Abstract
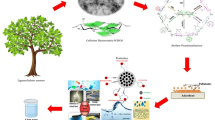
Heavy metal ions and dyes in wastewater pose a severe hazard to ecological system and human health. This study used sulfamic acid (SA) to modify cellulose for adsorbent material preparation. The results from the structural characterization indicated that cellulose was successfully modified by introducing sulfonic acid groups to obtain sulfamic acid modified cellulose (SAMC). Subsequently, SAMC was prepared into spheres via being dissolved in ionic liquid and obtaining in antisolvent. The adsorption performance of SAMC aerogel spheres was investigated using methylene blue (MB) and lead ions (Pb2+). The maximum absorption capacity of SAMC aerogel spheres to MB and Pb2+ achieved 14.53 mg/g and 112.15 mg/g, respectively. The adsorption process conformed to the pseudo-second-order (PSO) model and Langmuir model. The adsorption mainly involved chemical action via coordination interaction between -SO32− and MB/Pb2+. Thermodynamic experiments confirmed that the adsorption process in the experiment was a spontaneous endothermic process. Therefore, this study provided a simple adsorbent production method for wastewater treatment.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials need to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper.
References
Al-Mhyawi SR, Abdel-Tawab NA, El Nashar RM (2023) Synthesis and characterization of orange peel modified hydrogels as efficient adsorbents for Methylene Blue (MB). Polymers 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020277
Baghdadi M, Jafari A, Pardakhti A (2016) Removal of crystal violet from aqueous solutions using functionalized cellulose microfibers: a beneficial use of cellulosic healthcare waste. RSC Adv 6:61423–61433. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA08901A
Bagheri A, Hoseinzadeh H, Hayati B, Mahmoodi NM, Mehraeen E (2021) Post-synthetic functionalization of the metal-organic framework: clean synthesis, pollutant removal, and antibacterial activity. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104590
Basu M, Guha AK, Ray L (2017) Adsorption of lead on cucumber peel. J Cleaner Prod 151:603–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.028
Bolisetty S, Peydayesh M, Mezzenga R (2019) Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: review and analysis. Chem Soc Rev 48:463–487. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00493E
Chen K, He J, Li Y, Cai X, Zhang K, Liu T, Hu Y, Lin D, Kong L, Liu J (2017) Removal of cadmium and lead ions from water by sulfonated magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 494:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.082
Dai C, Mondal AN, Wu L, Wu Y, Xu T (2017) Crosslinked PVA-based hybrid membranes containing di-sulfonic acid groups for alkali recovery. Sep Purif Technol 184:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.04.032
French AD, Santiago Cintrón M (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 20:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
He Y, Dietrich AM, Jin Q, Lin T, Yu D, Huang H (2022) Cellulose adsorbent produced from the processing waste of brewer’s spent grain for efficient removal of Mn and Pb from contaminated water. Food Bioprod Process 135:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2022.08.005
Hokkanen S, Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2016) A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res 91:156–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.008
Hosseinabadi-Farahani Z, Hosseini-Monfared H, Mahmoodi NM (2015) Graphene oxide nanosheet: preparation and dye removal from binary system colored wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 56:2382–2394. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.960462
Hou QX, Liu W, Liu ZH, Bai LL (2007) Characteristics of wood cellulose fibers treated with periodate and bisulfite. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:7830–7837. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0704750
Jiang H, Wu S, Zhou J (2023) Preparation and modification of nanocellulose and its application to heavy metal adsorption: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 236:123916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123916
Li B, Zhang Q, Pan Y, Li Y, Huang Z, Li M, Xiao H (2020) Functionalized porous magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4 beads prepared from ionic liquid for removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 163:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.280
Liu M, Jia S, Gong Y, Song C, Guo X (2013) Effective hydrolysis of cellulose into glucose over sulfonated sugar-derived carbon in an ionic liquid. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:8167–8173. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400571e
Liu C, Omer AM, Ouyang X-k (2018) Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye using carboxymethyl cellulose/k-carrageenan/activated montmorillonite composite beads: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Int J Biol Macromol 106:823–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.084
Liu Y, Li F, Deng J, Wu Z, Lei T, Tan M, Wu Z, Qin X, Li H (2021) Mechanism of sulfamic acid modified biochar for highly efficient removal of tetracycline. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 158:105247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105247
Luo J, Semenikhin N, Chang H, Moon RJ, Kumar S (2018) Post-sulfonation of cellulose nanofibrils with a one-step reaction to improve dispersibility. Carbohydr Polym 181:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.077
Mahar FK, He L, Wei K, Mehdi M, Zhu M, Gu J, Zhang K, Khatri Z, Kim I (2019) Rapid adsorption of lead ions using porous carbon nanofibers. Chemosphere 225:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.131
Mahmoodi NM, Mokhtari-Shourijeh Z (2016a) Modified poly(vinyl alcohol)-triethylenetetramine nanofiber by glutaraldehyde: preparation and dye removal ability from wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 57:20076–20083. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1109562
Mahmoodi NM, Mokhtari-Shourijeh Z (2016b) Preparation of aminated nanoporous nanofiber by solvent casting/porogen leaching technique and dye adsorption modeling. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 65:378–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.05.042
Mahmoodi NM, Hosseinabadi-Farahani Z, Chamani H (2017) Dye adsorption from single and binary systems using NiO-MnO2 nanocomposite and artificial neural network modeling. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 36:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12452
Mahmoodi N M, Karimi B, Mazarji M, Moghtaderi H (2018) Cadmium selenide quantum dot-zinc oxide composite: Synthesis, characterization, dye removal ability with UV irradiation, and antibacterial activity as a safe and high-performance photocatalyst. J Photochem Photobiol B 188:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.08.023
Momina, Mohammad S, Isamil S (2020) Study of the adsorption/desorption of MB dye solution using bentonite adsorbent coating. J Water Process Eng 34:101155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101155
Moors SLC, Deraet X, Van Assche G, Geerlings P, De Proft F (2017) Aromatic sulfonation with sulfur trioxide: mechanism and kinetic model. Chem Sci 8:680–688. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC03500K
Oun AA, Kamal KH, Farroh K, Ali EF, Hassan MA (2021) Development of fast and high-efficiency sponge-gourd fibers (Luffa cylindrica)/hydroxyapatite composites for removal of lead and methylene blue. Arab J Chem 14:103281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103281
Pan Y, Shi X, Cai P, Guo T, Tong Z, Xiao H (2018) Dye removal from single and binary systems using gel-like bioadsorbent based on functional-modified cellulose. Cellulose 25:2559–2575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1711-9
Pereira PHF, Voorwald HJC, Cioffi MOH, Da Silva MLCP, Rego AMB, Ferraria AM, De Pinho MN (2014) Sugarcane bagasse cellulose fibres and their hydrous niobium phosphate composites: synthesis and characterization by XPS, XRD and SEM. Cellulose 21:641–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0113-2
Peydayesh M, Suter MK, Bolisetty S, Boulos S, Handschin S, Nyström L, Mezzenga R (2020) Amyloid fibrils aerogel for sustainable removal of organic contaminants from water. Adv Mater 32:1907932. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201907932
Qin L, Ishizaki T, Takeuchi N, Takahashi K, Kim KH, Li OL (2020) Green sulfonation of carbon catalysts via gas-liquid interfacial plasma for cellulose hydrolysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:5837–5846. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07156
Rabeie B, Mahmoodi NM (2023) Hierarchical ternary titanium dioxide decorated with graphene quantum dot/ZIF-8 nanocomposite for the photocatalytic degradation of doxycycline and dye using visible light. J Water Process Eng 54:103976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.103976
Rocha I, Hattori Y, Diniz M, Mihranyan A, Strømme M, Lindh J (2018) Spectroscopic and physicochemical characterization of sulfonated cladophora cellulose beads. Langmuir 34:11121–11125. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01704
Sabar S, Abdul Aziz H, Yusof NH, Subramaniam S, Foo KY, Wilson LD, Lee HK (2020) Preparation of sulfonated chitosan for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. React Funct Polym 151:104584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104584
Shahnaz T, Bedadeep D, Narayanasamy S (2022) Investigation of the adsorptive removal of methylene blue using modified nanocellulose. Int J Biol Macromol 200:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.081
Shen G, Pan L, Zhang R, Sun S, Hou F, Zhang X, Zou J-J (2020) Low-spin-state hematite with superior adsorption of anionic contaminations for water purification. Adv Mater 32:1905988. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201905988
Shen J, Jiang F, Wang N, Ouyang X k, Jin M-c (2022) Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid (DPTA)-modified Magnetic Cellulose Nanocrystals can Efficiently Remove Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution. J Polym Environ 30:1344-1354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02278-0
Shi C, Tao F, Cui Y (2018) Evaluation of nitriloacetic acid modified cellulose film on adsorption of methylene blue. Int J Biol Macromol 114:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.146
Suhas GVK, Carrott PJM, Singh R, Chaudhary M, Kushwaha S (2016) Cellulose: a review as natural, modified and activated carbon adsorbent. Bioresour Technol 216:1066–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.106
Sun F, Liu W, Dong Z, Deng Y (2017) Underwater superoleophobicity cellulose nanofibril aerogel through regioselective sulfonation for oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 330:774–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.142
Suopajärvi T, Liimatainen H, Karjalainen M, Upola H, Niinimäki J (2015) Lead adsorption with sulfonated wheat pulp nanocelluloses. J Water Process Eng 5:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.06.003
Thiangtham S, Runt J, Manuspiya H (2019) Sulfonation of dialdehyde cellulose extracted from sugarcane bagasse for synergistically enhanced water solubility. Carbohydr Polym 208:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.080
Tondro H, Zilouei H, Zargoosh K, Bazarganipour M (2020) Investigation of heterogeneous sulfonated graphene oxide to hydrolyze cellulose and produce dark fermentative biohydrogen using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol 306:123124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123124
Wu L, Sun J, Wu M (2017) Modified cellulose membrane prepared from corn stalk for adsorption of methyl blue. Cellulose 24:5625–5638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1523-3
Xu X, Ouyang X-k, Yang L-Y (2021) Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions using crosslinked carboxylated chitosan/carboxylated nanocellulose hydrogel beads. J Mol Liq 322:114523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114523
Zhang J, Jiang N, Dang Z, Elder TJ, Ragauskas AJ (2008) Oxidation and sulfonation of cellulosics. Cellulose 15:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9193-1
Zhu Y, Yu Z, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Ren X, Jiang F (2022) Developing flame-retardant lignocellulosic nanofibrils through reactive deep eutectic solvent treatment for thermal insulation. Chem Eng J 445:136748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136748
Funding
This work was supported by the Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (32271800), the Basic Research Integration Projects of Science, Education, and Industry of Qilu University of Technology (2022PY039), Jinan Innovation Team (2021GXRC023), the QUTJBZ Program (2022JBZ01-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.S.: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft preparation. H.J.: Methodology, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing- Reviewing and Editing. X.J.: Methodology, Formal analysis. Z.T.: Formal analysis, Reviewing and Editing. J.C.: Formal analysis, Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors listed agreed to the enclosed manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Ji, H., Ji, X. et al. Cellulose modification using sulfamic acid for adsorption of methylene blue and lead ions. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05880-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05880-2