Summary
-
1.
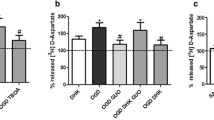
The effect of guanosine on L-[3H] glutamate uptake was investigated in brain cortical slices within physio-pathological range of glutamate(1–1000 μ M). In these conditions, glutamate uptake was significantly enhanced in slices treated with 100 μ M guanosine only at 100 and 300 μ M glutamate (44 and 52%, respectively).
-
2.
Evaluation of kinetic parameters showed that guanosine affected significantly only uptake Vmax (23%).
-
3.
The guanosine withdrawal did not abolish its significant effect on glutamate uptake when 100 or 300 μ M glutamate were used (an increase of 66 and 35%, respectively).
-
4.
These results support the hypothesis of a protective role for guanosine during excitotoxic conditions when glutamate levels are enhanced (e.g. brain ischemia and seizures), possibly by activating glutamate uptake. Moreover, our results may contribute to understand the antiexcitotoxic mechanism of guanosine on glutamate transport, giving new information concerning its mechanism of action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C. M., and Swanson, R. A. (2000). Astrocyte glutamate transport: Review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 32(1):1–14.
Asai, S., Zhao, H., Yamashita, A., Jike, T., Kunimatsu, T., Nagata, T., Kohno, T., and Ishikawa, K. (1999). Nicergoline enhances glutamate re-uptake and protects against brain damage in rat global brain ischemia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 383:267–274.
Brundege, J. M., and Dunwiddie, T. V. (1997). Role of adenosine as a modulator of synaptic activity in the central nervous system. Adv. Pharmacol. 39:353–391.
Ciccarelli, R., Di Iorio, P., Giuliani, P., D’Alimonte, I., Ballerini, P., Caciagli, F., and Rathbone, M. P. (1999). Rat cultured astrocytes release guanine-based purines in basal conditions and after hypoxia/hypoglycemia. Glia 25:93–98.
Danbolt, N. C. (2001). Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 65:1–105.
Dobolyi, Á., Reichart, A., Szikra, T., Nyitrai, G., Kékesi, K. A., and JuhÁsz, G. (2000). Sustained depolarization induces changes in the extracellular concentrations of purine and pyrimidine nucleosides in the rat thalamus. Neurochem. Int. 37:71–79.
Duan, S. M., Anderson, C. M., Stein, B. A., and Swanson, R. A. (1999). Glutamate induces rapid upregulation of astrocyte glutamate transport and cell-surface expression of GLAST. J. Neurosci. 19:10193–10200.
Frizzo, M. E., Lara, D. R., Dahm, K. C. S., Prokopiuk, A. S., Swanson, R. A., and Souza, D. O. (2001). Activation of glutamate uptake by guanosine in primary astrocyte cultures. NeuroReport 12:879– 881.
Frizzo, M. E., Lara, D. R., Prokopiuk, A. S., Vargas, C. R., Salbego, C. G., Wajner, M., and Souza, D. O. (2002). Guanosine enhances glutamate uptake in brain cortical slices at normal and excitotoxic conditions. Cell. Mol. Neurob. 22:353–363.
Frizzo, M. E., Soares, F. A., Dall’Onder, L. P., Lara, D. R., Swanson, R. A., and Souza, D. O. (2003). Extracellular conversion of guanine-based purines to guanosine specifically enhances astrocyte glutamate uptake. Brain Res. 972:84–89.
Gegelashvili, G., Civenni, G., Racagni, G., Danbolt, N. C., Schousboe, I., and Schousboe, A. (1996). Glutamate receptor agonists up-regulate glutamate transporter GLAST in astrocytes. NeuroReport 8:261–265.
Greene, J. G., and Greenamyre, J. T. (1996). Bioenergetics and glutamate excitotoxicity. Prog. Neurobiol. 48:613–634.
Izquierdo, I., Medina, J. H., Vianna, M. R., Izquierdo, L. A., and Barros, D. M. (1999). Separate mechanisms for short- and long-term memory. Behav. Brain Res. 103: 1–11.
Lara, D. R., Schmidt, A. P., Frizzo, M. E., Burgos, J. S., Ramírez, G., and Souza, D. O. (2001). Effect of orally administered guanosine on seizures and death induced by glutamatergic agents. Brain Res. 912:176–180.
Lee, J. M., Zipfel, G. J., and Choi, D. W. (1999). The changing landscape of ischaemic brain injury mechanisms. Nature 399:A7–A14.
Maragakis, N. J., and Rothstein, J. D. (2004). Glutamate transporters: Animal models to neurologic disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 15:461–473.
Meldrum, B. S., Akbar, M. T., and Chapman, A. G. (1999). Glutamate receptors and transporters in genetic and acquired models of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 36:189–204.
Meldrum, B. S. (2000). Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: Review of physiology and pathology. J. Nutr. 130:1007S–1015S.
Munir, M., Correale, D. M., and Robinson, M. B. (2000). Substrate-induced up-regulation of Na+-dependent glutamate transport activity. Neurochem. Int. 37:147–162.
Nishizawa, Y. (2001). Glutamate release and neuronal damage in ischemia. Life Sci. 69:369–381.
Ozawa, S., Kamiya, H., and Tsuzuki, K. (1998). Glutamate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 54:581–618.
Oliveira, D. L., Horn, J. F., Rodrigues, J. M., Frizzo, M. E., Moriguchi, E., Souza, D. O., and Wofchuk, S. (2004). Quinolinic acid promotes seizures and decreases glutamate uptake in young rats: Reversal by orally administered guanosine. Brain Res. 1018:48–54.
Peterson, G. L.(1997). A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal. Biochem. 83:346–356.
Phillis, J. W., and O’Regan, M. H. (2003). Characterization of modes of release of amino acids in the ischemic/reperfused rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem. Int. 43: 461–467.
Schmidt, A. P., Lara, D. R., Maraschin, J. F., Perla, A. S., and Souza, D. O. (2000). Guanosine and GMP prevent seizures induced by quinolinic acid in mice. Brain Res. 864:40–43.
Schmidt, A. P., Ávila, T. T., and Souza, D. O. (2005). Intracerebroventricular guanine-based purines protect against seizures induced by quinolinic acid in mice. Neurochem. Res. 30:69–73.
Segovia, G., Porras, A., Del Arco, A., and Mora, F. (2001). Glutamatergic neurotransmission in aging: A critical perspective. Mech. Ageing Dev. 122:1–29.
Shimada, F., Shiga, Y., Morikawa, M., Kawazura, H., Morikawa, O., Matsuoka, T., Nishizaki, T., and Saito, N. (1999). The neuroprotective agent MS-153 stimulates glutamate uptake. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 386:263–270.
Soares, F. A., Schmidt, A. P., Farina, M., Frizzo, M. E., Tavares, R. G., Portela, L. V., Lara, D. R., and Souza, D. O. (2004). Anticonvulsant effect of GMP depends on its conversion to guanosine. Brain Res. 1005:182–186.
Uemura, Y., Miller, J. M., Matson, W. R., and Beal, M. F. (1991). Neurochemical analysis of focal ischemia in rats. Stroke 22:1548–1553.
Vinadé, E. R., Schmidt, A. P., Frizzo, M. E., Izquierdo, I., Elisabetsky, E., and Souza, D. O. (2003). Chronically administered guanosine is anticonvulsant, amnesic and anxiolytic in mice. Brain Res. 977:97–102.
Vinadé, E. R., Schmidt, A. P., Frizzo, M. E., Portela, L. V., Soares, F. A., Schwalm, F. D., Elisabetsky, E., Izquierdo, I., and Souza, D. O. (2005). Effects of chronic administered guanosine on behavioral parameters and brain glutamate uptake in rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 79:248–253.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frizzo, M.E., Schwalm, F.D., Frizzo, J.K. et al. Guanosine Enhances Glutamate Transport Capacity in Brain Cortical Slices. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25, 913–921 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-005-4939-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-005-4939-5