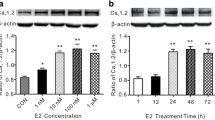
Abstract
The Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) is an important bidirectional transporter of calcium in neurons and has been shown to be involved in neuroprotection. Calcium can activate a number of cascades that can result in apoptosis and cell death, and NCX is a key factor in regulating the cytoplasmic concentration of this ion. 17-β-estradiol and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) are known neuroprotective hormones with interacting mechanisms and effects on intracellular calcium; however, their relationship with the NCX has not been explored. In this article, the effects of these two hormones on neuronal NCX were tested using the whole-cell patch clamp technique on rat primary culture neurons. Both 17-β-estradiol and IGF-1 produced an increase in the NCX-mediated inward current and a decrease in the NCX-mediated outward current. However, the IGF-1 effect was lower than that of 17-β-estradiol, and the effect of both agents together was greater than the sum of each agent alone. Neither of the agents affected the pattern of regulation by extracellular or intrapipette calcium. Inhibitors of the IGF-1 and 17-β-estradiol receptors and inhibitors of the main signaling pathways failed to change the observed effects, indicating that these actions were not mediated by the classical receptors of these hormones. These effects on the NCX could be a mechanism explaining the neuroprotective actions of 17-β-estradiol and IGF-1, and these findings could help researchers to understand the role of the NCX in neuroprotection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amantea D, Russo R, Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT (2005) From clinical evidence to molecular mechanisms underlying neuroprotection afforded by estrogens. Pharmacol Res 52:119–132
Amoroso S, Tortiglione A, Secondo A, Catalano A, Montagnani S, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (2000) Sodium nitroprusside prevents chemical hypoxia-induced cell death through iron ions stimulating the activity of the Na+–Ca2+ exchanger in C6 glioma cells. J Neurochem 74:1505–1513
Anderson SE, Kirkland DM, Beyschau A, Cala PM (2005) Acute effects of 17beta-estradiol on myocardial pH, Na+, and Ca2+ and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C57–C64
Andreeva N, Khodorov B, Stelmashook E, Cragoe E Jr, Victorov I (1991) Inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange enhances delayed neuronal death elicited by glutamate in cerebellar granule cell cultures. Brain Res 548:322–325
Annunziato L, Pignataro G, Di Renzo GF (2004) Pharmacology of brain Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: from molecular biology to therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol Rev 56:633–654
Aperghis M, Johnson IP, Cannon J, Yang SY, Goldspink G (2004) Different levels of neuroprotection by two insulin-like growth factor-I splice variants. Brain Res 1009:213–218
Araujo IM, Carreira BP, Pereira T, Santos PF, Soulet D, Inacio A, Bahr BA, Carvalho AP, Ambrosio AF, Carvalho CM (2007) Changes in calcium dynamics following the reversal of the sodium-calcium exchanger have a key role in AMPA receptor-mediated neurodegeneration via calpain activation in hippocampal neurons. Cell Death Differ 14:1635–1646
Azcoitia I, Sierra A, Garcia-Segura LM (1999) Neuroprotective effects of estradiol in the adult rat hippocampus: interaction with insulin-like growth factor-I signalling. J Neurosci Res 58:815–822
Ba F, Pang PK, Davidge ST, Benishin CG (2004) The neuroprotective effects of estrogen in SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cell cultures. Neurochem Int 44:401–411
Bains M, Cousins JC, Roberts JL (2007) Neuroprotection by estrogen against MPP+-induced dopamine neuron death is mediated by ERalpha in primary cultures of mouse mesencephalon. Exp Neurol 204:767–776
Bano D, Young KW, Guerin CJ, Lefeuvre R, Rothwell NJ, Naldini L, Rizzuto R, Carafoli E, Nicotera P (2005) Cleavage of the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in excitotoxicity. Cell 120:275–285
Behl C (2002a) Estrogen can protect neurons: modes of action. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:195–197
Behl C (2002b) Oestrogen as a neuroprotective hormone. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:433–442
Bence-Hanulec KK, Marshall J, Blair LA (2000) Potentiation of neuronal L calcium channels by IGF-1 requires phosphorylation of the alpha1 subunit on a specific tyrosine residue. Neuron 27:121–131
Bers DM, Weber CR (2002) Na/Ca exchange function in intact ventricular myocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 976:500–512
Beuckelmann DJ, Wier WG (1989) Sodium-calcium exchange in guinea-pig cardiac cells: exchange current and changes in intracellular Ca2+. J Physiol 414:499–520
Blair LA, Marshall J (1997) IGF-1 modulates N and L calcium channels in a PI 3-kinase-dependent manner. Neuron 19:421–429
Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ (1999) Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev 79:763–854
Bondy CA, Cheng CM (2004) Signaling by insulin-like growth factor 1 in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 490:25–31
Brann DW, Dhandapani K, Wakade C, Mahesh VB, Khan MM (2007) Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions of estrogen: basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Steroids 72:381–405
Brywe KG, Mallard C, Gustavsson M, Hedtjarn M, Leverin AL, Wang X, Blomgren K, Isgaard J, Hagberg H (2005) IGF-I neuroprotection in the immature brain after hypoxia-ischemia, involvement of Akt and GSK3beta? Eur J Neurosci 21:1489–1502
Busa W (1996) Regulation of intracellular free calcium. In: Shultz S, Andreoli T, Brown A, Frambrough D, Hoffman J, Welsh M (eds) Molecular biology of membrane transport disorders. Plenum Press, New York, pp 427–446
Cardona-Gomez GP, Mendez P, Garcia-Segura LM (2002) Synergistic interaction of estradiol and insulin-like growth factor-I in the activation of PI3 K/Akt signaling in the adult rat hypothalamus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 107:80–88
Carro E, Trejo JL, Nunez A, Torres-Aleman I (2003) Brain repair and neuroprotection by serum insulin-like growth factor I. Mol Neurobiol 27:153–162
Condrescu M, Opuni K, Hantash BM, Reeves JP (2002) Cellular regulation of sodium-calcium exchange. Ann N Y Acad Sci 976:214–223
Czyz A, Kiedrowski L (2002) In depolarized and glucose-deprived neurons, Na+ influx reverses plasmalemmal K+-dependent and K+-independent Na+/Ca2+ exchangers and contributes to NMDA excitotoxicity. J Neurochem 83:1321–1328
Diaz-Horta O, Van Eylen F, Herchuelz A (2003) Na/Ca exchanger overexpression induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, caspase-12 release, and apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:430–432
DiPolo R, Beauge L (1987) Characterization of the reverse Na/Ca exchange in squid axons and its modulation by Cai and ATP. Cai-dependent Nai/Cao and Nai/Nao exchange modes. J Gen Physiol 90:505–525
DiPolo R, Beauge L (1990) Asymmetrical properties of the Na-Ca exchanger in voltage-clamped, internally dialyzed squid axons under symmetrical ionic conditions. J Gen Physiol 95:819–835
Ehara T, Matsuoka S, Noma A (1989) Measurement of reversal potential of Na+–Ca2+ exchange current in single guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol 410:227–249
Fernandez S, Fernandez AM, Lopez-Lopez C, Torres-Aleman I (2007) Emerging roles of insulin-like growth factor-I in the adult brain. Growth Horm IGF Res 17:89–95
Filardo EJ, Thomas P (2005) GPR30: a seven-transmembrane-spanning estrogen receptor that triggers EGF release. Trends Endocrinol Metab 16:362–367
Fink K, Meder WP, Clusmann H, Gothert M (2002) Ca2+ entry via P/Q-type Ca2+ channels and the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in rat and human neocortical synaptosomes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 366:458–463
Gibney GT, Zhang JH, Douglas RM, Haddad GG, Xia Y (2002) Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger expression in the developing rat cortex. Neuroscience 112:65–73
Gonthier B, Nasarne C, Rudiger T (2005). Protocol for the primary culture of cortical neurons. In: Poindron P (ed) New methods for culturing cells from nervous tissue. Bio Valley Monographs, Karger, Basel, pp 12–22
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch 391:85–100
Hilgemann DW, Collins A, Matsuoka S (1992) Steady-state and dynamic properties of cardiac sodium-calcium exchange. Secondary modulation by cytoplasmic calcium and ATP. J Gen Physiol 100:933–961
Hinata M, Yamamura H, Li L, Watanabe Y, Watano T, Imaizumi Y, Kimura J (2002) Stoichiometry of Na+–Ca2+ exchange is 3:1 in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol 545:453–461
Honda K, Shimohama S, Sawada H, Kihara T, Nakamizo T, Shibasaki H, Akaike A (2001) Nongenomic antiapoptotic signal transduction by estrogen in cultured cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 64:466–475
Iwamoto T, Watano T, Shigekawa M (1996) A novel isothiourea derivative selectively inhibits the reverse mode of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in cells expressing NCX1. J Biol Chem 271:22391–22397
Jeffs GJ, Meloni BP, Bakker AJ, Knuckey NW (2007) The role of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) in neurons following ischaemia. J Clin Neurosci 14:507–514
Jeffs GJ, Meloni BP, Sokolow S, Herchuelz A, Schurmans S, Knuckey NW (2008) NCX3 knockout mice exhibit increased hippocampal CA1 and CA2 neuronal damage compared to wild-type mice following global cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 210:268–273
Kang TM, Hilgemann DW (2004) Multiple transport modes of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Nature 427:544–548
Kimura J, Miyamae S, Noma A (1987) Identification of sodium-calcium exchange current in single ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol 384:199–222
Kimura J, Watanabe Y, Li L, Watano T (2002) Pharmacology of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Ann N Y Acad Sci 976:513–519
Matsuoka S, Hilgemann DW (1992) Steady-state and dynamic properties of cardiac sodium-calcium exchange. Ion and voltage dependencies of the transport cycle. J Gen Physiol 100:963–1001
Mendez P, Azcoitia I, Garcia-Segura LM (2005a) Interdependence of oestrogen and insulin-like growth factor-I in the brain: potential for analysing neuroprotective mechanisms. J Endocrinol 185:11–17
Mendez P, Cardona-Gomez GP, Garcia-Segura LM (2005b) Interactions of insulin-like growth factor-I and estrogen in the brain. Adv Exp Med Biol 567:285–303
Mendez P, Wandosell F, Garcia-Segura LM (2006) Cross-talk between estrogen receptors and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in the brain: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Front Neuroendocrinol 27:391–403
Micevych P, Dominguez R (2009) Membrane estradiol signaling in the brain. Front Neuroendocrinol 30:315–327
Minelli A, Castaldo P, Gobbi P, Salucci S, Magi S, Amoroso S (2007) Cellular and subcellular localization of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger protein isoforms, NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3 in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of adult rat. Cell Calcium 41:221–234
Miura Y, Kimura J (1989) Sodium-calcium exchange current. Dependence on internal Ca and Na and competitive binding of external Na and Ca. J Gen Physiol 93:1129–1145
Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, Enmark E, Pettersson K, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2001) Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev 81:1535–1565
Philipson KD, Nicoll DA (2000) Sodium-calcium exchange: a molecular perspective. Annu Rev Physiol 62:111–133
Philipson KD, Nicoll DA, Ottolia M, Quednau BD, Reuter H, John S, Qiu Z (2002) The Na+/Ca2+ exchange molecule: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci 976:1–10
Pignataro G, Gala R, Cuomo O, Tortiglione A, Giaccio L, Castaldo P, Sirabella R, Matrone C, Canitano A, Amoroso S, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (2004a) Two sodium/calcium exchanger gene products, NCX1 and NCX3, play a major role in the development of permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 35:2566–2570
Pignataro G, Tortiglione A, Scorziello A, Giaccio L, Secondo A, Severino B, Santagada V, Caliendo G, Amoroso S, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (2004b) Evidence for a protective role played by the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in cerebral ischemia induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in male rats. Neuropharmacology 46:439–448
Quesada A, Micevych PE (2004) Estrogen interacts with the IGF-1 system to protect nigrostriatal dopamine and maintain motoric behavior after 6-hydroxdopamine lesions. J Neurosci Res 75:107–116
Sanchez JC, Powell T, Staines HM, Wilkins RJ (2006) Electrophysiological demonstration of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in bovine articular chondrocytes. Biorheology 43:83–94
Sanchez JC, Lopez-Zapata DF, Romero-Leguizamon CR (2010) Calcium transport mechanisms in neuroprotection and neurotoxicity. Rev Neurol 51:624–632
Segars JH, Driggers PH (2002) Estrogen action and cytoplasmic signaling cascades. Part I: membrane-associated signaling complexes. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:349–354
Shono Y, Kamouchi M, Kitazono T, Kuroda J, Nakamura K, Hagiwara N, Ooboshi H, Ibayashi S, Iida M (2010) Change in intracellular pH causes the toxic Ca2+ entry via NCX1 in neuron- and glia-derived cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30:453–460
Shughrue PJ, Lane MV, Merchenthaler I (1997) Comparative distribution of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta mRNA in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 388:507–525
Szydlowska K, Tymianski M (2010) Calcium, ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 47:122–129
Thomas P, Dong J (2006) Binding and activation of the seven-transmembrane estrogen receptor GPR30 by environmental estrogens: a potential novel mechanism of endocrine disruption. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 102:175–179
Thomas P, Pang Y, Filardo EJ, Dong J (2005) Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 146:624–632
Torok TL (2007) Electrogenic Na+/Ca2+-exchange of nerve and muscle cells. Prog Neurobiol 82:287–347
Tortiglione A, Pignataro G, Minale M, Secondo A, Scorziello A, Di Renzo GF, Amoroso S, Caliendo G, Santagada V, Annunziato L (2002) Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in Na+ efflux-Ca2+ influx mode of operation exerts a neuroprotective role in cellular models of in vitro anoxia and in vivo cerebral ischemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci 976:408–412
Ullrich ND, Koschak A, MacLeod KT (2007) Oestrogen directly inhibits the cardiovascular L-type Ca2+ channel Cav1.2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:522–527
Vasudevan N, Pfaff DW (2008) Non-genomic actions of estrogens and their interaction with genomic actions in the brain. Front Neuroendocrinol 29:238–257
Acknowledgments
We thank to the Red de Universidades Públicas del Eje Cafetero Alma Máter and Colciencias for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, J.C., López-Zapata, D.F., Francis, L. et al. Effects of Estradiol and IGF-1 on the Sodium Calcium Exchanger in Rat Cultured Cortical Neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 619–627 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9657-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9657-6