Abstract
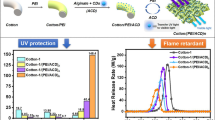
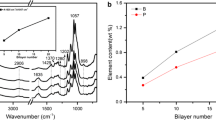
Boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots (BN-CDs) were synthesized using one-pot hydrothermal carbonization. The synthesized CDs were then combined with alginate and polyethyleneimine to create a multilayered coating on cotton fabric through layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly. The CD-containing coating emitted visible blue light under a 365 nm UV lamp. The UV protection, thermal stability, flame retardancy, and wash durability of the CD-treated cotton fabric were subsequently investigated. The ultraviolet protection factors of pure cotton fabric and cotton fabric treated with 12 bilayer CD-containing coating were 6.48 and 64.10, respectively. This indicated that the synthesized CD is an efficient UV absorber. In the TGA test, more char residue was observed at 700 °C for CD coated cotton fabrics under a nitrogen atmosphere. After B, N co-doped CDs were enriched in the PEI/alginate multilayered coating, the peak heat release rate (PHRR) of cotton-CDs-12BL was reduced by 15%, and the TPHRR of cotton-CDs-12BL was improved by 26.4 °C in the microscale combustion calorimeter test. These results indicate that B, N co-doped CDs which possess UV absorption and environmental friendliness, have potential application as a flame retardant on the surface of cotton fiber.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in the manuscript. Data can be available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Chen X, Fang F, Zhang X et al (2016) Flame-retardant, electrically conductive and antimicrobial multifunctional coating on cotton fabric via layer-by-layer assembly technique. Rsc Adv 6(33):27669–27676. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra26914h
Chen CC, Xu ZQ, Qiu JM et al (2022) Synthesis of carbon dots with carbogenic p-conjugated domains for full-band UV shielding. ACS Appl Nano Mater 5(7):9140–9149. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c01444
Chen, Wang Z, Liu R et al (2019) A facile preparation of flexible and porous reduced graphene oxide woven fabric/polydimethylsiloxane composites for EMI shielding. Mater Res Express 6(10):11. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab422a
Deb A, Konwar A, Chowdhury D (2020) pH-responsive hybrid jute carbon dot-cotton patch. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(19):7394–7402. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01221
Devadas B, Imae T (2018) Effect of carbon dots on conducting polymers for energy storage applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(1):127–134. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01858
Durairaj A, Maruthapandi M, Luong JHT et al (2022) Enhanced UV protection, heavy metal detection, and antibacterial properties of biomass-derived carbon dots coated on protective fabrics. ACS Appl Bio Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.2c00798
Hu TW, Zeng LF, Li YQ et al (2022) Multifunctional chitosan non-woven fabrics modified with terylene carbon dots for selective detection and efficient adsorption of cr(VI). Chem Eng J 432:134202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134202
Islam MDZ, Dong YB, Khoso NA et al (2019) Continuous dyeing of graphene on cotton fabric: binder-free approach for electromagnetic shielding. Appl Surf Sci 496:143636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143636
Isnaeni, Herbani Y, Suliyanti MM (2018) Concentration effect on optical properties of carbon dots at room temperature. J Lumines 198:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.02.012
Krysmann MJ, Kelarakis A, Dallas P et al (2012) Formation mechanism of carbogenic nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence emission. J Am Chem Soc 134(2):747–750. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204661r
Lan CT, Zou LH, Wang N et al (2021) Multi-reflection-enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding performance of conductive nanocomposite coatings on fabrics. J Colloid Interface Sci 590:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.01.074
Liu Q, Gao S, Zhao YL et al (2021) Review of layer-by-layer self-assembly technology for fire protection of flexible polyurethane foam. J Mater Sci 56(16):9605–9643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-05904-3
Liu SQ, Liu HL, Chen QQ et al (2022) Preparation of boronic acid-modified polymer dots under mild conditions and their applications in pH and glucose detection. Microchim Acta 189(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05137-w
Mintz KJ, Guerrero B, Leblanc RM (2018) Photoinduced electron transfer in carbon dots with long-wavelength photoluminescence. J Phys Chem C 122(51):29507–29515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b06868
Niu XQ, Liu GS, Li LY et al (2015) Green and economical synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots from vegetables for sensing and imaging applications. Rsc Adv 5(115):95223–95229. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra17439b
Pan Y, Fu L, Du J et al (2022) Layer-by-layer self-assembly coating for multi-functionalized fabrics: a scientometric analysis in citespace (2005–2021). Molecules 27(19):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196767
Pan Y, Liu LX, Zhao HT (2018) Recyclable flame retardant paper made from layer-by-layer assembly of zinc coordinated multi-layered coatings. Cellulose 25(9):5309–5321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1922-0
Park Y, Yoo J, Lim B et al (2016) Improving the functionality of carbon nanodots: doping and surface functionalization. J Mater Chem A 4(30):11582–11603. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta04813g
Qiu JM, Ye WH, Xu XK et al (2022) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbonized polymer dots with full-band absorption for skin protection. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10(36):11958–11968. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c03324
Rednic MI, Lu ZM, Wang P et al (2015) Fluorescent carbon ‘quantum’ dots from thermochemical functionalization of carbon nanoparticles. Chem Phys Lett 639:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2015.08.069
Rimal V, Shishodia S, Srivastava PK (2020) Novel synthesis of high-thermal stability carbon dots and nanocomposites from oleic acid as an organic substrate. Appl Nanosci 10(2):455–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01178-z
Shishodia S, Rimal V, Srivastava PK (2021) Synthesis of tunable high-thermal stability carbon dots via functionalization for applications in high-temperature environment. Appl Nanosci 11(5):1691–1706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01814-7
Shuai Q, Xu L, Sun S et al (2022) Boron-nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots, on cotton fabric for imparting anti-ultraviolet properties. Cell Chem Technol 56(5–6):657–665
Wu SS, Li W, Sun YQ et al (2020) Facile fabrication of a CD/PVA composite polymer to access light-responsive shape-memory effects. J Mater Chem C 8(26):8935–8941. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tc00910e
Xie Z, Du QQ, Wu YZ et al (2016) Full-band UV shielding and highly daylight luminescent silane-functionalized graphene quantum dot nanofluids and their arbitrary polymerized hybrid gel glasses. J Mater Chem C 4(41):9879–9886. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc02035f
Xu J, Niu YJ, Xie ZP et al (2023) Synergistic flame retardant effect of carbon nanohorns and ammonium polyphosphate as a novel flame retardant system for cotton fabrics. Chem Eng J 451:21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138566
Xue CH, Wu Y, Guo XJ et al (2020) Superhydrophobic, flame-retardant and conductive cotton fabrics via layer-by-layer assembly of carbon nanotubes for flexible sensing electronics. Cellulose 27(6):3455–3468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03013-z
Yang P, Zhu ZQ, Chen MZ et al (2018) Microwave-assisted synthesis of xylan-derived carbon quantum dots for tetracycline sensing. Opt Mater 85:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.06.034
Zhang T, Yan HQ, Fang ZP et al (2014) Superhydrophobic and conductive properties of carbon nanotubes/polybenzoxazine nanocomposites coated ramie fabric prepared by solution-immersion process. Appl Surf Sci 309:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.05.013
Zheng LZ, Su XJ, Lai XJ et al (2019) Conductive superhydrophobic cotton fabrics via layer-by-layer assembly of carbon nanotubes for oil-water separation and human motion detection. Mater Lett 253:230–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.06.078
Zhu C, Fu YJ, Liu CA et al (2017) Carbon dots as fillers inducing healing/self-healing and anticorrosion properties in polymers. Adv Mater 29(32):8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201701399
Zuo DY, Liang N, Xu J et al (2019) UV protection from cotton fabrics finished with boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots. Cellulose 26(6):4205–4212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02365-5
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (21878064, 41977017), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY21E030009) and Zhejiang Provincial Key Research and Development Program (2022C01174).
Funding
Natural Science Foundation of China: 41977017. Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province: LY21E030009. Zhejiang Provincial Key Research and Development Program: 2022C01174.
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animals rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Liang, Q., Du, J. et al. Influences of boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dot based coating fabricated via layer-by-layer self-assembly on the UV protection and flame retardancy of cotton fabric. Cellulose 30, 11249–11259 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05541-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05541-w