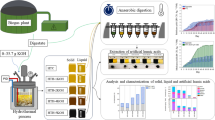
Abstract
Biomass-based aerogels have received attention these days due to their environmentally friendly and easily degradable nature. However, aerogel production is challenged by the generation of acid in aerogel manufacturing. This work aims at understanding how acid originating from biomass would impact aerogel production. In this study, alkali pre-extraction was carried out to demonstrate how the acidic substances released from poplar in a green inorganic molten salt hydrate solvent (LiBr·3H2O) would impact the properties of biomass-based aerogels. To understand the impact of lignin on aerogel production, the aerogel production was carried out on lignin-free biomass. The results confirmed that alkali pretreatment of biomass could be an effective method to accelerate the production of biomass-based aerogels. The biomass and particle size primarily affected the properties and microstructure of aerogels. Also, lignin has a substantial adverse effect on such aerogel production. Therefore, selecting suitable alkali treatment conditions, biomass content and particle size have crucial effects on the preparation of lignin-containing aerogels and lignin-free aerogels.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Calado V, Barreto DW, D’Almeida J (2000) The effect of a chemical treatment on the structure and morphology of coir fibers. J Mater Sci Lett 19(23):2151–2153. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026743314291
Chen HB, Wang YZ, Schiraldi DA (2014) Preparation and flammability of poly(vinyl alcohol) composite aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(9):6790–6796. https://doi.org/10.1021/am500583x
Chen C, Zhu J, Jia S, Mi S, Tong Z, Li Z, Huang Z (2018) Effect of ethanol on Mulberry bark hydrothermal liquefaction and bio-oil chemical compositions. Energy 162:460–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.08.026
Chen Y, Zhou L, Chen L, Duan G, Mei C (2019) Anisotropic nanocellulose aerogels with ordered structures fabricated by directional freeze-drying for fast liquid transport. Cellulose (London, England) 26(11):6653–6667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02557-z
Colom X, Carrillo F (2002) Crystallinity changes in lyocell and viscose-type fibres by caustic treatment. Eur Polym J 38(11):2225–2230. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-3057(02)00132-5
Dealmeida RM, Li J, Nederlof C, O’Connor P, Makkee M, Moulijn J (2010) Cellulose conversion to isosorbide in molten salt hydrate media. Chemsuschem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.200900260
Deng W, Kennedy JR, Tsilomelekis G, Zheng W, Nikolakis V (2015) Cellulose hydrolysis in acidified LiBr molten salt hydrate media. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(19):5226–5236. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00757
Du A, Zhou B, Zhang Z, Shen J (2013) A Special material or a new state of matter: a review and reconsideration of the aerogel. Materials 6(3):941–968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6030941
Fischer S, Leipner H, Thümmler K, Brendler E, Peters J (2003) Inorganic molten salts as solvents for cellulose. Cellulose 10(3):227–236. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025128028462
Ghaffari Mosanenzadeh S, Alshrah M, Saadatnia Z, Park CB, Naguib HE (2020) Double dianhydride backbone polyimide aerogels with enhanced thermal insulation for high-temperature applications. Macromol Mater Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201900777
Green JW, Pearl IA, Hardacker KW, Andrews B, Haigh FC (1977) Peeling reaction in alkaline pulping. Tappi 60(10):120–125
Jie C, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S, Zhang L (2010) Cellulose aerogels from aqueous alkali hydroxide-urea solution. Chemsuschem 1(1–2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.200700039
Labudek JI, Martiník L (2011) Aerogel material of the future for civil engineering. Trans Vb Technical Univ Ostrava Civil Eng 11:1–9
Li F, Chen ZL (2008) Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 142(1–3):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2008.06.007
Li J, Lu Y, Yang D, Sun Q, Liu Y, Zhao H (2011a) Lignocellulose aerogel from wood-ionic liquid solution (1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride) under freezing and Thawing conditions. Biomacromol 12(5):1860. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm200205z
Li N, Wang Z, Qu T, Kraft J, Oh J-H, van Pijkeren J-P, Pan X (2019a) High-yield synthesis of glucooligosaccharides (GlOS) as potential prebiotics from glucosevianon-enzymatic glycosylation. Green Chem 21(10):2686–2698. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc00663j
Li S, Qin J, Wang B, Zheng T, Hu Y (2019b) Design and compressive behavior of a photosensitive resin-based 2-D lattice structure with variable cross-section core. Polymers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11010186
Li Z, Sutandar E, Goihl T, Zhang X, Pan X (2020) Cleavage of ethers and demethylation of lignin in acidic concentrated lithium bromide (ACLB) solution. Green Chem 22(22):7989–8001. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0gc02581j
Li N, Bian H, Zhu JY, Ciesielski PN, Pan X (2021) Tailorable cellulose II nanocrystals (CNC II) prepared in mildly acidic lithium bromide trihydrate (MALBTH). Green Chem 23(7):2778–2791. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc00145k
Liao Y, Pang Z, Pan X (2019) Fabrication and mechanistic study of aerogels directly from whole biomass. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(21):17723–17736. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04032
Lindman B, KarlstroM G, Stigsson L (2010) On the mechanism of dissolution of cellulose. J Mol Liq 156(1):76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2010.04.016
Liu C, Wei L, Yin X, Pan X, Wang K (2021) Synthesis of furfural from xylan in γ-valerolactone/molten salt hydrate biphasic system. Chem Eng J 425(15):130608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130608
Liu G, Xie Y, Wei C, Liu C, Song F, Sun X, Cui H (2022) Synergistic catalysis of species in molten salt hydrate for conversion of cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Biomass Bioenergy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2022.106363
Lu F, Ralph J (2010) Non-degradative dissolution and acetylation of ball-milled plant cell walls: high-resolution solution-state NMR. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 35(4):535–544. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01817.x
Lu Y, Sun Q, Yang D, She X, Yao X, Zhu G, Li J (2012) Fabrication of mesoporous lignocellulose aerogels from wood via cyclic liquid nitrogen freezing–thawing in ionic liquid solution. J Mater Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm31310c
Ma R, Wang Y, Qi H, Shi C, Wei G, Xiao L, Guo Z (2019) Nanocomposite sponges of sodium alginate/graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol as potential wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Compos Part B 167:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.006
Ning L, Yanding L, Geun YC, Xiaohui Y, Xuliang L, John R, Xuejun P (2018) An uncondensed lignin depolymerized in the solid state and isolated from lignocellulosic biomass: a mechanistic study. Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC00953H
Penfield MP, Axelson ML (1999) The behaviour of cellulose in hydrated melts of the composition LiXċn H2O (X=I−, NO3−, CH3COO−, ClO4−). Cellulose 6(3):213–219. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009269614096
Perrut G (1998) Polyurethane-based organic aerogels’ thermal performance. J Non-Cryst Solids. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(98)00103-3
Rodriguez Quiroz N, Norton AM, Nguyen H, Vasileiadou E, Vlachos DG (2019) Homogeneous metal salt solutions for biomass upgrading and other select organic reactions. ACS Catal 9(11):9923–9952. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b01853
Sen S, Martin JD, Argyropoulos DS (2013) Review of cellulose non-derivatizing solvent interactions with emphasis on activity in inorganic molten salt hydrates. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 1(8):858–870. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400085a
Shi H, Fatehi P, Xiao H, Ni Y (2011) A combined acidification/PEO flocculation process to improve the lignin removal from the pre-hydrolysis liquor of kraft-based dissolving pulp production process. Bioresour Technol 102(8):5177–5182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.01.073
Shi H, Zhou M, Li C, Sheng X, Yang Q, Li N, Niu M (2019) Surface sediments formation during auto-hydrolysis and its effects on the benzene-alcohol extractive, absorbability and chemical pulping properties of hydrolyzed acacia wood chips. Bioresour Technol 289:121604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121604
Vlachos DG, Quiroz NR, Norton AM, Nguyen H, Vasiliadou ES (2019) A review of homogeneous metal salt solutions for biomass upgrading and other select organic reactions. ACS Catal. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b01853
Wang L, Shi H, Sun Y, Hou M, Sheng X, Li N, Niu M (2020) Highly efficient lignin removal from the waste liquor of chemical pulping with an integrated polyaluminium chloride-assisted acidification/activated carbon adsorption process. J Cleaner Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122005
Xie A, Wu F, Sun M, Dai X, Xu Z, Qiu Y, Wang M (2015) Self-assembled ultralight three-dimensional polypyrrole aerogel for effective electromagnetic absorption. Appl Phys Lett. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4921180
Yang YJ, Shin JM, Kang TH, Kimura S, Wada M, Kim UJ (2014) Cellulose dissolution in aqueous lithium bromide solutions. Cellulose 21(3):1175–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0183-9
Yang X, Li N, Lin X, Pan X, Zhou Y (2016) Selective cleavage of the aryl ether bonds in lignin for depolymerization by acidic lithium bromide molten salt hydrate under mild conditions. J Agric Food Chem 64(44):8379–8387. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03807
Yang F, Zhao X, Xue T, Yuan S, Huang Y, Fan W, Liu T (2020) Superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/polyimide nanofiber composite aerogels for thermal insulation under extremely humid and hot environment. Sci China Mater 64(5):1267–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-020-1518-4
Yang SC, Liao Y, Karthikeyan KG, Pan XJ (2021) Mesoporous cellulose-chitosan composite hydrogel fabricated via the co-dissolution-regeneration process as biosorbent of heavy metals. Environ Pollut 286:117324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117324
Yoo C, Li N, Swannell M, Pan X (2017a) Isomerization of glucose to fructose catalyzed by lithium bromide in water. Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7GC02145C
Yoo CG, Li N, Swannell M, Pan X (2017b) Isomerization of glucose to fructose catalyzed by lithium bromide in water. Green Chem 19(18):4402–4411. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7gc02145c
Zhang L, Couturier M, Oztop MH, Walton JH (2014) The impact of alkali pretreatment and post-pretreatment conditioning on the surface properties of rice straw affecting cellulose accessibility to cellulases. Bioresour Technol 167:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.122
Zhang L, Liao Y, Wang YC, Zhang S, Yang W, Pan X, Wang ZL (2020) Cellulose II aerogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv Funct Mater 30(28):2001763. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202001763
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the fifinancial support by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31971608), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2019-ZD-0125), the Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (2019), and Innovative Talents in Liaoning Universities and Colleges (2020).
Funding
This project was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31971608), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2019-ZD-0125), the Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (2019), and Innovative Talents in Liaoning Universities and Colleges (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing original draft, Visualization. XC: Paper structure, Date analysis. TX: Methodology, analysis. MH: Methodology, Formal analysis. CL: Methodology, Formal analysis. XS: Validation, Formal analysis. YG: Methodology, Formal analysis. YS: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation. PF: Writing-review & editing, Writing-Revised Manuscript Paper structure HS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Resources, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing, Supervision, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Cao, X., Xiao, T. et al. Effect of lignin and released acid on the gelation and aerogel fabrication of whole biomass in the lithium bromide molten salt hydrate system. Cellulose 30, 6233–6246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05280-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05280-y