Summary
1. Aims: Epinephrine (EPI) synthesizing enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT, EC 2.1.1.28) is primarily localized in the adrenal medulla (AM). We have recently described existence of the PNMT gene expression in cardiac atria and ventricles and in sympathetic ganglia of adult rats and mice. The aim of the present work was to study regulation of the PNMT gene expression in corticotropin-releasing hormone knockout mice (CRH KO) and matched control wild-type mice (WT) under normal and stress conditions.
2. Methods: Levels of the PNMT mRNA were determined by RT-PCR; PNMT immunoprotein and protein of transcription factor EGR-1 by Western Blot. Plasma EPI and corticosterone (CORT) levels were determined by radioenzymatic and RIA methods. Immobilization (IMMO) was used as a stressor.
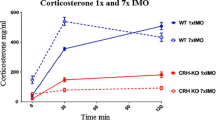
3. Results: Stress-induced increases in the PNMT mRNA and protein levels observed in WT mice were almost completely absent in CRH KO mouse adrenal medulla, stellate ganglia, and cardiac atria, while ventricular PNMT mRNA elevation was not CRH-dependent. Plasma EPI and CORT levels were markedly reduced in CRH KO compared to WT mice both before and after the stress. Levels of EGR-1, crucial transcription factor for regulation of the PNMT were highly increased in stressed WT and CRH KO mice in cardiac areas, but not in the adrenal medulla.
4. Conclusions: Data show that the CRH deficiency can markedly prevent immobilization-triggered induction of the PNMT mRNA and protein levels in the adrenal medulla and stellate ganglia. Reduced plasma epinephrine and corticosterone levels and adrenal medullary EGR-1 protein levels in CRH knockout versus WT mice during stress indicate that the HPA axis plays a crucial role in regulation of the PNMT gene expression in these organs.
Cardiac atrial PNMT gene expression with stress is also dependent on intact HPA axis. However, in cardiac ventricles, especially after the single stress exposure, its expression is not impaired by CRH deficiency. Since cardiac EGR-1 protein levels in CRH KO mice are also not affected by the single stress exposure, we propose existence of different regulation of the PNMT gene expression, especially in the cardiac ventricles.
Overall, our findings reveal that the PNMT gene expression is regulated through the HPA in both sympathoadrenal system and the heart and also via EGR-1 in the adrenal medulla, but apparently not in the heart. Regulation of the PNMT gene expression in various compartments of heart includes both corticosterone-dependent and independent mechanisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aguilera, G., Wynn, P. C., Harwood, J. P., Hauger, R. L., Millan, M. A., Grewe, C., and Catt, K. J. (1986). Receptor-mediated actions of corticotropin-releasing factor in pituitary gland and nervous system. Neuroendocrinology 43:79–88.
Andreassi, J. L., Eggleston, W. B., and Stewart, J. K. (1998). Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase mRNA in rat spleen and thymus. Neurosci. Lett. 241:75–78.
Axelrod, J. (1957). O-methylation of catechol amines in vitro and in vivo. Science 126:400–401.
Axelrod, J. (1962). Purification and properties of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 237:1657–1660.
Axelrod, J., and Tomchick, R. (1958). Enzymatic O-methylation of norepinephrine and other catechols. J.Biol. Chem. 233:702–705.
Betito, K., Mitchell, J. B., Bhatnagar, S., Boksa, P., and Meaney, M. J. (1994). Regulation of the adrenomedullary catecholaminergic system after mild, acute stress. Am. J. Physiol. 267:R212–R220.
Bohn, M. C., and Engele, J. (1992). Development of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) in cultures of dissociated embryonic rat medulla oblongata. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 10:481–489.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254.
Bruhn, T. O., Engeland, W. C., Anthony, E. L., Gann, D. S., and Jackson, I. M. (1987). Corticotropin-releasing factor in the dog adrenal medulla is secreted in response to hemorrhage. Endocrinology 120:25–33.
Cizza, G., Pacak, K., Kvetnansky, R., Palkovits, M., Goldstein, D. S., Brady, L. S., Fukuhara, K., Bergamini, E., Kopin, I. J., and Blackman, M. R. (1995). Decreased stress responsivity of central and peripheral catecholaminergic systems in aged 344/N Fischer rats. J. Clin. Invest. 95:1217–1224.
Ebert, S. N., Baden, J. M., Mathers, L. H., Siddall, B. J., and Wong, D. L. (1996). Expression of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in the embryonic rat heart. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 28:1653–1658.
Ebert, S. N., Balt, S. L., Hunter, J. P., Gashler, A., Sukhatme, V., and Wong, D. L. (1994). Egr-1 activation of rat adrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 269:20885–20898.
Ebert, S. N., Ficklin, M. B., Her, S., Siddall, B. J., Bell, R. A., Ganguly, K., Morita, K., and Wong, D. L. (1998). Glucocorticoid-dependent action of neural crest factor AP-2: Stimulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene expression. J. Neurochem. 70:2286–2295.
Ebert, S. N., and Wong, D. L. (1995). Differential activation of the rat phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene by Sp1 and Egr-1. J.Biol.Chem. 270:17299–17305.
Elayan, H. H., Kennedy, B. P., and Ziegler, M. G. (1990). Cardiac atria and ventricles contain different inducible adrenaline synthesizing enzymes. Cardiovasc. Res. 24:53–56.
Etches, R. J. (1976). A radioimmunoassay for corticosterone and its application to the measurement of stress in poultry. Steroids 28:763–773.
Goncalvesova, E., Micutkova, L., Mravec, B., Ksinantova, L., Krizanova, O., Fabian, J., and Kvetnansky, R. (2004). Changes in gene expression of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in the transplanted human heart. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1018:430–436.
Gupta, M. P., Gupta, M., Zak, R., and Sukhatme, V. P. (1991). Egr-1, a serum-inducible zinc finger protein, regulates transcription of the rat cardiac alpha-myosin heavy chain gene. J. Biol. Chem. 266:12813–6.
Her, S., Bell, R. A., Bloom, A. K., Siddall, B. J., and Wong, D. L. (1999). Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene expression. Sp1 and MAZ potential for tissue-specific expression. J. Biol. 274:8698–8707.
Huang, M. H., Bahl, J. J., Wu, Y., Hu, F., Larson, D. F., Roeske, W. R., and Ewy, G. A. (2005). Neuroendocrine properties of intrinsic cardiac adrenergic cells in fetal rat heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288:H497–H503.
Huang, M. H., Friend, D. S., Sunday, M. E., Singh, K., Haley, K., Austen, K. F., Kelly, R. A., and Smith, T. W. (1996). An intrinsic adrenergic system in mammalian heart. J. Clin. Invest. 98:1298–1303.
Iwaki, K., Sukhatme, V. P., Shubeita, H. E., and Chien, K. R. (1990). Alpha- and beta-adrenergic stimulation induces distinct patterns of immediate early gene expression in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Fos/jun expression is associated with sarcomere assembly; Egr-1 induction is primarily an alpha 1-mediated response. J. Biol. Chem. 265:13809–17.
Jelokova, J., Rusnak, M., Kubovcakova, L., Buckendahl, P., Krizanova, O., Sabban, E. L., and Kvetnansky, R. (2002). Stress increases gene expression of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in spleen of rats via pituitary-adrenocortical mechanism. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27:619–633.
Jeong, K. H., Jacobson, L., Pacak, K., Widmaier, E. P., Goldstein, D. S., and Majzoub, J. A. (2000). Impaired basal and restraint-induced epinephrine secretion in corticotropin-releasing hormone-deficient mice. Endocrinology 3:1142–1150.
Jiang, W., Uht, R., and Bohn, M. C. (1989). Regulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) mRNA in the rat adrenal medulla by corticosterone. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 7:513–520.
Kennedy, B., Bigby, T. D., and Ziegler, M. G. (1995). Nonadrenal epinephrine-forming enzymes in humans. Characteristics, distribution, regulation, and relationship to epinephrine levels. J. Clin. Invest. 95:2896–2902.
Kennedy, B., Elayan, H., and Ziegler, M. G. (1990). Lung epinephrine synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. 258:L227–L231.
Kennedy, B., and Ziegler, M. G. (2000). Ontogeny of epinephrine metabolic pathways in the rat: Role of glucocorticoids. Int.J. Dev. Neurosci. 18:53–59.
Krizanova, O., Micutkova, L., Jelokova, J., Filipenko, M., Sabban, E., and Kvetnansky, R. (2001). Existence of cardiac PNMT mRNA in adult rats: Elevation by stress in a glucocorticoid-dependent manner. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 281:H1372–H1379.
Kubovcakova, L., Tybitanclova, K., Sabban, E. L., Majzoub, J., Zorad, S., Vietor, I., Wagner, E. F., Krizanova, O., and Kvetnansky, R. (2004). Catecholamine synthesizing enzymes and their modulation by immobilization stress in knockout mice. Ann.N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1018:458–65.
Kvetnansky, R. (2004). Stressor specificity and effect of prior experience on catecholamine biosynthetic enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1032:117–29.
Kvetnansky, R., Fukuhara, K., Pacak, K., Cizza, G., Goldstein, D. S., and Kopin, I. J. (1993). Endogenous glucocorticoids restrain catecholamine synthesis and release at rest and during immobilization stress in rats. Endocrinology 133:1411–1419.
Kvetnansky, R., McCarty, R., and Axelrod, J. (1992). Stress: Neuroendocrine and Molecular Approaches. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York.
Kvetnansky, R., Micutkova, L., Kubovcakova, L., Sabban, E. L., Palkovits, M., and Krizanova, O. (2004a). Localization and regulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene expression in the heart of rats and mice during stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1018:405–417.
Kvetnansky, R., Micutkova, L., Rychkova, N., Kubovcakova, L., Mravec, B., Filipenko, M., Sabban, E. L., and Krizanova, O. (2004b). Quantitative evaluation of catecholamine enzymes gene expression in adrenal medulla and sympathetic ganglia of stressed rats. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1018:356–369.
Kvetnansky, R., and Mikulaj, L. (1970). Adrenal and urinary catecholamines in rats during adaptation to repeated immobilization stress. Endocrinology 87:738–743.
Kvetnansky, R., Pacak, K., Fukuhara, K., Viskupic, E., Hiremagalur, B., Nankova, B., Goldstein, D. S., Sabban, E. L., and Kopin, I. J. (1995). Sympathoadrenal system in stress. Interaction with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 771:131–158.
Kvetnansky, R., and Sabban, E. L. (1993). Stress-induced changes in tyrosine hydroxylase and other catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes, Tyrosine Hydroxylase, VSP, Utrecht, The Netherlands.
Kvetnansky, R., Sun, C. L., Lake, C. R., Thoa, N., Torda, T., and Kopin, I. J. (1978). Effect of handling and forced immobilization on rat plasma levels of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Endocrinology 103:1868–1874.
Kvetnansky, R., Weise, V. K., Thoa, N. B., and Kopin, I. J. (1979). Effect of chronic guanethidine treatment and adrenal medullectomy on plasma levels of catecholamines and corticosterone in forcibly immobilized rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 209:287–291.
Micutkova, L., Rychkova, N., Sabban, E. L., Krizanova, O., and Kvetnansky, R. (2003). Quantitation of changes in gene expression of norepinephrine biosynthetic enzymes in rat stellate ganglia induced by stress. Neurochem. Int. 43:235–242.
Muglia, L. J., Jacobson, L., Dikkes, P., and Majzoub, J. A. (1995). Corticotropin-releasing hormone deficiency reveals major fetal but not adult glucocorticoid need. Nature 373:427–432.
Muglia, L. J., Jacobson, L., and Luedke, C. (2000). Corticotropin-releasing hormone links pituitary adrenocorticotropin gene expression and release during adrenal insufficiency. J. Clin. Invest. 9:1269–1277.
Muglia, L. J., Jacobson, L., Weninger, S. C., Luedke, C. E., Bae, D. S., Jeong, K. H., and Majzoub, J. A. (1997). Impaired diurnal adrenal rhytmicity restored by constant infusion of corticotropin-releasing hormone in corticotropin-releasing hormone knockout mice. J. Clin. Invest. 99:2923–2929.
Muglia, L. J., Jacobson, L., Weninger, S. C., Karalis, K. P., Jeong, K., and Majzoub, J. A. (2001). The physiology of corticotropin-releasing hormone deficiency in mice. Peptides 22:725–731.
Newsome, H., Clements, A. S., and Borum, E. H. (1972). The simultaneous assay of cortisol, corticosterone, 11-deoxycortisol, and cortisone in human plasma. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 34:473–483.
Pacak, K., Kvetnansky, R., Palkovits, M., Fukuhara, K., Yadid, G., Kopin, I. J., and Goldstein, D. S. (1993). Adrenalectomy augments in vivo release of norepinephrine in the paraventricular nucleus during immobilization stress. Endocrinology 133:1404–1410.
Pendleton, R. G., Gessner, G., and Sawer, J. (1978). Studies on the distribution of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase and epinephrine in the rat. Res.Comun.Chem.Pathol.Pharmacol. 21:315–325.
Peuler, J. D., and Johnson, G. A. (1977). Simultaneous single isotope radioenzymatic assay of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. Life Sci. 21:625–636.
Saadane, N., Alpert, L., and Chalifour, L. E. (1999). TAFII250, Egr-1, and D-type cyclin expression in mice and neonatal rat cardiomyocytes treated with doxorubicin. Am. J. Physiol. 276:H803–H814.
Saavedra, J. M. (1979). Brain catecholamines during development of DOCA-salt hypertension in rats. Brain Res. 179:121–127.
Sabban, E. L., and Kvetnansky, R. (2001). Stress-triggered activation of gene expression in catecholaminergic systems: Dynamics of transcriptional events. Trends Neurosci. 24:91–98.
Shamim, A., Pelzer, T., Grohe, C., and Neyses, L. (1999). Induction of Egr-1 mRNA and protein by endothelin 1, angiotensin II and norepinephrine in neonatal cardiac myocytes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 195:11–17.
Suh, Y. H., Chun, Y. S., Lee, I. S., Kim, S. S., Choi, W., Chong, Y. H., Hong, L., Kim, S. H., Park, C. W., and Kim, C. G. (1994). Complete nucleotide sequence and tissue-specific expression of the rat phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene. J. Neurochem. 63:1603–1608.
Tai, T. C., Claycomb, R., Her, S., Bloom, A. K., and Wong, D. L. (2002). Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the rat phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene. Mol. Pharmacol. 61:1385–1392.
Udelsman, R., Harwood, J. P., Millan, M. A., Chrousos, G. P., Goldstein, D. S., Zimlichman, R., Catt, K. J., and Aguilera, G. (1986). Functional corticotropin releasing factor receptors in the primate peripheral sympathetic nervous system. Nature 319:147–150.
Usdin, E., Kvetnansky, R., and Axelrod, J. (1984). Stress: The Role of Catecholamines and Other Neurotransmitters. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York.
Van Loon, G. R., Kvetnansky, R., McCarty, R., and Axelrod, J. (1989). Stress: Neurochemical and Humoral Mechanisms. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York.
Venihaki, M., Gravanis, A., and Margioris, A. N. (1997). Comparative study between normal rat chromaffin and PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells: Production and effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone. Endocrinology 138:698–704.
Venihaki, M., and Majzoub, J. (2002). Lessons from CRH knockout mice. Neuropeptides 36:96–102.
Viskupic, E., Kvetnansky, R., Sabban, E. L., Fukuhara, K., Weise, V. K., Kopin, I. J., and Schwartz, J. P. (1994). Increase in rat adrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase mRNA level caused by immobilization stress depends on intact pituitary-adrenocortical axis. J. Neurochem. 63:808–814.
Vrezas, I., Willenberg, H. S., Mansmann, G., Hiroi, N., Fritzen, R., and Bornstein, S. R. (2003). Ectopic adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) and corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) production in the adrenal gland: Basic and clinical aspects. Microsc. Res. Tech. 61:308–314.
Wang, B., Fang, Q., Williams, W. V., and Weiner, D. B. (1992). Double-stranded DNA sequencing by linear amplification with Taq DNA polymerase. Biotechniques 13:527–530.
Warthan, M. D., Freeman, J. G., Loesser, K. E., Lewis, C. W., Hong, M., Conway, C. M., and Stewart, J. K. (2002). Phenyletanolamine N-methyltransferase expression in mouse thymus and spleen. Brain Behav. Immun. 16:493–499.
Weinshilboum, R. M., Kvetnansky, R., Axelrod, J., and Kopin, I. J. (1971). Elevation of serum dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity with forced immobilization. Nat. New Biol. 230:287–288.
Wong, D. L., Ebert, S. N., and Morita, K. (1998a). Neural control of phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase via cholinergic activation of Egr-I. Adv. Pharmacol. 42:77–81.
Wong, D. L., Siddall, B. J., Ebert, S. N., Bell, R. A., and Her, S. (1998b). Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene expression: Synergistic activation by Egr-1, AP-2 and the glucocorticoid receptor. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 61:154–161.
Wong, D. L., Siddall, B., and Wang, W. (1995). Hormonal control of rat adrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. Enzyme activity, the final critical pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology 13:223–234.
Wong, D. L., Tai, T. C., Wong-Faull, D. C., Claycomb, R., and Kvetnansky, R. (2004). Genetic mechanisms for adrenergic control during stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1018:387–397.
Wurtman, R. J. (2002). Stress and the adrenocortical control of epinephrine synthesis. Metabolism 51:11–14.
Yoshida-Hiroi, M., Bradbury, M. J., Eisenhofer, G., Hiroi, N., Vale, W. W., Novotny, G. E., Hartwig, H. G., Scherbaum, W. A., and Bornstein, S. R. (2002). Chromaffin cell function and structure is impaired in corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1-null mice. Mol. Psychiatry 7:967–974.
Ziegler, M. G., Bao, X., Kennedy, B. P., Joyner, A., and Enns, R. (2002). Location, development, control, and function of extraadrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 971:76–82.
Ziegler, M. G., Bao, X., Mahata, S., Kennedy, B. P., and Joiner, A. (2003). Genomic control of cardiac adrenaline synthesizing enzymes. Endocr. Regul. 37:134.
Ziegler, M. G., Kennedy, B. P., and Houts, F. W. (1998). Extra-adrenal nonneuronal epinephrine and phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase, Advances in Pharmacology, San Diego, CA.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by SP/028 08 00/028 08 02, Slovak Grant Agency VEGA grant No. 2/5125, APVT 51-027-404, Slovak-American Scientific-Technical Grant 002/2004, and NIH grant NS44218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kvetnansky, R., Kubovcakova, L., Tillinger, A. et al. Gene Expression of Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase in Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Knockout Mice During Stress Exposure. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 733–752 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9063-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9063-7