Abstract
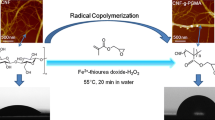
Nitrate glycerol ether cellulose (NGEC) is a potential cellulose substitute for the substrate of gun propellants in the future, but interfacial compatibility with high energy solid filler has remained an ongoing challenge. In this study, NGEC, modified with polydopamine (PDA), were prepared with various reaction time, to obtain composite energetic cellulose core-shell materials with improved hydrophilic and adiabatic safety by combining advantage of self-polymerization of dopamine (DA). The composition, distribution, and hydrophilicity of the molecular groups of the composite energetic cellulose were evaluated, as well as the thermodynamic behavior and safety properties in the adiabatic environment. Results demonstrated that the structure of NGEC remained unchanged when PDA formed dense nanofilm on the surface of NGEC, and the introduction of hydroxyl group in PDA significantly improved the hydrophilicity of NGEC by WCA analysis. Most notably, according to DSC and TGA data, after applying PDA coating, both the activation energy (Ea) and weight loss ratio (Wr) of high-energy cellulose showed a slight decrease. Specifically, the Ea of NGEC@PDA-6 h was very similar to that of NGEC and showed the lowest Wr. The PDA coating might also substantially increase the initial temperature and pressure of the adiabatic decomposition of the NGEC by the ARC results. In summary, without altering the intrinsic properties of the NGEC, PDA could increase the safety properties of the adiabatic environment, providing a method for hydrophilic modification of the energetic cellulose surfaces.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri ML, Weil T, Ng DYW, Ball V (2022) Polydopamine at biological interfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 305:102689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2022.102689
An C-W, Li F-S, Song X-L, Wang Y, Guo X-D (2009) Surface coating of RDX with a composite of TNT and an energetic-polymer and its safety investigation. propellants, explosives. Pyrotechnics 34:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1002/prep.200700286
Chen W, Chen L, Lu J, Geng D, Wu J, Zhao P (2020) Effects of temperature and wax binder on thermal conductivity of RDX: a molecular dynamics study. Comput Mater Sci 179:109698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2020.109698
Chen J, He S, Huang B, Wu P, Qiao Z, Wang J, Zhang L, Yang G, Huang H (2017) Enhanced thermal decomposition properties of CL-20 through space-confining in three-dimensional hierarchically ordered porous carbon. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:10684–10691. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b00287
Chen L, Li Q, Liu S, Bei Y, Ding Y, Liu J, He W (2021) Bio-inspired synthesis of energetic microcapsules core-shell structured with improved thermal stability and reduced sensitivity via in situ polymerization for application potential in propellants. Adv Mater Interfaces 8:2101248. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202101248
Chen L, Li Q, Wang X, Zhang J, Xu G, Cao X, Liu J, Nan F, He W (2022) Electrostatic spraying synthesis of energetic RDX@NGEC nanocomposites. Chem Eng J (Lausanne) 431:133718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133718
da Costa Mattos E, Moreira ED, Diniz MF, Dutra RC, da Silva G, Iha K, Teipel U (2008) Characterization of polymer-coated RDX and HMX particles. Propellants Explos Pyrotech 33:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/prep.200800207
Damse RS, Singh A (2009) Studies on the high-energy gun propellant formulations based on 1,5-diazido-3-nitrazapentane. J Hazard Mater 172:1699–1702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.149
Fallah F, Khorasani M, Ebrahimi M (2018) Factors affecting the properties of nitrocellulose emulsions: a comparative study. Carbohydr Polym 189:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.002
Flynn JH, Wall LA (1966) A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. J Polym Sci Part C Polym Lett 4:323–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1966.110040504
Friedman HL (2007) Kinetics of thermal degradation of char-forming plastics from thermogravimetry. Application to a phenolic plastic. J Polym Sci Part C Polym Symposia 6:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/polc.5070060121
Ghosh M, Venkatesan V, Sikder A, Sikder N (2012) Preparation and characterisation of ε-CL-20 by solvent evaporation and precipitation methods. Def Sci J 62:390–398. https://doi.org/10.14429/dsj.62.1428
Gong F, Zhang J, Ding L, Yang Z, Liu X (2017) Mussel-inspired coating of energetic crystals: a compact core–shell structure with highly enhanced thermal stability. Chem Eng J (Lausanne) 309:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.020
Guo S, Wang Q, Sun J, Liao X, Wang ZS (2009) Study on the influence of moisture content on thermal stability of propellant. J Hazard Mater 168:536–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.073
Kissinger HE (1957) Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem 29:1702–1706
Kwon IS, Tang G, Chiang PJ, Bettinger CJ (2018) Texture-dependent adhesion in polydopamine nanomembranes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:7681–7687. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b15608
Lee HA, Ma Y, Zhou F, Hong S, Lee H (2019) Material-independent surface chemistry beyond polydopamine coating. Acc Chem Res 52:704–713. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00583
Li Q, Chen L, Huang J, Meng D, Nan F, He W (2023) Electrostatic spraying construction strategy and performance of NGEC-based core-shell nanoenergetic material. FirePhysChem 3:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpc.2022.08.004
Li J, Yin X, Liu Z, Gu Z, Niu J (2019) Reaction yield model of nitrocellulose alkaline hydrolysis. J Hazard Mater 371:603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.044
Lin C, Gong F, Yang Z, Zhao X, Li Y, Zeng C, Li J, Guo S (2019a) Core-shell structured HMX@Polydopamine energetic microspheres: synergistically enhanced mechanical, thermal, and safety performances. Polym (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030568
Lin C, Huang B, Gong F, Yang Z, Liu J, Zhang J, Zeng C, Li Y, Li J, Guo S (2019b) Core@Double-Shell structured energetic composites with reduced sensitivity and enhanced mechanical properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:30341–30351. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b10506
Lin C, Liu S, Qian W, Gong F, Zhao X, Pan L, Zhang J, Yang Z, Li J, Guo S (2020a) Controllable tuning of energetic crystals by bioinspired polydopamine. Energetic Mater Front 1:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmf.2020.09.002
Lin C, Wen Y, Huang X, Yang Z, Gong F, Zhao X, Hao S, Pan L, Ding L, Li J, Guo S (2020b) Tuning the mechanical performance efficiently of various LLM-105 based PBXs via bioinspired interfacial reinforcement of polydopamine modification. Compos Part B Eng 186:107824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107824
Ma X, Li Y, Hussain I, Shen R, Yang G, Zhang K (2020) Core-shell structured nanoenergetic materials: preparation and fundamental properties. Adv Mater 32:e2001291. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202001291
Quintana JR, ACiller J, Serna FJ (1992) Thermal behaviour of HMX/RDX mixtures. Propellants Explos Pyrotech 17:106–109. https://doi.org/10.1002/prep.19920170303
Ryu JH, Messersmith PB, Lee H (2018) Polydopamine surface chemistry: a decade of Discovery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:7523–7540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b19865
Sabri T, Karim BM, Djalal T, Samir B, Abderrahmane M, Amina FM (2021) Understanding the compatibility of nitrocellulose with polyester based polyurethane binder. J Energ Mater. https://doi.org/10.1080/07370652.2021.1942592
Shen J, Liu Z, Xu B, Liang H, Zhu Y, Liao X, Wang Z (2019) Influence of carbon nanofibers on thermal and mechanical properties of NC-TEGDN-RDX triple-base gun propellants. Propellants Explos Pyrotechn 44:355–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/prep.201800257
Sovizi MR, Hajimirsadeghi SS, Naderizadeh B (2009) Effect of particle size on thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. J Hazard Mater 168:1134–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.146
Takeo O (1965) A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 38:1881–1886. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.38.1881
Wang S, An C, Wang J, Ye B (2018) Reduce the sensitivity of CL-20 by improving thermal conductivity through carbon nanomaterials. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2496-3
Xu W, Wang J, Peng J, Liang X, Li H, Wang J (2019) Study on the influencing factors of ultrafine spherical RDX during spray drying with Low Speed. J Nanomate 2019:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7915129
Yang Z, Si J, Cui Z, Ye J, Wang X, Wang Q, Peng K, Chen W, Chen SC (2017) Biomimetic composite scaffolds based on surface modification of polydopamine on electrospun poly(lactic acid)/cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr Polym 174:750–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.07.010
Zhang J-y, Guo X-y, Jiao Q-j, Zhang H-l, Li H (2017) Effects of desensitizers on phase transitions, thermal behavior, and sensitivity of ε-CL-20. J Energ Mater 36:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/07370652.2017.1326188
Zhang S, Kou K, Zhang J, Jia Q, Xu Y (2019) Compact energetic crystals@ urea-formaldehyde resin micro-composites with evident insensitivity. Compos Commun 15:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2019.07.002
Zhang Y, Shao Z, Gao K, Li J, Wu X, Wang W, Wang F, Liu Y (2014a) Rheological characteristics of nitrate glycerol ether cellulose gel based on phase separation in ternary system. Cellulose 21:4135–4143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0355-7
Zhang Y, Shao Z, Gao K, Wu X, Liu Y (2014b) Tensile properties of nitrate glycerol ether cellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Integr Ferroelectr 154:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2014.904717
Zhang Y, Shao Z, Li J, Gao K, Liu Y (2015) Aerogel of nitrate glycerol ether cellulose based on phase separation in acetone/ethanol mixed solvents system. J Appl Polym Sci 132:n. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41405
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Dr. Weidong He and Dr. Ling Chen for technical suggestions on experiments and analyses of NGEC thermal properties. This work thanks to the supporting of Jiangsu Funding Program for Excellent Postdoctoral Talent, and Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023TQ0158) In addition, the authors thank Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the support of XPS and WCA test.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL and BW are co-first authors of the article. QL wrote the main manuscript text. BW and JH, LC and WH provided some test method. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors announce that there have no known competing economic interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this manuscript. All the authors listed have approved the enclosed manuscript and for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Wang, B., Huang, J. et al. Biomimetic modification strategy of nitrate glycerol ether cellulose with polydopamine and its thermal decomposition behavior. Cellulose 31, 217–233 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05656-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05656-0