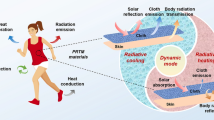
Abstract
Herein, we report a cooling fabric with thermal conduction and radiative cooling capabilities through grafting hydroxylated boron nitride (BN-OH) nanosheets onto the surface of cotton fibers. The thermal conduction layer formed by BN-OH nanosheets enables the modified fabric with excellent thermal conductivity, which is 42% higher than that of the original cotton fabric. Resulting in the modified fabric exhibits great cooling power and increases the cooling setpoint temperature by 1 °C, which corresponds to reduced 11.2% indoor cooling energy consumption. Additionally, the Mid-infrared emissivity and solar reflectivity are increased to 90% and 70.4%, respectively, suggesting that wearing modified fabric under direct sunlight can enable the artificial skin to avoid overheating by 7.8 °C compared to bare skin. Moreover, the modified fabric also presents a considerable contact cool feeling, impressive wearability, and durability. We expect this work to present new insights for the design of personal thermal management textiles.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Adegun MH et al (2023) Anisotropic thermally superinsulating boron nitride composite aerogel for building thermal management. Compos A 169:107522
Brown DJA, Brugger H, Boyd J, Paal P (2012) Accidental hypothermia. New Engl J Med 367:1930–1938
Cai C, Wei Z, Huang Y, Wang P, Song J, Deng L, Fu Y (2020) Bioinspired structure-robust cellulose nanocrystal films with enhanced water resistance, photothermal conversion ability, and fluorescence. Cellulose 27:10241–10257
Cao C et al (2023) Pressureless consolidation of boron nitride fiber ceramics via a chemical bonding approach. J Eur Ceram Soc 43:5223–5230
Cassabois G, Valvin P, Gil B (2016) Hexagonal boron nitride is an indirect bandgap semiconductor. Nat Photonics 10:262–266
Charkoudian N (2016) Human thermoregulation from the autonomic perspective. Auton Neurosci 196:1–2
Chen F, Tian Q, Wang T, Ma L, Liu R, Wang S (2023) Fabrication of a multifunctional antibacterial cotton-based fabric for personal cooling. Appl Surf Sci 609:155291
Fan C, Zhang Y, Long Z, Mensah A, Wang Q, Lv P, Wei Q (2023) Dynamically tunable subambient daytime radiative cooling metafabric with Janus wettability. Adv Funct Mater 33:2300794
Ferraris S et al (2014) Chemical, mechanical and antibacterial properties of silver nanocluster/silica composite coated textiles for safety systems and aerospace applications. Appl Surf Sci 317:131–139
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Gamage S et al (2021) Reflective and transparent cellulose-based passive radiative coolers. Cellulose 28:9383–9393
Gao T et al (2017) Three-dimensional printed thermal regulation textiles. ACS Nano 11:11513–11520
Harris DC et al (2017) Refractive index of infraredtransparent polycrystalline alumina. Opt Eng 56:077103
He H et al (2023) Biomass based active-cum-passive aerogel heater with enhanced thermal insulation property derived from hollow cellulose kapok fiber for personal thermal management. Cellulose 30:7031–7045
Hoyt T, Lee KH, Zhang H, Arens E, TomWebster (2009) Energy savings from extended air temperature setpoints and reductions in room air mixing. Paper presented at the International Conference on Environmental Ergonomics, Boston, August 2–7
Hsu PC et al (2015) Personal thermal management by metallic nanowire-coated textile. Nano Lett 15:365–371
Hsu PC et al (2016) Radiative human body cooling by nanoporous polyethylene textile. Science 353:1019–1023
Lee YS, Kshetri T, Kim NH, Park O-K, Lee JH (2023) Boron nitride nanosheet reinforced polyethylene nanocomposite film for high-performance hot-melt adhesive type thermal interfacial material. Polymer 275:125934
Li Q, Zhang G, Liu F, Han K, Gadinski MR, Xiong C, Wang Q (2015) Solution-processed ferroelectric terpolymer nanocomposites with high breakdown strength and energy density utilizing boron nitride nanosheets. Energy Environ Sci 8:922–931
Luo M, Arens E, Zhang H, Ghahramani A, Wang Z (2018) Thermal comfort evaluated for combinations of energy-efficient personal heating and cooling devices. Build Environ 143:206–216
Malitson IH (1965) Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica. J Opt Soc Am A 55:1205–1209
Mangat A, Hes L, Bajzik V (2017) Effect of biopolishing on warm–cool feeling of knitted fabric: a subjective and an objective evaluations. Autex Res J 17:95–102
Owais M, Shiverskii A, Sulimov A, Ostrizhiniy D, Popov Y, Mahato B, Abaimov SG (2022) Scalable fabrication of thermally conductive layered nacre-like self-assembled 3D BN-based PVA aerogel framework nanocomposites. Polymers 14:3316
Pakdel A, Bando Y, Golberg D (2014) Nano boron nitride flatland. Chem Soc Rev 43:934–959
Qi Q, Wang Y, Wang W, Yu D (2021) Surface self-assembled multi-layer MWCNTs-COOH/BN-PDA/CF for flexible and efficient solar steam generator. J Cleaner Prod 279:123626
Rah Y, Jin Y, Kim S, Yu K (2019) Optical analysis of the refractive index and birefringence of hexagonal boron nitride from the visible to near-infrared. Opt Lett 44:3797–3800
Sainsbury T, Satti A, May P, Wang Z, McGovern I, Gun’ko YK, Coleman J (2012) Oxygen radical functionalization of boron nitride nanosheets. J Am Chem Soc 134:18758–18771
Santamouris M, Feng J (2018) Recent progress in daytime radiative cooling: Is it the air conditioner of the future? Buildings 8:168
Schneider AM, Holcombe BV (1991) Properties influencing coolness to the touch of fabrics. Text Res J 61:488–495
Shen H, Guo J, Wang H, Zhao N, Xu J (2015) Bioinspired modification of h-BN for high thermal conductive composite films with aligned structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:5701–5708
Shen L, Jiang J, Liu J, Fu F, Diao H, Liu X (2022) Cotton fabrics with antibacterial and antiviral properties produced by a simple pad-dry-cure process using diphenolic acid. Appl Surf Sci 600:154152
Sim M-J, Cha S-H, Lee J-C (2022) Controllable surface functionalization of boron nitride by heat treatment. Appl Surf Sci 600:154073
Smalyukh II (2021) Thermal management by engineering the alignment of nanocellulose. Adv Mater 33:e2001228
Speakman JB, Chamberlain NH (1930) 3—The thermal conductivity of textile materials and fabrics. J Text Inst Trans 21:T29–T56
Tang L, Lyu B, Gao D, Jia Z, Ma J (2023) A wearable textile with superb thermal functionalities and durability towards personal thermal management. Chem Eng J 465:142829
Viscusi G, Lamberti E, D’Amico F, Tammaro L, Vigliotta G, Gorrasi G (2023) Design and characterization of polyurethane based electrospun systems modified with transition metals oxides for protective clothing applications. Appl Surf Sci 617:156563
Vriens J, Nilius B, Voets T (2014) Peripheral thermosensation in mammals. Nat Rev Neurosci 15:573–589
Wang X, Ji S-L, Wang X-Q, Bian H-Y, Lin L-R, Dai H-Q, Xiao H (2019) Thermally conductive, super flexible and flame-retardant BN-OH/PVA composite film reinforced by lignin nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 7:14159–14169
Wang P, Zhang M, Qu J, Wang L, Geng J, Fu F, Liu X (2022) Antibacterial cotton fabric prepared by a “grafting to” strategy using a QAC copolymer. Cellulose 29:3569–3581
Wang L, Chen M, Cai R, Jiang J, Xiang S, Liu X, Diao H (2023) Surface engineered long-lasting antibacterial Janus cotton fabrics with excellent moisture/thermal management properties. Chem Eng J 475:146386
Xiao Y et al (2022a) Durably antibacterial cotton fabric prepared by a combination of betaine and carboxymethyl chitosan. Fibers Polym 3:617–625
Xiao Y et al (2022b) Remarkable durability of the antibacterial function achieved via a coordination effect of Cu(II) ion and chitosan grafted on cotton fibers. Cellulose 29:1003–1015
Yu Q et al (2019) Enhanced thermal conductivity of flexible cotton fabrics coated with reactive MWCNT nanofluid for potential application in thermal conductivity coatings and fire warning. Cellulose 26:7523–7535
Yu X, Li Y, Wang X, Si Y, Yu J, Ding B (2020) Thermoconductive, moisture-permeable, and superhydrophobic nanofibrous membranes with interpenetrated boron nitride network for personal cooling fabrics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:32078–32089
Zhang X et al (2021) Personal thermal management by thermally conductive composites: a review. Compos Commun 23:100595
Zhang F, Xu K, Bai Y, Wang P (2023) Multifunctional cellulose paper-based materials. Cellulose 30:8539–8569
Zhao G, Zhang F, Wu Y, Hao X, Wang Z, Xu X (2016) One-step exfoliation and hydroxylation of boron nitride nanosheets with enhanced optical limiting performance. Adv Opt Mater 4:141–146
Zhao J, Zhou J, Li H, Xiao A (2022) Directional fabricating of flexible and compressible cellulose nanofibril composite cryogel with excellent thermal insulation, flame-retardancy and radiative cooling for efficient thermal management. Cellulose 29:9671–9691
Acknowledgments
All authors would like to thank shiyanjia lab (https://www.shiyanjia.com) for the support of XPS analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51873195, 51803186), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LZ22E030004), and Special Support Program for High-Level Talents of Zhejiang Province, Outstanding Talent Project (No. 2021R51003), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFA1301100, 2021YFA1301101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Y.X.: data curation, writing-original draft. S.X., S.Z. and F.F.: investigation and supervision. X.L.: writing-review and editing. all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and informed consent
Volunteers in the experiment gave written and informed consent before participation in the experiments. There was no damage to the human body during the experiment and no tissue samples were collected from the volunteers, hence approval from a national or institutional ethics board/committee was not obtained prior to the current study.
Consent for publication
All authors had read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Xiang, S., Zhao, S. et al. Boron nitride nanosheets enhanced the thermo-optical properties of cotton fabric for energy saving and personal heat management. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05887-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05887-9