Abstract
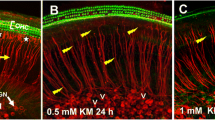
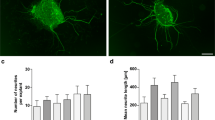
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play an important role in modeling of the extracellular matrix. There is increasing evidence that these proteases are important in neurite elongation and axonal guidance during development in the central nervous system and retina. Moreover, they are also expressed after acute injury and can be the key mediators of pathogenesis. However, the role of MMPs in the inner ear is largely unknown. Our group recently demonstrated that general inhibition of MMPs resulted in auditory hair cell loss in vitro. In the present study, we investigated the role of MMPs in inner ear spiral ganglion neuron (SGN) survival, neuritogenesis and neurite extension by blocking MMPs known to be involved in axonal guidance, neurite elongation, and apoptosis in other neuronal systems. Spiral ganglion (SG) explants from 5-day-old Wistar rats were treated with different concentrations of the general MMP inhibitor GM6001, a specific MMP-2 inhibitor, and a specific MMP-9 inhibitor, in vitro. The general inhibitor of MMPs and the specific inhibition of MMP-2 significantly reduced both the number of neurites that extended from SG explants, as well as the length of individual neurites. However, neither the general inhibitor of MMPs nor the specific inhibition of MMP-2 influenced SGN survival. Inhibition of MMP-9 had no influence on SGNs. The data suggest that MMPs, and more specifically MMP-2, influence the growth of developing afferent neurites in the mammalian inner ear in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal SM, Lau L, Yong VW (2008) MMPs in the central nervous system: where the good guys go bad. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19:42–51
Aletsee C, Mullen L, Kim D, Pak K, Brors D, Dazert S, Ryan AF (2001) The disintegrin kistrin inhibits neurite extension from spiral ganglion explants cultured on laminin. Audiol Neurootol 6:57–65
Aletsee C, Brors D, Palacios S, Pak K, Mullen L, Dazert S, Ryan AF (2002) The effects of laminin-1 onganglion neurons are dependent on the MEK/ERK signaling pathway and are partially independent of Ras. Hear Res 164:1–11
Brors D, Aletsee C, Schwager K, Mlynski R, Hansen S, Schäfers M, Ryan AF, Dazert S (2002) Interaction of spiral ganglion neuron processes with alloplastic materials in vitro. Hear Res 167:110–121
Chang DI, Hosomi N, Lucero J, Heo JH, Abumiva T, Mazar AP, del Zoppo GJ (2003) Activation systems for latent matrix metalloproteinase-2 are upregulated immediately after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1408–1419
Chintala SK (2006) The emerging role of proteases in retinal ganglion cell death. Exp Eye Res 82:5–12
Chintala SK, Zhang X, Austin JS, Fini ME (2002) Deficiency in matrix metalloproteinase gelatinase B (MMP-9) protects against retinal ganglion cell death after optic nerve ligation. J Biol Chem 277:47461–47468
Clark AW, Krekoski CA, Bou SS, Chapman KR, Edwards DR (1997) Increased gelatinase A (MMP-2) and gelatinase B (MMP-9) activities in human brain after focal ischemia. Neurosci Lett 238:53–56
Echteler SM, Nofsinger YC (2000) Development of ganglion cell topography in the postnatal cochlea. J Comp Neurol 425:436–446
Ernfors P, Van De Water T, Loring J, Jaenisch R (1995) Complementary roles of BDNF and NT-3 in vestibular and auditory development. Neuron 14:1153–1164
Evans AR, Euteneuer S, Chavez E, Mullen LM, Hui EE, Bhatia SN, Ryan AF (2007) Laminin and fibronectin modulate inner ear spiral ganglion neurite outgrowth in an in vitro alternate choice assay. Dev Neurobiol 67:1721–1730
Faissner A, Pyka M, Geissler M, Sobik T, Frischknecht R, Gundelfinger ED, Seidenbecher C (2010) Contributions of astrocytes to synapse formation and maturation: potential functions of the perisynaptic extracellular matrix. Brain Res Rev 63:26–38
Fredrich M, Illing RB (2011) Deafferentation-induced redistribution of MMP-2, but not MMO-9, depends on the emergence of GAP-43 positive axons in the adult cochlear nucleus. Neural Plast 2011:859359
Fujioka H, Dairyo Y, Yasunaga K, Emoto K (2012) Neural functions of matrix metalloproteinases: plasticity, neurogenesis and disease. Biochem Res Int 2012:789083
Genepaint (2013) http://www.genepaint.org. Accessed 30 June 2013
Giannelli G, Falk-Marzillier J, Schiraldi O, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Quaranta V (1997) Induction of cell migration by matrix metalloprotease-2 cleavage of laminin-5. Science 277:225–228
Hansen MR, Zha XM, Bok J, Green SH (2001) Multiple distinct signal pathways, including an autocrine neurotrophic mechanism, contribute to the survival-promoting effect of depolarization on spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. J Neuorosci 21:2256–2267
Henley CM, Owings MH, Stagner BB, Martin GK, Lonsbury-Martin BL (1989) Postnatal development of 2f1–f2 otoacoustic emissions in pigmented rat. Hear Res 43:141–148
Hertzano R, Puligilla C, Chan SL, Timothy C, Depireux DA, Ahmed Z, Wolf J, Eisenman DJ, Friedman TB, Riazuddin S, Kelley MW, Strome SE (2010) CD44 is a marker for the outer pillar cells in the early postnatal mouse inner ear. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 11:407–418
Hu BH, Cai Q, Hu Z, Patel M, Bard J, Jamison J, Coling D (2012) Metalloproteinases and their associated genes contribute to the functional integrity and noise-induced damage in the cochlear sensory epithelium. J Neurosci 32:14927–14941
Ispanovic E, Haas TL (2006) JNK and PI3K differentially regulate MMP-2 and MT1-MMP mRNA and protein in response to actin cytoskeleton reorganization in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291:579–588
Kundu S, Tyagi N, Sen U, Tyagi SC (2009) Matrix imbalance by inducing expression of metalloproteinase and oxidative stress in cochlea of hyperhomocysteinemic mice. Mol Cell Biochem 332:215–224
Lallemend K, Hadjab S, Hans G, Moonen G, Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B (2005) Activation of protein kinaseCbetal constitutes a new neurotrophic pathway for deafferented spiral ganglion neurons. J Cell Sci 118:4511–4525
Lallemend F, Vandenbosch R, Hadjab S, Bodson M, Breuskin I, Moonen G, Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B (2007) New insights into peripherin expression in cochlear. Neurons Neurosci 150:212–222
Mullen LM, Pak KK, Chavez E, Kondo K, Brand Y, Ryan AF (2012) Ras/p38 and PI3K/Akt but not Mek/Erk signaling mediate BDNF-induced neurite formation on neonatal cochlear spiral ganglion explants. Brain Res 1430:24–34
Page-McCaw A, Ewald J, Werb Z (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remoldeling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:221–233
Reuter A, Nestl A, Zwacka RM, Tuckermann J, Waldherr R, Wagner EM, Meyer zum Gottesberge AM, Angel P, Weiher H (1998) Expression of the recessive glomerulosclerosis gene Mpv17 regulates MMP-2 expression in fibroblasts, the kidney, and the inner ear of mice. Mol Biol Cell 9:1675–1682
Rosenberg GA (2009) Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol 8:205–216
Rybak LP, Whitworth C, Scott V (1992) Development of endocochlear potential and compound action potential in the rat. Hear Res 59:189–194
Setz C, Brand Y, Radojevic V, Hanusek C, Mullen PJ, Levano S, Listyo A, Boderm D (2011) Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in the cochlea: expression and activity after aminoglycoside exposition. Neuroscience 181:28–39
Sorokin L (2010) The impact of extracellular matrix on inflamation. Nat Rev Immunol 10:712–723
Vaillant C, Meissirel C, Mutin M, Belin MF, Lund RF, Thomasset N (2003) MMP-9 deficiency affects axonal outgrowth, migration, and apoptosis in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:395–408
Van de Water TR, Ruben RJ (1971) Organ culture of the mammalian inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 71:303–312
Webber CA, Hocking JC, Yong VW, Stange CL, McFarlane S (2002) Metalloproteases and guidance of retinal ganglion axons in the developing visual system. J Neurosci 22:8091–8100
Whitlon DS, Zhang X, Pecelunas K, Greiner MA (1999a) A temporospatial map of adhesive molecules in the organ of Corti of the mouse cochlea. J Neurocytol 28:955–968
Whitlon DS, Zhang X, Kusakabe M (1999b) Tenascin-C in the cochlea of the developing mouse. J Comp Neurol 406:361–374
Woolf NK, Koehrn FJ, Ryan AF (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of fibronectin-like protein in the inner ear of the developing gerbil and rat. Dev Brain Res 65:21–33
Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W, Rosemberg GA (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:697–709
Yong VW (2005) Metalloproteinases: mediators of pathology and regeneration in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:931–944
Zhang X, Chintala SK (2004) Influence of interleukin-1 beta induction and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation on optic nerve ligation-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation in the retina. Exp Eye Res 78:849–860
Zhang Y, Klassen HJ, Tucker BA, Perez MT, Young MJ (2007) CNS progenitor cells promote a permissive environment for neurite outgrowth via a matrix metalloproteinase-2-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci 27:4499–4506
Zhang H, Chang M, Hansen CM, Basso DM, Noble-Haeusslein LJ (2011) Role of matrix metalloproteinases and therapeutic benefits of their inhibition in spinal cord injury. Neurotherapeutics 8:206–220
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by Medizinische Abteilung der Margarete und Walter Lichtsteiner-Stiftung, Basel, Switzerland.
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Michael Sung and Eric Wei have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, M., Wei, E., Chavez, E. et al. Inhibition of MMP-2 but not MMP-9 Influences Inner Ear Spiral Ganglion Neurons In Vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 1011–1021 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0077-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0077-2