Abstract
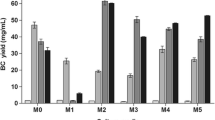
Extensive work on bacterial cellulose (BC) cultivation is crucial in optimizing BC performance and versatility in application. Herein, this study aims to investigate the lignin content in oil palm frond (OPF) juice medium that could affect the BC production by Acetobacter xylinum 0416 in static culture. The effects of lignin content were observed by the performances of BC production from the raw and pre-treated OPF juice medium fermentation with Hestrin-Schramm (HS) medium as a point of comparison. The TAPPI methods analysis outlined up to 3.719 g/L of total lignin content in raw OPF juice and FTIR analysis depicted the functional group of a typical lignin compound, thus confirming its presence as a component inhibitor. The raw OPF juice was further pre-treated using an alkaline precipitation method resulting in acid-insoluble lignin removal up to 75.47% of the total lignin content. The results revealed that the BC yield from the raw OPF juice fermentation was lower compared to the HS medium with dried BC content of 0.152 g/L and 2.52 g/L, respectively. The BC cultivation using the pre-treated OPF juice medium was improved as the BC yield significantly increased to 1.91 g/L. Therefore, a proper pre-treatment strategy on OPF juice medium for lignin content removal could improve the medium capability in BC cultivation for higher-scale production.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All of the material is owned by the authors and no permissions are required.
References
Abdullah SSS, Shirai Y, Bahrin EK, Hassan MA (2015) Fresh oil palm frond juice as a renewable, non-food, non-cellulosic and complete medium for direct bioethanol production. Ind Crops Prod 63:357–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.10.006
Ajao O, Jeaidi J, Benali M et al (2018) Quantification and variability analysis of lignin optical properties for colour-dependent industrial applications. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020377
Alzagameem A, Klein SE, Bergs M et al (2019) Antimicrobial activity of lignin and lignin-derived cellulose and chitosan composites against selected pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms. Polymers (basel) 11:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040670
Andriani D, Apriyana AY, Karina M (2020) The optimization of bacterial cellulose production and its applications: a review. Cellulose 27:6747–6766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03273-9
Arisht SN, Roslan R, Gie GA et al (2021) Effect of nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) on biohydrogen production in anaerobic fermentation of oil palm frond juice using Clostridium butyricum JKT37. Biomass Bioenergy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2021.106270
Che Maail CMH, Ariffin H, Hassan MA et al (2014) Oil palm frond juice as future fermentation substrate: a feasibility study. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/465270
Cheng Z, Yang R, Liu X et al (2017) Green synthesis of bacterial cellulose via acetic acid pre-hydrolysis liquor of agricultural corn stalk used as carbon source. Bioresour Technol 234:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.131
De S, Mishra S, Poonguzhali E et al (2020) Fractionation and characterization of lignin from waste rice straw: biomass surface chemical composition analysis. Int J Biol Macromol 145:795–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.068
El-Gendi H, Taha TH, Ray JB, Saleh AK (2022) Recent advances in bacterial cellulose: a low-cost effective production media, optimization strategies and applications. Springer, Netherlands
Esa F, Tasirin SM, Rahman NA (2014) Overview of bacterial cellulose production and application. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 2:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2014.11.017
Fagerstedt KV, Saranpää P, Tapanila T et al (2015) Determining the composition of lignins in different tissues of silver birch. Plants 4:183–195. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4020183
Ghazanfar M, Irfan M, Nadeem M et al (2022a) Bioethanol production optimization from KOH-pretreated bombax ceiba using saccharomyces cerevisiae through response surface methodology. Fermentation. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040148
Ghazanfar M, Nadeem M, Shakir HA et al (2022b) Valorization of bombax ceiba waste into bioethanol production through separate hydrolysis and fermentation and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Fermentation. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8080386
He X, Meng H, Song H et al (2020) Novel bacterial cellulose membrane biosynthesized by a new and highly efficient producer Komagataeibacter rhaeticus TJPU03. Carbohydr Res 493:108030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2020.108030
Ho Jin Y, Lee T, Kim JR et al (2019) Improved production of bacterial cellulose from waste glycerol through investigation of inhibitory effects of crude glycerol-derived compounds by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. J Ind Eng Chem 75:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.017
Hong F, Qiu K (2008) An alternative carbon source from konjac powder for enhancing production of bacterial cellulose in static cultures by a model strain Acetobacter aceti subsp. xylinus ATCC 23770. Carbohydr Polym 72:545–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.09.015
Khan H, Kadam A, Dutt D (2020) Studies on bacterial cellulose produced by a novel strain of Lactobacillus genus. Carbohydr Polym 229:115513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115513
Klemm D, Petzold-Welcke K, Kramer F et al (2021) Biotech nanocellulose: a review on progress in product design and today’s state of technical and medical applications. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117313
Leonarski E, Cesca K, Zanella E et al (2021) Production of kombucha-like beverage and bacterial cellulose by acerola byproduct as raw material. Lwt 135:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110075
Li J, Zhang J, Zhang S et al (2018) Alkali lignin depolymerization under eco-friendly and cost-effective NaOH/urea aqueous solution for fast curing bio-based phenolic resin. Ind Crops Prod 120:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.027
Lim HJ, Cheng WK, Tan KW, Yu LJ (2022) Oil palm-based nanocellulose for a sustainable future: where are we now? J Environ Chem Eng 10:107271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107271
Malaysian Palm Oil Board (2022) Palm Oil Area 2022
Manan S, Ullah MW, Ul-Islam M et al (2022) Bacterial cellulose: Molecular regulation of biosynthesis, supramolecular assembly, and tailored structural and functional properties. Prog Mater Sci 129:100972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100972
Mohamad S, Abdullah LC, Jamari SS et al (2022a) Production and characterization of bacterial cellulose nanofiber by acetobacter xylinum 0416 using only oil palm frond juice as fermentation medium. J Nat Fibers 19:16005–16016. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2022.2140243
Mohamad S, Abdullah LC, Jamari SS et al (2022b) Influence of drying method on the crystal structure and thermal property of oil palm frond juice-based bacterial cellulose. J Mater Sci 57:1462–1473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06685-5
Mohd Yusof SJH, Roslan AM, Ibrahim KN et al (2019) Life cycle assessment for bioethanol production from oil palm frond juice in an oil palm based biorefinery. Sustain. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU11246928
Montané D, Nabarlatz D, Martorell A et al (2006) Removal of lignin and associated impurities from xylo-oligosaccharides by activated carbon adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:2294–2302. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie051051d
Navya PV, Gayathri V, Samanta D, Sampath S (2022) Bacterial cellulose: a promising biopolymer with interesting properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol 220:435–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.08.056
Prasertsan P, Nutongkaew T, Leamdum C et al (2022) Direct biotransformation of oil palm frond juice to ethanol and acetic acid by simultaneous fermentation of co-cultures and the efficacy of its culture filtrate as an antifungal agent against black seed rot disease. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 12:5283–5292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01482-1
Said Azmi SNN, Mohd Fabli SNNF, Faisul Aris FA et al (2019) Fresh oil palm frond juice as a novel and alternative fermentation medium for bacterial cellulose production. Mater Today Proc 42:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.220
Said Azmi SNN, Asyiqin SZ, Mohd Asnawi ASF et al (2023) The production and characterization of bacterial cellulose pellicles obtained from oil palm frond juice and their conversion to nanofibrillated cellulose. Carbohydr Polym Technol Appl 5:100327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2023.100327
Santoso SP, Chou CC, Lin SP et al (2020) Enhanced production of bacterial cellulose by Komactobacter intermedius using statistical modeling. Cellulose 27:2497–2509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02961-5
Singhania RR, Patel AK, Tseng YS et al (2022) Developments in bioprocess for bacterial cellulose production. Bioresour Technol 344:126343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126343
Srimachai T, Nuithitikul K, O-Thong S, et al (2015) Optimization and kinetic modeling of ethanol production from oil palm frond juice in batch fermentation. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Supian NNI, Zakaria J, Amin KNM et al (2021) Effect of fermentation period on bacterial cellulose production from oil palm frond (OPF) juice. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 1092:012048. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1092/1/012048
Syed Abdullah SS, Bahrin EK, Shirai Y, Hassan MA (2021) Influence of storage conditions on oil palm frond juice as a renewable feedstock for bioethanol production. Biomass Bioenerg 150:106101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2021.106101
Tan JP, Jahim JM, Harun S et al (2016) Utilization of oil palm fronds as a sustainable carbon source in biorefineries. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:4896–4906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.08.034
Tan JP, Luthfi AAI, Manaf SFA et al (2018) Incorporation of CO2 during the production of succinic acid from sustainable oil palm frond juice. J CO2 Util 26:595–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2018.06.006
Zahari MAKM, Zakaria MR, Ariffin H et al (2012) Renewable sugars from oil palm frond juice as an alternative novel fermentation feedstock for value-added products. Bioresour Technol 110:566–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.119
Zahari MAKM, Ariffin H, Mokhtar MN et al (2015) Case study for a palm biomass biorefinery utilizing renewable non-food sugars from oil palm frond for the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) bioplastic. J Clean Prod 87:284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.010
Zani SHM, Asri FM, Azmi NS et al (2019) Optimization of process parameters for bioethanol production from oil palm frond juice by Saccharomyces cerevisiae using response surface methodology as a tool. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/702/1/012003
Acknowledgments
The research was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme No. FRGS/1/2018/TK05/UMP/03/3 (RDU190154). The authors would like to acknowledge Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) and Universiti Malaysia Pahang Al-Sultan Abdullah (UMPSA) for their technical support during the study period. Finally, our gratitude also goes to UMPSA and MOHE for the provision of study leave and scholarship for the first author.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Specifically, SM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Investigation & Formal analysis, LCA: Supervision, Review, Visualization & Data Validation, SSJ: Supervision, Review & Editing, and SFSM: Review, Editing & Funding Acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamad, S., Abdullah, L.C., Jamari, S.S. et al. Lignin content analysis in oil palm frond juice base medium: effect on bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum 0416. Cellulose 31, 1467–1479 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05698-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05698-4