioblastoma cells. J Neurosurg 2016(1):129–136. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.JNS1426.test
Kiang KM, Zhang XQ, Leung GK (2015) Long non-coding RNAs: the key players in glioma pathogenesis. Cancers (Basel) 7(3):1406–1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7030843
Li K, Lu D, Guo Y, Wang C, Liu X, Liu Y, Liu D (2018) Trends and patterns of incidence of diffuse glioma in adults in the United States, 1973–2014. Cancer Med 7(10):5281–5290. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1757
Liang WC, Fu WM, Wong CW, Wang Y, Wang WM, Hu GX, Zhang L, Xiao LJ, Wan DC, Zhang JF, Waye MM (2015) The lncRNA H19 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by functioning as miRNA sponges in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 6(26):22513–22525. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4154
Liang W, Guo B, Ye J, Liu H, Deng W, Lin C, Zhong X, Wang L (2019) Vasorin stimulates malignant progression and angiogenesis in glioma. Cancer Sci 110(8):2558–2572. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14103
Lin L, Cai J, Jiang C (2017) Recent advances in targeted therapy for glioma. Curr Med Chem 24(13):1365–1381. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666161223150242
Lu C, Jia S, Zhao S, Shao X (2019) MiR-342 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark Sect A of Dis Mark 25(1):115–126. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-192399
Ostrom QT, Cote DJ, Ascha M, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2018) Adult glioma incidence and survival by race or ethnicity in the United States from 2000 to 2014. JAMA Oncol 4(9):1254–1262. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.1789
Peng Z, Liu C, Wu M (2018) New insights into long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol Cancer 17(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0812-2
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29(4):452–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.010
Shea A, Harish V, Afzal Z, Chijioke J, Kedir H, Dusmatova S, Roy A, Ramalinga M, Harris B, Blancato J, Verma M, Kumar D (2016) MicroRNAs in glioblastoma multiforme pathogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Med 5(8):1917–1946. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.775
Shi Y, Wang Y, Luan W, Wang P, Tao T, Zhang J, Qian J, Liu N, You Y (2014) Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes glioma cell invasion by deriving miR-675. PLoS ONE 9(1):e86295. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086295
Sun SL, Shu YG, Tao MY (2019) miR-503 inhibits proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of glioma by acting on VEGFA through targeting LRIG2. Cancer Manag Res 11:10599–10608. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s222681
Wang SH, Ma F, Tang ZH, Wu XC, Cai Q, Zhang MD, Weng MZ, Zhou D, Wang JD, Quan ZW (2016) Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates FOXM1 expression by competitively binding endogenous miR-342-3p in gallbladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 35(1):160. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0436-6
Weng W, Okugawa Y, Toden S, Toiyama Y, Kusunoki M, Goel A (2016) FOXM1 and FOXQ1 are promising prognostic biomarkers and novel targets of tumor-suppressive miR-342 in human colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 22(19):4947–4957. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-0360
Xu H, Cai T, Carmona GN, Abuhatzira L, Notkins AL (2016) Small cell lung cancer growth is inhibited by miR-342 through its effect of the target gene IA-2. J Trans Med 14(1):278. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-1036-0
Yuan M, Da Silva A, Arnold A, Okeke L, Ames H, Correa-Cerro LS, Vizcaino MA, Ho CY, Eberhart CG, Rodriguez FJ (2018) MicroRNA (miR) 125b regulates cell growth and invasion in pediatric low grade glioma. Sci Rep 8(1):12506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30942-4
Zeira E, Abramovitch R, Meir K, Even Ram S, Gil Y, Bulvik B, Bromberg Z, Levkovitch O, Nahmansson N, Adar R, Reubinoff B, Galun E, Gropp M (2015) The knockdown of H19lncRNA reveals its regulatory role in pluripotency and tumorigenesis of human embryonic carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 6(33):34691–34703
Zhang T, Wang YR, Zeng F, Cao HY, Zhou HD, Wang YJ (2016) LncRNA H19 is overexpressed in glioma tissue, is negatively associated with patient survival, and promotes tumor growth through its derivative miR-675. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(23):4891–4897
Zhang L, Zhu Y, Cheng H, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Chen H, Chen L, Qi H, Ren G, Tang J, Zhong M, Hua W, Shi X, Li Q (2019) The increased expression of estrogen-related receptor α correlates with Wnt5a and poor prognosis in patients with glioma. Mol Cancer Ther 18(1):173–184. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-17-0782
Zhou Y, Kipps TJ, Zhang S (2017) Wnt5a signaling in normal and cancer stem cells. Stem Cells Int 2017:5295286. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5295286
Acknowledgements
Thanks to National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81803582) for supporting our work.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81803582), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province for Young Scholar (No. 2020JJ5957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was designed by W-LK and QZ. Z-ZL made great contribution to the data collection of this study. HW and QZ were responsible for the data analysis and ascertained the integrity as well as accuracy of the data. QZ and W-LK prepared and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to Participate
All patients were informed of the study and signed the written consent.
Consent for Publication
The informed consent is obtained from study participants.
Ethical Approval
All experiments were conducted with the approval of the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Xiangya Hospital of Central South University.
Research Involving Human and/or Animal Participants
Animal handling and experimental procedures were permitted by the Animal Experimental Ethics Committee of Xiangya Hospital of Central South University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Liu, ZZ., Wu, H. et al. LncRNA H19 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Angiogenesis of Glioma by Regulating Wnt5a/β-Catenin Pathway via Targeting miR-342. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 1065–1077 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00995-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00995-z