Abstract
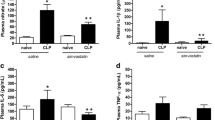
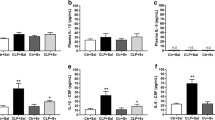
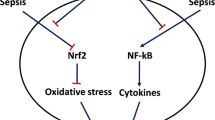
This present research work reports the possible effects and the underlying mechanism of atorvastatin on survival rate and cognitive disorders after sepsis. Sepsis is a life-threatening dysfunction that arises when the body’s response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. Diffuse sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture surgery (CLP) in ICR mice. 0.2 mg/kg body weight of atorvastatin was administrated intraperitoneally at 12 h before surgery. The survival of mice was calculated 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after CLP surgery. Two weeks later, open-field test and Morris water maze test were conducted to evaluate the protective effect of atorvastatin. Inflammatory cytokines in plasma, oxidative stress parameters, number of astrocytes, and neuronal cell deaths in the CA3 region of the hippocampus were examined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunohistochemistry. The results indicate that pretreatment with atorvastatin can increase survival percentage and improve cognitive function. Atorvastatin reversed all these alterations in parallel with a decrease in circulating levels of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, and TNF-α) in plasma, inhibited the activities of oxidative stress parameters (lower TBARS levels, ratio of GSH/GSSH, and activities of SOD and CAT), enhanced the activity of citrate synthase in brain, and reduced the number of astrocytes and neuronal cell deaths in CA3 region of hippocampus. Overall, our results indicated that atorvastatin exhibited protective effects on survival rate and cognitive disorders after sepsis by inhibiting the release of inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and neuronal apoptosis in brain tissue.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data used in your manuscript are all placed in our manuscript.
References
Ando H, Takamura T, Ota T, Nagai Y, Kobayashi K (2000) Cerivastatin improves survival of mice with lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294(3):1043–1046
Angus DC, Pires Pereira CA, Silva E (2006) Epidemiology of severe sepsis around the world. Endocr Metab Immune Disord. https://doi.org/10.2174/187153006777442332
Blanco-Colio LM, Tunon J, Martin-Ventura JL, Egido J (2003) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of statins. Kidney Int 63(1):12–23. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00744.x
Buras JA, Holzmann B, Sitkovsky M (2005) Model organisms: animal models of sepsis: setting the stage. Dress Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(10):854–865. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1854
Calisto KL, Carvalho Bde M, Ropelle ER, Mittestainer FC, Camacho AC, Guadagnini D, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ (2010) Atorvastatin improves survival in septic rats: effect on tissue inflammatory pathway and on insulin signaling. PLoS ONE 5(12):e14232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014232
Catalao CH, Santos-Junior NN, da Costa LH, Souza AO, Alberici LC, Rocha MJ (2016) Brain oxidative stress during experimental sepsis is attenuated by simvastatin administration. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0218-3
Coldewey SM, Thiemermann C (2014) Pleiotropic effects of atorvastatin in experimental sepsis: preservation of beta1-adrenoreceptor signaling in the heart. Shock 41(5):458–459. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000154
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb S, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R (2012) Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including The Pediatric S (2013) Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Med 39(2):165–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8
dos Santos RS, Donadio MV, da Silva GV, Blattner CN, Melo DA, Nunes FB, Dias FS, Squizani ED, Pedrazza L, Gadegast I, de Oliveira JR (2014) Immediate effects of chest physiotherapy on hemodynamic, metabolic, and oxidative stress parameters in subjects with septic shock. Respir Care 59(9):1398–1403. https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.02859
El-Nabarawi N, El-Wakd M, Salem M (2017) Atorvastatin, a double weapon in osteoporosis treatment: an experimental and clinical study. Drug Des Dev Ther 11:1383–1391. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S133020
Hernandes MS, D’Avila JC, Trevelin SC, Reis PA, Kinjo ER, Lopes LR, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Cunha FQ, Britto LR, Bozza FA (2014) The role of Nox2-derived ROS in the development of cognitive impairment after sepsis. J Neuroinflamm 11:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-36
Hopkins RO, Weaver LK, Chan KJ, Orme JF (2004) Quality of life, emotional, and cognitive function following acute, respiratory distress syndrome. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 10(07):1005–1017. https://doi.org/10.1017/s135561770410711x
Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM (2010) Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA 304(16):1787–1794. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.1553
Jawad I, Lukši I, Rafnsson SB (2012) Assessing available information on the burden of sepsis: global estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality. J Glob Health 2(1):10404. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.02.010404
Kandasamy K, Prawez S, Choudhury S, More AS, Ahanger AA, Singh TU, Parida S, Mishra SK (2011) Atorvastatin prevents vascular hyporeactivity to norepinephrine in sepsis: role of nitric oxide and alpha(1)-adrenoceptor mRNA expression. Shock 36(1):76–82. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e31821a4002
Kim JS, Kwon WY, Suh GJ, Kim KS, Jung YS, Kim SH, Lee SE (2016) Plasma glutathione reductase activity and prognosis of septic shock. J Surg Res 200(1):298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2015.07.044
Kruger PS, Freir NM, Venkatesh B, Robertson TA, Roberts MS, Jones M (2009) A preliminary study of atorvastatin plasma concentrations in critically ill patients with sepsis. Intensive Care Med 35(4):717–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1358-3
Li Y, Wang F, Luo Y (2017) Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy through beclin 1-independent autophagy in mice. J Surg Res 207:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.08.080
Ma M, Uekawa K, Hasegawa Y, Nakagawa T, Katayama T, Sueta D et al (2013) Pretreatment with rosuvastatin protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res 1519:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.04.040
Mantzarlis K, Tsolaki V, Zakynthinos E (2017) Role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis and potential therapies. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:5985209. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5985209
Marco R, Pestana A, Sebastian J, Sols A (1974) Oxaloacetate metabolic crossroads in liver. Enzyme compartmentation and regulation of gluconeogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 3(1):53–70
Mekontso-Dessap A, Brun-Buisson C (2006) Statins: the next step in adjuvant therapy for sepsis? Intensive Care Med 32(1):11–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-005-2860-5
Merx MW, Liehn EA, Janssens U, Lutticken R, Schrader J, Hanrath P, Weber C (2004) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor simvastatin profoundly improves survival in a murine model of sepsis. Circulation 109(21):2560–2565. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000129774.09737.5B
Merx MW, Liehn EA, Graf J, van de Sandt A, Schaltenbrand M, Schrader J, Hanrath P, Weber C (2005) Statin treatment after onset of sepsis in a murine model improves survival. Circulation 112(1):117–124. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.502195
Ou SY, Chu H, Chao PW, Ou SM, Lee YJ, Kuo SC, Li SY, Shih CJ, Chen YT (2014) Effect of the use of low and high potency statins and sepsis outcomes. Intensive Care Med 40(10):1509–1517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-014-3418-1
Rachoin JS, Cerceo E, Dellinger RP (2013) A new role for statins in sepsis. Crit Care 17(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc11907
Reis PA, Alexandre PCB, D’Avila Joana C, Siqueira LD, Bozza FA (2016) Statins prevent cognitive impairment after sepsis by reverting neuroinflammation, and microcirculatory/endothelial dysfunction. Brain Behav Immun 60:293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.11.006
Reis PA, Alexandre PC, D’Avila JC, Siqueira LD, Antunes B, Estato V, Tibirica EV, Verdonk F, Sharshar T, Chretien F, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Bozza FA (2017) Statins prevent cognitive impairment after sepsis by reverting neuroinflammation, and microcirculatory/endothelial dysfunction. Brain Behav Immun 60:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.11.006
Scaini G, Rochi N, Benedet J, Ferreira GK, Teodorak BP, Comim CM, Constantino Lde S, Vuolo F, Constantino LC, Quevedo J, Streck EL, Dal-Pizzol F (2011) Inhibition of brain citrate synthase activity in an animal model of sepsis. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 23(2):158–163
Sharshar T, Carlier R, Bernard F, Guidoux Céline, Brouland JP, Nardi O et al (2007) Brain lesions in septic shock: a. Intensive Care Med 33(5):798–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-007-0598-y
Sierra S, Ramos MC, Molina P, Esteo C, Vazquez JA, Burgos JS (2011) Statins as neuroprotectants: a comparative in vitro study of lipophilicity, blood-brain-barrier penetration, lowering of brain cholesterol, and decrease of neuron cell death. J Alzheimers Dis 23(2):307–318. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-101179
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC (2016) The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 315(8):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0287
Thangamalai R, Kandasamy K, Sukumarn SV, Reddy N, Singh V, Choudhury S, Parida S, Singh TU, Boobalan R, Mishra SK (2014) Atorvastatin prevents sepsis-induced downregulation of myocardial beta1-adrenoceptors and decreased cAMP response in mice. Shock 41(5):406–412. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000138
Tsiotou AG, Sakorafas GH, Anagnostopoulos G, Bramis J (2005) Septic shock; current pathogenetic concepts from a clinical perspective. Med Sci Monit 11(3):RA76–RA85
Wang XQ, Luo NS, Salah ZQ, Lin YQ, Gu MN, Chen YX (2014) Atorvastatin attenuates TNF-alpha production via heme oxygenase-1 pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Biomed Environ Sci 27(10):786–793. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2014.114
Funding
This work was supported by the Jiangsu province natural science foundation of China (BK20151204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Tai, Y., Shi, M. et al. Atorvastatin Relieves Cognitive Disorder After Sepsis Through Reverting Inflammatory Cytokines, Oxidative Stress, and Neuronal Apoptosis in Hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40, 521–530 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00750-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00750-z