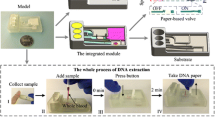
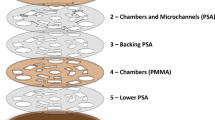
Abstract
Rapid nucleic acid testing (NAT) technology as an effective tool for point-of-care testing (POCT), has been widely used for health, food additive, and environmental pollution monitoring. Nucleic acid extraction (NAE) is a vital first step of NAT technology, including sample lysis, washing and elution. At present, storage of sample lysis solution for rapid NAE methods is expensive, complex and environmentally unfriendly. To address these drawbacks, a low-cost, rapid, simple, and portable material is urgently needed. Herein, we developed a pH-responsive carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate/polyethylene glycol (CMCS/SA/PEG) composite hydrogel that works as a physical crosslink, then used it to store sample lysis solutions for the dry immersion method for NAE. Results showed that the CMCS/SA/PEG6000 composite hydrogel had large pore size (256.58 ± 5.58 μm), good wet strength (282.3 Kpa), excellent swelling rate (706.91 ± 6.69%), high loading capacity (90.46 ± 1.13%), good degradation capacity (77.87 ± 1.45%), and rapid response time (15 s). The CMCS/SA/PEG6000 composite hydrogel could be loaded into a syringe and combined with filter paper to function as a simple NAE device. Efficiency of lysis of nucleic acid of saliva, whole blood, E.coli and S.aureus was 20.71 ± 0.12%, 9.59 ± 0.12%, 16.57 ± 0.19%, and 29.16 ± 0.07%, respectively. Also, nucleic acid was successfully extracted from a 30 μL sample of saliva so the method has potential to be integrated into other platforms for NAT.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezerra CS, Portilh MM, Frota CC, Villar LM (2021) Comparison of four extraction methods for the detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in dried blood spot samples. Microbiologyopen 10:e1161. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.1161
Bhattacharyy A, Mukherje D, Mishra R, Kundu PP (2016) Development of pH sensitive polyurethane–alginate nanoparticles for safe and efficient oral insulin delivery in animal models. RSC Adv 6:41835–41846. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra06749b
Burke G, Cao Z, Devine DM, Major IJP (2019) Preparation of biodegradable polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate hydrogels via thiol-ene chemistry. Polymers 11:1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081339
Chen P, Chen C, Liu Y, Du W, Feng X, Liu BF (2019) Fully integrated nucleic acid pretreatment, amplification, and detection on a paper chip for identifying EGFR mutations in lung cancer cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 283:472–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.060
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (2006) The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction: twenty-something years on. Nat Protoc 1:581–585. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.83
Damian F, Blaton N, Naesens L, Balzarini J, Kinget R, Augustijns P, Mooter G (2000) Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of the antiviral agent UC. Eur J Pharm Sci 10(4):311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-0987(00)00084-1
Darvishi R, Moghadas H, Moshkriz A (2022) Oxidized gum arabic cross-linked pectin/O-carboxymethyl chitosan: an antibiotic adsorbent hydrogel. Korean J Chem Eng 39:1350–1360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-1038-3
Duan J, Huang Y, Zong S, Jiang JJP (2020) Preparation and drug release properties of a thermo sensitive GA hydrogel. Polymers 13:119. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010119
Duscher G, Peschke R, Wille-Piazzai W, Joachim A (2009) Parasites on paper–The use of FTA Elute((R)) for the detection of Dirofilaria repens microfilariae in canine blood. Vet Parasitol 161:349–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.01.007
Fattahpour S, Shamanian M, Tavakoli N, Fathi M, Sadeghi-Aliabadi H, Sheykhi SR, Fesharaki M, Fattahpour S (2020) An injectable carboxymethyl chitosan-methylcellulose-pluronic hydrogel for the encapsulation of meloxicam loaded nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 151:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.002
French AD, Cintro´n MS (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the segal crystallinity index. Cellulose 20:583–588.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
Gan W, Gu Y, Han J, Cx Li, Sun J, Liu PJA (2017a) Chitosan-modified filter paper for nucleic acid extraction and “in situ PCR” on a thermoplastic microchip. Anal Chem 89:3568–3575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04882
Gan W, Gu Y, Han J, Li CX, Sun J, Liu P (2017b) Chitosan-modified filter paper for nucleic acid extraction and “in situ PCR” on a thermoplastic microchip. Anal Chem 89:3568–3575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04882
Ghauri ZH, Islam A, Qadir MA, Ghaffar A, Gull N, Azam M, Mehmood A, Ghauri AA, Khan RUJMC, Physics (2022) Novel pH-responsive chitosan/sodium alginate/PEG based hydrogels for release of sodium ceftriaxone. Mater Chem Phys 277:125456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125456
Ghauri ZH, Islam A, Qadir MA, Gull N, Haider B, Khan RU, Riaz TJS (2021) Development and evaluation of pH-sensitive biodegradable ternary blended hydrogel films (Chitosan/Guar gum/PVP) for drug delivery application. Sci Rep 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00452-x
Gonzalez-Urias A, Licea-Claverie A, Sañudo-Barajas JA, González-Ayón MS (2022) NVCL-based hydrogels and composites for biomedical applications: progress in the last ten years. Int J Mol Sci 23:4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094722
Huang S, An Y, Xi B, Gong X, Chen Z, Shao S, Ge S, Zhang J, Zhang D, Xia N (2023) Ultra-fast, sensitive and low-cost real-time PCR system for nucleic acid detection. Lab Chip 23:2611–2622. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3lc00174a
Jing H, Du X, Mo L, Wang H (2021) Self-coacervation of carboxymethyl chitosan as a pH-responsive encapsulation and delivery strategy. Int J Biol Macromol 192:1169–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.072
Jing H, Huang X, Du X, Mo L, Ma C, Wang HJCP (2022) Facile synthesis of pH-responsive sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads promoted by hydrogen bond. Carbohyd Polym 278:118993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118993
Kang J, Park C, Lee J, Namkung J, Hwang SY, Kim YSJBJ (2017) Automated nucleic acids purification from fecal samples on a microfluidic cartridge. BioChip J 11:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-016-1205-5
Karthikeyan K, Saranya R, Bharath R, Vidya R, Itami T, Sudhakaran R (2020) A simple filter paper-based method for transporting and storing Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei DNA from infected Litopenaeus vannamei tissues. J Invertebr Pathol 169:10. https://doi.org/10.16/j.jip.2019.107305
Kellner MJ, Koob JG, Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, Zhang F (2019) SHERLOCK: nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat Protoc 14:2986–3012. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0210-2
Li J, Weber E, Guth-Gundel S, Schuleit M, Kuttler A, Halleux C, Accart N, Doelemeyer A, Basler A, Tigani B, Wuersch K, Fornaro M, Kneissel M, Stafford A, Freedman BR, Mooney DJ (2018) Tough composite hydrogels with high loading and local release of biological drugs. Adv Healthc Mater 7:e1701393. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201701393
Li L, Shen G, Wu M, Jiang J, Xia Q, Lin P (2022) CRISPR-Cas-mediated diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol 40:1326–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.04.006
Li M, Yin F, Song L, Mao X, Li F, Fan C, Zuo X, Xia Q (2021) Nucleic acid tests for clinical translation. Chem Rev 121:10469–10558. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00241
Li Y, Qin Y, Liu S, Xing R, Yu H, Li K, Li P (2016) Preparation, characterization, and insecticidal activity of avermectin-grafted-carboxymethyl chitosan. Biomed Res Int 2016:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9805675
Ma T, Zhai X, Huang Y, Zhang M, Li P, Du Y (2022) Cerium ions crosslinked sodium alginate-carboxymethyl chitosan spheres with antibacterial activity for wound healing. J Rare Earths 40:1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2021.10.007
Mandal G, Das S, Padmanabhan S (2018) Development of a membrane-based method for isolation of genomic DNA from human blood. J Biomol Tech 29:46–53. https://doi.org/10.7171/jbt.18-2902-001
Molaee N, Abtahi H, Ghannadzadeh MJ, Karimi M, Ghaznavi-Rad E (2015) Application of Reverse Transcriptase –PCR (RT-PCR) for rapid detection of viable in drinking water samples. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0177-z
Oliveira M, Coaglio T, kalapothakis E, Luis R, Jorge C (2017) Comparison of five methods of extraction of Staphylococcus aureus DNA for molecular detection by PCR. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 51:528–532. https://doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0352-2017
Patel R, Kuwar U, Dhote N, Alexander NK (2023) Natural polymers as a carrier for the effective delivery of antineoplastic drugs. Curr Drug Deliv. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201820666230112170035
Paul R, Ostermann E, Wei Q (2020) Advances in point-of-care nucleic acid extraction technologies for rapid diagnosis of human and plant diseases. Biosens Bioelectron 169:112592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112592
Pearlman SI, Leelawong M, Richardson KA, Adams AM, Russ PK, Pask ME, Wolfe AE, Wessely C, Haselton FR (2023) Low-resource nucleic acid extraction method enabled by high-gradient magnetic separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:12457–12467. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21564
Petralia S, Sciuto EL, Conoci S (2017) A novel miniaturized biofilter based on silicon micropillars for nucleic acid extraction. Analyst 142:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6an02049f
Rahmani S, Olad A, Rahmani Z (2022) Preparation of self-healable nanocomposite hydrogel based on Gum Arabic/gelatin and graphene oxide: study of drug delivery behavior. Polym Bull 80:4117–4138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04247-6
Song M, Li L, Zhang Y, Chen K, Wang H, Gong R (2017) Carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin grafted chitosan nanoparticles as oral delivery carrier of protein drugs. React Funct Polym 117:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.05.008
Sun G, Zhang XZ, Chu CC (2008) Effect of the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the properties of chitosan-PEG-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:2865–2872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3410-9
Tang R, Li M, Yan X, Xie M, Liu LN, Li Z, Xu F (2022) Comparison of paper-based nucleic acid extraction materials for point-of-care testing applications. Cellulose (Lond) 29:2479–2495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04444-6
Tang R, Yan X, Li M, Du A, Yang H, Yin H, Xie M (2023) A wash-free, elution-free and low protein adsorption paper-based material for nucleic acid extraction. Anal Methods 15:3240–3250. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ay00695f
Tang R, Yang H, Gong Y, You M, Liu Z, Choi JR, Wen T, Qu Z, Mei Q, Xu F (2017) A fully disposable and integrated paper-based device for nucleic acid extraction, amplification and detection. Lab Chip 17:1270–1279. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6lc01586g
Tian B, Liu J (2023) Smart stimuli-responsive chitosan hydrogel for drug delivery: A review. Int J Biol Macromol 123902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123902
Trachsel L, Romio M, Zenobi M, Benetti EM (2021) Hydrogels generated from cyclic Poly(2-Oxazoline)s display unique swelling and mechanical properties. Macromol Rapid Commun 42:e2000658. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202000658
Wang H, Wu Y, Wu P, Chen S, Guo X, Meng G, Peng B, Wu J, Liu Z (2017) Environmentally benign chitosan as reductant and supporter for synthesis of Ag/AgCl/chitosan composites by one-step and their photocatalytic degradation performance under visible-light irradiation. Front Mater Sci 11:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-017-0383-y
Wu L, Li L, Pan L, Wang H, Bin Y (2021) MWCNTsreinforced conductive, self-healing polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized sodium alginate hydrogel as the strain sensor. J Appl Polym Sci 138:5a6. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49800
Xiangbin L, Qu G, Yu Q, Zhang N, Wang L, Wang J (2020) Synthesis of Poly(ethylene glycol) grafted polyamidoamine dendrimer hydrogels and their temperature and pH sensitive properties. Polym Sci Ser B 62:400–410. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1560090420040089
Xie CX, Tian TC, Yu ST, Li LS (2019) pH-sensitive hydrogel based on carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate and its application for drug delivery. J Appl Polym Sci 136:46911. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46911
Xu W, Koydemir HCJL (2022) Non-invasive biomedical sensors for early detection and monitoring of bacterial biofilm growth at the point of care. Lab Chip 22:4758–4773. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2lc00776b
Yang M, Bt L, Gao G, Xl L, Fq L (2010) Poly(maleic anhydride-co-acrylic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels with pH- and ionic-strength-responses. Chin J Polym Sci 28:951–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-010-9191-x
Yang Y, Liu Y, Chen S, Cheong KL, Teng B (2020) Carboxymethyl beta-cyclodextrin grafted carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel-based microparticles for oral insulin delivery. Carbohydr Polym 246:116617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116617
Yu C, Dai S, Li S, Li J, Hu H, Meng J, Wei C, Wu JJJM (2022) Nucleic acid detection with ion concentration polarization microfluidic chip for reduced cycle numbers of polymerase chain reaction. Micromachines 13:1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091394
Zainal SH, Mohd NH, Suhaili N, Anuar FH, Lazim AM, Othaman RR (2021) Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: a review. J Market Res 10:935–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.12.012
Zhang H, Gu Z, Li W, Guo L, Wang L, Guo L, Ma S, Han B, Chang J (2022a) pH-sensitive O-carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate nanohydrogel for enhanced oral delivery of insulin. Int J Biol Macromol 223:433–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.274
Zhang W, Chen S, Jiang W, Zhang Q, Liu N, Wang Z, Li Z, Zhang D (2023) Double-network hydrogels for biomaterials: Structure-property relationships and drug delivery. Eur Polym J 111807. 185:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111807
Zhang Z, Wang J, Xia W, Cao D, Wang X, Kuang Y, Luo Y, Yuan C, Lu J, Liu XJ (2022b) Application of hydrogels as carrier in tumor therapy: a review. Chemistry–Asian J 17:e202200740. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202200740
Zhang Z, Wang R, Yuan M, Huang X, Ding C, Wu H, Wang S, Liu A (2022c) Magnetically driven pH-responsive composite hydrogel for controlled drug delivery. Funct Mater Lett 15:2250022. 15:https://doi.org/10.1142/s1793604722500229
Funding
This work was supported by the key research and development Plan of Shaanxi Province (2023-YBSF-154), the Natural Science Research Foundation of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology (2017BJ-35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, writing–revision, review & editing, supervision, funding acquisition are performed by Ruihua Tang. Validation methodology, formal analysis, investigation, Data curation, writing – original draft were performed by Xueyan Yan and John P. Giesy. Writing, review & edition was performed by Jie Hu, Yuwei Xie, Huancai Yin, Yining Luo and John P. Giesy.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to submit the manuscript to Cellulose.
Ethical approval
This article involved human saliva sample has been approved by the patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, R., Yan, X., Hu, J. et al. Carboxymethyl chitosan/alginate/polyethylene glycol composite hydrogel for nucleic acid lysis solution storage at the point of care. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05889-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05889-7