Abstract
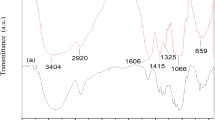
Separators are regarded as an essential component of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to their critical roles in the electrochemical performance and safety of these batteries. The purpose of this study was to examine the structural and electrochemical properties of a new separator based on zwitterionic cellulose (Cell). The free radical polymerization method was used to graft 4-vinyl pyridinium propane sulfonate (4-VPPS) onto the hydroxyl groups of Cell, and the polymer solution in trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) solvent was prepared to form a thin membrane using an automatic film applicator. The results showed that the modified Cell (MCell) separator had significantly higher tensile strength and elastic modulus, as well as superior thermal and dimensional stability, when compared to control separators (polypropylene (PP) at transverse direction and unmodified Cell). The improved separator material effectively reduced the growth of lithium dendrites, which cause short circuits and battery failure. Furthermore, the zwitterionic Cell separator demonstrated improved cycling stability and rate capability. Overall, this study suggests that using MCell separators with 4-VPPS is a promising alternative for improving LIB performance. The findings help to advance battery technology by increasing safety, efficiency, and overall battery life.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anirudhan T, Rauf TA, Rejeena S (2012) Removal and recovery of phosphate ions from aqueous solutions by amine functionalized epichlorohydrin-grafted cellulose. Desalination 285:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.10.014
Badini Pourazar M, Mohammadi T, Jafari Nasr MR, Bakhtiari O, Javanbakht M (2020) Preparation and characterization of poly (vinylidene fluoride)-13X zeolite mixed matrix membranes for lithium ion batteries’ separator with enhanced performance. J Appl Polym Sci 137:49367. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49367
Balbuena PB, Wang YX (2004) Lithium-ion batteries: solid-electrolyte interphase. World Scientific, Carolina, USA. https://doi.org/10.1142/p291
Chen W, Shi L, Wang Z, Zhu J, Yang H, Mao X, Chi M, Sun L, Yuan S (2016) Porous cellulose diacetate-SiO2 composite coating on polyethylene separator for high-performance lithium-ion battery. Carbohydr Polym 147:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.046
Choi ES, Lee SY (2011) Particle size-dependent, tunable porous structure of a SiO 2/poly (vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene)-coated poly (ethylene terephthalate) nonwoven composite separator for a lithium-ion battery. J Mater Chem 21:14747–14754. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM12246K
Costa C, Kundu M, Cardoso VF, Machado AV, Silva MM, Lanceros-Méndez S (2018) Silica/poly (vinylidene fluoride) porous composite membranes for lithium-ion battery separators. J Membr Sci 564:842–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.07.092
Croce F, Focarete ML, Hassoun J, Meschini I, Scrosati B (2011) A safe, high-rate and high-energy polymer lithium-ion battery based on gelled membranes prepared by electrospinning. Energy Environ Sci 4:921–927. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0EE00348D
Deimede V, Elmasides C (2015) Separators for lithium-ion batteries: a review on the production processes and recent developments. Energy Technol 3:453–468. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201402215
Evans J, Vincent CA, Bruce PG (1987) Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 28:2324–2328. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(87)90394-6
Ghasemi S, Harandi ZA (2018) Thermo-responsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly (ionic liquid) of pyridinium sulfonate immobilized Pd nanoparticles in C-C coupling reactions. RSC Adv 8:14570–14578. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01303A
Hu J, Liu Y, Zhang M, Jinlin H, Peihong N (2020) A separator based on cross-linked nano-SiO2 and cellulose acetate for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 334:135585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.201R9.135585
Huang X (2011) Separator technologies for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 15:649–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1264-9
Huang H, Chen K, Li C, Zhou Z, Wang W, Deng B, Liu S, Qian C, Yue M, Chi Z, Xu J, Zhang Y (2024) Zwitterion grafted polyimide separator for improving lithium-ion transport and its application in LiCoO2 batteries. Chem Eng J 481:148577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.148577
Li M, Wang X, Yang Y, Chang Z, Wu YP, Holze R (2015) A dense cellulose-based membrane as a renewable host for gel polymer electrolyte of lithium ion batteries. J Membr Sci 476:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.10.056
Liao H, Hong H, Zhang H, Li Z (2016a) Preparation of hydrophilic polyethylene/methylcellulose blend microporous membranes for separator of lithium-ion batteries. J Membr Sci 498:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.09.064
Liao H, Zhang H, Hong H, Li Z, Qin G, Zhu H, Lin Y (2016b) Novel cellulose aerogel coated on polypropylene separators as gel polymer electrolyte with high ionic conductivity for lithium-ion batteries. J Membr Sci 514:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.05.009
Liu K, Liu Y, Lin D, Pei A, Cui Y (2018) Materials for lithium-ion battery safety. Sci Adv 4:eaas9820. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aas9820
Lizundia E, Costa CM, Alves R, Lanceros-Méndez S (2020) Cellulose and its derivatives for lithium ion battery separators: A review on the processing methods and properties. Carbohydr Polym Technol Appl 1:100001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2020.100001
Lv D, Chai J, Wang P, Zhu L, Liu C, Nie S, Li B, Cui G (2021) Pure cellulose lithium-ion battery separator with tunable pore size and improved working stability by cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr Polym 251:116975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116975
Maier J (2013) Thermodynamics of electrochemical lithium storage. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:4998–5026. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201205569
Mao X, Shi L, Zhang H, Wang Z, Zhu J, Qiu Z, Zhao Y, Zhang M, Yuan S (2017) Polyethylene separator activated by hybrid coating improving Li+ ion transference number and ionic conductivity for Li-metal battery. J Power Sources 342:816–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.01.006
Masudy-Panah S, Katal R, Khiavi ND, Shekarian E, Hu J, Gong X (2019) A high-performance cupric oxide photocatalyst with palladium light trapping nanostructures and a hole transporting layer for photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution. J Mater Chem A 7:22332–22345. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA06771J
Mirzaeian M, Abbas Q, Ogwu A, Hall P, Goldin M, Mirzaeian M, Fathinejad Jirandehi H (2017) Electrode and electrolyte materials for electrochemical capacitors. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:25565–25587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.241
Phiri I, Bon CY, Mwemezi M, Hamenu L, Madzvamuse L, Park JH, Lee KS, Ko JM, Lu Y (2020) Enhanced electrolyte performance by adopting Zwitterionic lithium-silica sulfobetaine silane as electrolyte additive for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Chem Phys 243:122577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122577
Rahman MM, Mateti S, Cai Q, Sultana I, Fan Y, Wang X, Hou C, Chen Y (2019) High temperature and high rate lithium-ion batteries with boron nitride nanotubes coated polypropylene separators. Energy Storage Mater 19:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2019.03.027
Sadat-Shojai M, Asadnia M, Zarei-fard N, Arvaneh A-R (2022) Electrospinning of liquefied banana stem residue in conjugation with hydroxyapatite nanocrystals: towards new scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Cellulose 29:4039–4056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04542-5
Shekarian E, Jafari Nasr MR, Mohammadi T, Bakhtiari O, Javanbakht M (2019) Enhanced wettability and electrolyte uptake of coated commercial polypropylene separators with inorganic nanopowders for application in lithium-ion battery. J Nanostructures 9:736–750. https://doi.org/10.22052/JNS.2019.04.015
Sheng J, Tong S, He Z, Yang R (2017) Recent developments of cellulose materials for lithium-ion battery separators. Cellulose 24:4103–4122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1421-8
Shi C, Dai J, Li C, Shen X, Peng L, Zhang P, Wu D, Sun D, Zhao J (2017) A modified ceramic-coating separator with high-temperature stability for lithium-ion battery. Polymers 9:159. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9050159
Song D, Xu C, Chen Y, He J, Zhao Y, Li P, Lin W, Fu F (2015) Enhanced thermal and electrochemical properties of PVDF-HFP/PMMA polymer electrolyte by TiO2 nanoparticles. Solid State Ion 282:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2015.09.017
Su Z, He Y, Liu S, Li J, Xiao X, Nan J, Zuo X (2022) Uniform Lithium Deposition Achieved by SnO2/Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose Composite Separator toward Ultrastable Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS Appl Energy Mater 5:10264–10275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.2c01972
Sun X, Xu W, Zhang X, Lei T, Lee SY, Wu Q (2021) ZIF-67@ Cellulose nanofiber hybrid membrane with controlled porosity for use as Li-ion battery separator. J Energy Chem 52:170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2020.04.057
Wang S, Zhang D, Shao Z, Liu S (2019) Cellulosic materials-enhanced sandwich structure-like separator via electrospinning towards safer lithium-ion battery. Carbohydr Polym 214:328–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.049
Wu Y, Wen Z, Li J (2011) Hierarchical carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanoplate microspheres with high electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries. Adv Mater 23:1126–1129. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201003713
Wu D, Shi C, Huang S, Qiu X, Wang H, Zhan Z, Zhang P, Zhao J, Sun D, Lin L (2015) Electrospun nanofibers for sandwiched polyimide/poly (vinylidene fluoride)/polyimide separators with the thermal shutdown function. Electrochim Acta 176:727–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.07.072
Xiao W, Zhao L, Gong Y, Wang S, Liua J, Yana C (2015) Preparation of high performance lithium-ion batteries with a separator–cathode assembly. Rsc Adv 5:34184–34190. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA03769G
Yu L, Miao J, Jin Y, Lin JY (2017) A comparative study on polypropylene separators coated with different inorganic materials for lithium-ion batteries. Front Chem Sci Eng 11:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-017-1648-9
Zahn R, Lagadec MF, Hess M, Wood V (2016) Improving ionic conductivity and lithium-ion transference number in lithium-ion battery separators. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:32637–32642. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12085
Zhang SS (2007) A review on the separators of liquid electrolyte Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 164:351–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.10.065
Zhang J, Sun B, Huang X, Chen S, Wang G (2014) Honeycomb-like porous gel polymer electrolyte membrane for lithium ion batteries with enhanced safety. Sci Rep 4:6007. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06007
Zhang Z, Yuan W, Li L (2018) Enhanced wettability and thermal stability of nano-SiO2/poly (vinyl alcohol)-coated polypropylene composite separators for lithium-ion batteries. Particuology 37:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2017.10.001
Zolin L, Destro M, Chaussy D, Penazzi N, Gerbaldid C, Beneventiab D (2015) Aqueous processing of paper separators by filtration dewatering: towards Li-ion paper batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:14894–14901. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA03716F
Zuo X, Wu J, Ma X, Deng X, Cai J, Chen Q, Liu J, Nan J (2018) A poly (vinylidene fluoride)/ethyl cellulose and amino-functionalized nano-SiO2 composite coated separator for 5 V high-voltage lithium-ion batteries with enhanced performance. J Power Sources 407:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.10.056
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge funding from Shiraz University (No. 99GCB1M256440).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Asadnia: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Data Curation. M. Sadat-Shojai: Conceptualization, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. M. Moslehi: Writing—Review & Editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition. F. Hamidi: Software, Validation, Data Curation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
This study was conducted following Compliance with Ethical Standards, and it did not involve human participants, animals, and potential conflicts of interest.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Asadnia, M., Sadat-Shojai, M., Moslehi, M. et al. Zwitterionic cellulosic membrane as a new separator with enhanced ionic conductivity and performance for lithium-ion batteries. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05903-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05903-y