Abstract
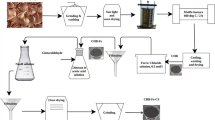
The wide application of polysaccharide-based aerogel is limited by its hydrophilicity. To solve this problem, silica nanoparticles and methyl trimethoxysilane were employed as hydrophobic modifiers to prepare the superhydrophobic sodium alginate/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (SA/CMC) aerogel in this study. Sodium alginate (SA) and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) were selected because of their degradability, renewability and low cost. After being modified by various routes, a three-dimensional aerogel with a density of 0.080 g/cm3, high porosity of 94% and great adsorption ability was achieved and applied for the adsorption of organic solvents which contain methylene blue and chloroform, etc. The results present that the superhydrophobic SA/CMC aerogel possesses excellent water stability, appropriate compressive strength and good adsorption capacity. Furthermore, the adsorption process is analyzed by adsorption kinetics. The remarkable adsorption performance proves that the superhydrophobic SA/CMC aerogel may have great potential of being used in the field of oil–water separation and textile dye wastewater treatment, etc.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The results/data/figures in this manuscript have not been published elsewhere, nor are they under consideration (from all authors) by another publisher.
References
Abhari N, Madadlou A, Dini A (2017) Structure of starch aerogel as affected by crosslinking and feasibility assessment of the aerogel for an anti-fungal volatile release. Food Chem 221:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.072
Alvarez-Lorenzo C, Blanco-Fernandez B, Puga AM, Concheiro A (2013) Crosslinked ionic polysaccharides for stimuli-sensitive drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 65:1148–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.04.016
Arriola NDA, Chater PI, Wilcox M, Lucini L, Rocchetti G, Dalmina M, Pearson JP, Amboni RDDC (2019) Encapsulation of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni aqueous crude extracts by ionic gelation—effects of alginate blends and gelling solutions on the polyphenolic profile. Food Chem 275:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.086
Autissier A, Le Visage C, Pouzet C, Chaubet F, Letourneur D (2010) Fabrication of porous polysaccharide-based scaffolds using a combined freeze-drying/cross-linking process. Acta Biomater 6:3640–3648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2010.03.004
Benbettaieb N, Gay JP, Karbowiak T, Debeaufort F (2016) Tuning the functional properties of polysaccharide-protein bio-based edible films by chemical, enzymatic, and physical cross-linking. Compr Rev Food Sci F 15:739–752. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12210
Cao LQ, Lu W, Mata A, Nishinari K, Fang YP (2020) Egg-box model-based gelation of alginate and pectin: a review. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116389
Cervin NT, Aulin C, Larsson PT, Wagberg L (2012) Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 19:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9629-5
Ene CD, Cucos P, Ianculescu A, Culita DC, Anghel EM, Cucos A, Atkinson I, Chifiriuc MC, Calderon-Moreno JM, Carp O (2022) Benign by design: porous spherical ZnO-alginate family via a dual-template synthesis. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.152231
Estella J, Echeverria JC, Laguna M, Garrido JJ (2007) Effects of aging and drying conditions on the structural and textural properties of silica gels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 102:274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.01.007
Feng JD, Nguyen ST, Fan Z, Duong HM (2015) Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem Eng J 270:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.034
Franco P, Cardea S, Tabernero A, De Marco I (2021) Porous aerogels and adsorption of pollutants from water and air: a review. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154440
Fu Y, Guo Z (2022) Natural polysaccharide-based aerogels and their applications in oil–water separations: a review. J Mater Chem A 10:8129–8158. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ta00708h
Gao C, Wang XL, An QD, Xiao ZY, Zhai SR (2021) Synergistic preparation of modified alginate aerogel with melamine/chitosan for efficiently selective adsorption of lead ions. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117564
Guan Y, Rao J, Wu YL, Gao H, Liu SQ, Chen GG, Peng F (2020) Hemicelluloses-based magnetic aerogel as an efficient adsorbent for congo red. Int J Biol Macromol 155:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.231
He W, Qiang H, Liang S, Guo FY, Wang R, Cao JZ, Guo ZH, Pang QY, Wei BR, Sun JW (2022) Hierarchically porous wood aerogel/polypyrrole (PPy) composite thick electrode for supercapacitor. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137331
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Jagadisha A, Rao KB, Nayak G, Kamath M (2021) Influence of nano-silica on the microstructural and mechanical properties of high-performance concrete of containing EAF aggregate and processed quarry dust. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124392
Jeong SI, Krebs MD, Bonino CA, Khan SA, Alsberg E (2010) Electrospun alginate nanofibers with controlled cell adhesion for tissue engineering. Macromol Biosci 10:934–943. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201000046
Jiao C, Xiong J, Tao J, Xu S, Zhang D, Lin H, Chen Y (2016) Sodium alginate/graphene oxide aerogel with enhanced strength-toughness and its heavy metal adsorption study. Int J Biol Macromol 83:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.11.061
Jing HJ, Huang X, Du XJ, Mo L, Ma CY, Wang HX (2022) Facile synthesis of pH-responsive sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads promoted by hydrogen bond. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118993
Kannan N, Sundaram MM (2001) Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—a comparative study. Dyes Pigments 51:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(01)00056-0
Lee CH, Tiwari B, Zhang D, Yap YK (2017) Water purification: oil–water separation by nanotechnology and environmental concerns. Environ Sci-Nano 4:514–525. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6en00505e
Li L, Xiang SL, Cao SQ, Zhang JY, Ouyang GF, Chen LP, Su CY (2013) A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2757
Li SH, Huang JY, Chen Z, Chen GQ, Lai YK (2017) A review on special wettability textiles: theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J Mater Chem A 5:31–55. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta07984a
Liang CX, Hirabayashi K (1992) Improvements of the physical-properties of fibroin membranes with sodium alginate. J Appl Polym Sci 45:1937–1943. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1992.070451108
Lin RJ, Li A, Lu LB, Cao Y (2016) Corrigendum to: Preparation of bulk sodium carboxymethyl cellulose aerogels with tunable morphology (vol 118, pg 126, 2015). Carbohydr Polym 151:1278–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.071
Maleki H (2016) Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: a review. Chem Eng J 300:98–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.098
Matias T, Marques J, Quina MJ, Gando-Ferreira L, Valente AJM, Portugal A, Duraes L (2015) Silica-based aerogels as adsorbents for phenol-derivative compounds. Colloid Surf 480:260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.01.074
Mayerhofer TG, Pahlow S, Popp J (2020) The Bouguer–Beer–Lambert Law: shining light on the obscure. ChemPhysChem 21:2029–2046. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202000464
Nadagouda MN, Varma RS (2007) Synthesis of thermally stable carboxymethyl cellulose/metal biodegradable nanocomposites for potential biological applications. Biomacromolecules 8:2762–2767. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm700446p
Nie HR, Liu MZ, Zhan FL, Guo MY (2004) Factors on the preparation of carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel and its degradation behavior in soil. Carbohydr Polym 58:185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.06.035
Perdigoto MLN, Martins RC, Rocha N, Quina MJ, Gando-Ferreira L, Patricio R, Duraes L (2012) Application of hydrophobic silica based aerogels and xerogels for removal of toxic organic compounds from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 380:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.04.062
Reches M, Gazit E (2003) Casting metal nanowires within discrete self-assembled peptide nanotubes. Science 300:625–627. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1082387
Robb CS, Geldart SE, Seelenbinder JA, Brown PR (2002) Analysis of green tea constituents by HPLC-FTIR. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 25:787–801. https://doi.org/10.1081/Jlc-120003036
Saarai A, Kasparkova V, Sedlacek T, Saha P (2013) On the development and characterisation of crosslinked sodium alginate/gelatine hydrogels. J Mech Behav Biomed 18:152–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.11.010
Shen S, Wang HB, Fu JJ (2021) A nanoporous three-dimensional graphene aerogel doped with a carbon quantum dot-TiO2 composite that exhibits superior activity for the catalytic photodegradation of organic pollutants. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151116
Shen S, Fu JJ, Yi J, Ma LY, Sheng FF, Li CY, Wang TT, Ning CA, Wang HB, Dong K, Wang ZL (2021) High-efficiency wastewater purification system based on coupled photoelectric-catalytic action provided by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano-Micro Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00695-3
Smirnova I, Suttiruengwong S, Arlt W (2004) Feasibility study of hydrophilic and hydrophobic silica aerogels as drug delivery systems. J Non-Cryst Solids 350:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2004.06.031
Sun QC, Zhang ZP, Zhang RJ, Gao RC, McClements DJ (2018) Development of functional or medical foods for oral administration of insulin for diabetes treatment: gastroprotective edible microgels. J Agr Food Chem 66:4820–4826. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00233
Tan CB, Fung BM, Newman JK, Vu C (2001) Organic aerogels with very high impact strength. Adv Mater 13:644–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095(200105)13:9%3c644::AID-ADMA644%3e3.0.CO;2-#
Tsougeni K, Tserepi A, Boulousis G, Constantoudis V, Gogolides E (2007) Control of nanotexture and wetting properties of polydimethylsiloxane from very hydrophobic to super-hydrophobic by plasma processing. Plasma Process Polym 4:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.200600185
Ulker Z, Erkey C (2014) An emerging platform for drug delivery: aerogel based systems. J Control Release 177:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.12.033
Vimonses V, Lei SM, Jin B, Chowd CWK, Saint C (2009) Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of congo red adsorption by clay materials. Chem Eng J 148:354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.09.009
Wang S, Jiang L (2007) Definition of superhydrophobic states. Adv Mater 19:3423–3424. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200700934
Wu FC, Tseng RL, Juang RS (2009) Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 153:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.04.042
Xiao JL, Lv WY, Song YH, Zheng Q (2018) Graphene/nanofiber aerogels: performance regulation towards multiple applications in dye adsorption and oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 338:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.156
Xu W, Huang L, Jin WP, Ge PP, Shah BR, Zhu DD, Jing JX (2019) Encapsulation and release behavior of curcumin based on nanoemulsions-filled alginate hydrogel beads. Int J Biol Macromol 134:210–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.200
Yan GH, Chen BL, Zeng XH, Sun Y, Tang X, Lin L (2020) Recent advances on sustainable cellulosic materials for pharmaceutical carrier applications. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116492
Yang YS, Chen XP, Li YM, Yin ZC, Bao MT (2021) Construction of a superhydrophobic sodium alginate aerogel for efficient oil absorption and emulsion separation. Langmuir 37:882–893. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03229
Zhang CZ, Dai C, Zhang HQ, Peng ST, Wei X, Hu YD (2017) Regeneration of mesoporous silica aerogel for hydrocarbon adsorption and recovery. Mar Pollut Bull 122:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.036
Zheng QY, Tian Y, Ye FY, Zhou Y, Zhao GH (2020) Fabrication and application of starch-based aerogel: technical strategies. Trends Food Sci Technol 99:608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.03.038
Zhou SK, Wang M, Chen X, Xu F (2015) Facile Template synthesis of microfibrillated cellulose/polypyrrole/silver nanoparticles hybrid aerogels with electrical conductive and pressure responsive properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:3346–3354. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01020
Zhou SK, You TT, Zhang XM, Xu F (2018) Superhydrophobic Cellulose nanofiber-assembled aerogels for highly efficient water-in-oil emulsions separation. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1:2095–2103. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b00079
Zuo LZ, Zhang YF, Zhang LS, Miao YE, Fan W, Liu TX (2015) Polymer/carbon-based hybrid aerogels: preparation, properties and applications. Materials 8:6806–6848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8105343
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Support by the Opening Project of China National Textile and Apparel Council Key Laboratory of Natural Dyes, Soochow University (No. SDHY2122), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX23_2473) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470509).
Funding
Funding was provided by the Opening Project of China National Textile and Apparel Council Key Laboratory of Natural Dyes, Soochow University (Grant Number No.SDHY2122), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant Number KYCX23_2473), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number No.31470509).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL: Conceptualization, investigation, data curation, writing. JH: Materials preparation. SS and CM: Review & editing. HW and JF: Review & editing, supervision & funding acquisition. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HL. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors gave their consent for publication.
Ethical approval
All authors state that they adhere to the Ethical Responsibilities of Authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Huang, J., Shen, S. et al. Superhydrophobic sodium alginate/cellulose aerogel for dye adsorption and oil–water separation. Cellulose 30, 7157–7175 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05307-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05307-4