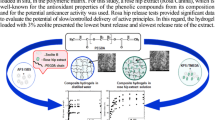
Abstract
Resveratrol (Res) has been widely used in personal-care and pharmaceutical products due to its anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective and anti-cancer properties. However, the direct application of Res as functional additives have been limited due to its insolubility and instability. In this work, Res is loaded on the biodegradable ethyl cellulose (EC) carrier to prepare highly porous EC/Res microspheres via a foam-transfer method to understand the sustained release and the degradation property. The experimental results show that when the PVA concentration = 2.5 wt%, the stirring rate = 600 rpm, the oil/water (O/W) ratio = 1:2, the polymer concentration = 1:25, the heating rate = 0.33 °C/min, and the viscosity of EC = 90 ~ 110 mpa.s, the EC/Res microspheres are obtained with a yield up to 80.70 wt% and an encapsulation efficiency of 73.89% via the batch-process; the EC/Res microspheres are further produced continuously with a higher encapsulation efficiency of 90.63% with a yield of 85.58 wt%. The EC/Res microsphere reaches a cumulative release rate up to 91.97 wt% in the phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH = 5.0 under 45 °C for 120 h. After the EC/Res microspheres degraded in PBS (pH = 7.4) for 45 days, the hardness decreased from 12.01 ± 0.56 MPa to 4.02 ± 0.45 MPa. This work thus provides a practical solution for Res’s application as sustained release functional additives.
Graphical abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Anal AK, Stevens WF, Remunan-Lopez C (2006) Ionotropic cross-linked chitosan microspheres for controlled release of ampicillin. Int J Pharm 312(1–2):166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.01.043
Babazadeh M, Edjlali L, Rashidian L (2007) Application of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate polymers in controlled release of 5-aminosalicylic acid as a colon-specific drug. J Polym Res 14(3):207–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-007-9099-5
Burns J, Yokota T, Ashihara H, Lean MEJ, Crozier A (2002) Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J Agric Food Chem 50(11):3337–3340. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0112973
Caddeo C, Teskac K, Sinico C, Kristl J (2008) Effect of resveratrol incorporated in liposomes on proliferation and UV-B protection of cells. Int J Pharmaceut 363(1–2):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.07.024
Cao J, Shen C, Wang X, Zhu Y, Bao S, Wu X, Fu Y (2021) A porous cellulose-based molecular imprinted polymer for specific recognition and enrichment of resveratrol. Carbohydr Polym 251:117026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117026
Chang CC, Lin KY, Peng KY, Day YJ, Hung LM (2016) Resveratrol exerts anti-obesity effects in high-fat diet obese mice and displays differential dosage effects on cytotoxicity, differentiation, and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. Endocr J 63(2):169–178. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ15-0545
Choi I, Li N, Zhong Q (2022) Enhancing bioaccessibility of resveratrol by loading in natural porous starch microparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 194:982–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.157
Davidov-Pardo G, McClements DJ (2015) Nutraceutical delivery systems: resveratrol encapsulation in grape seed oil nanoemulsions formed by spontaneous emulsification. Food Chem 167:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.06.082
Elshaer M, Chen YR, Wang XJ, Tang XW (2018) Resveratrol: an overview of its anti-cancer mechanisms. Life Sci 207:340–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.06.028
Ferreira PEB, Beraldi EJ, Borges SC, Natali MRM, Buttow NC (2018) Resveratrol promotes neuroprotection and attenuates oxidative and nitrosative stress in the small intestine in diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 105:724–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.030
Fibigr J, Satinsky D, Solich P (2016) A study of retention characteristics and quality control of nutraceuticals containing resveratrol and polydatin using fused-core column chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 120:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.12.014
Gambini J, Ingles M, Olaso G, Lopez-Grueso R, Bonet-Costa V, Gimeno-Mallench L, Mas-Bargues C, Abdelaziz KM, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Vina J, Borras C (2015) Properties of resveratrol: in vitro and in vivo studies about metabolism, bioavailability, and biological effects in animal models and humans. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/837042
He XJ, Hwang HM (2016) Nanotechnology in food science: functionality, applicability, and safety assessment. J Food Drug Anal 24(4):671–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2016.06.001
Huang XX, Huang XL, Gong YS, Xiao H, McClements DJ, Hu K (2016) Enhancement of curcumin water dispersibility and antioxidant activity using core-shell protein-polysaccharide nanoparticles. Food Res Int 87:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.06.009
Hussein MMA, Mahfouz MK (2016) Effect of resveratrol and rosuvastatin on experimental diabetic nephropathy in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 82:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.004
Isely C, Hendley MA, Murphy KP, Kader S, Annamalai P, Jabbari E, Gower RM (2019) Development of microparticles for controlled release of resveratrol to adipose tissue and the impact of drug loading on particle morphology and drug release. Int J Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118469
Juan ME, Buenafuente J, Casals I, Planas JM (2002) Plasmatic levels of trans-resveratrol in rats. Food Res Int 35(2–3):195–199
Juan ME, Alfaras I, Planas JM (2012) Colorectal cancer chemoprevention by trans-resveratrol. Pharmacol Res 65(6):584–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2012.03.010
Kamali H, Atamanesh M, Kaffash E, Mohammadpour F, Khodaverdi E, Hadizadeh F (2020) Elimination of residual solvent from PLGA microspheres containing risperidone using supercritical carbon dioxide. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec 57:101702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101702
Kanlayavattanakul M, Lourith N (2018) Skin hyperpigmentation treatment using herbs: a review of clinical evidences. J Cosmet Laser Ther 20(2):123–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/14764172.2017.1368666
Lee CW, Yen FL, Huang HW, Wu TH, Ko HH, Tzeng WS, Lin CC (2012) Resveratrol nanoparticle system improves dissolution properties and enhances the hepatoprotective effect of resveratrol through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. J Agric Food Chem 60(18):4662–4671. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2050137
Li GY, He YP, Han WQ, Yu Y, Zhu LH, Si T, Sun YL (2021a) An improved solvent evaporation method to produce poly (lactic acid) microspheres via foam-transfer. Int J Biol Macromol 172:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.031
Li GY, Yu Y, Han WQ, Zhu LH, Si T, Wang H, Li K, Sun YL, He YP (2021) Solvent evaporation self-motivated continual synthesis of versatile porous polymer microspheres via foaming-transfer. Colloids Surf A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126239
Lin YM, Asante FO, Xu X, Li SH, Ding HY, Xu LN, Yang XH, Xia JL, Li M (2021) A naturally tailored small molecule for the preparation of ethyl cellulose supramolecular composite film. Cellulose 28(1):289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03532-9
Luo SY, Gao MY, Pan XL, Wang Y, He YP, Zhu LH, Si T, Sun YL (2022) Fragrance oil microcapsules with low content of formaldehyde: preparation and characterization. Colloids Surf A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129019
Muschert S, Siepmann F, Leclercq B, Carlin B, Siepmann J (2009) Prediction of drug release from ethylcellulose coated pellets. J Controll Release 135(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.12.003
Oh A, Yun J, Kim HI (2011) Controlled release behavior of PCL/PEO/activated carbon composite microcapsule. J Polym Res 18(6):2441–2447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-011-9658-7
Pan XM, Mercade-Prieto R, York D, Preece JA, Zhang ZB (2013) Structure and mechanical properties of consumer-friendly PMMA microcapsules. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(33):11253–11265. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie303451s
Pandita D, Kumar S, Poonia N, Lather V (2014) Solid lipid nanoparticles enhance oral bioavailability of resveratrol, a natural polyphenol. Food Res Int 62:1165–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.05.059
Pauluk D, Padilha AK, Khalil NM, Mainardes RM (2019) Chitosan-coated zein nanoparticles for oral delivery of resveratrol: formation, characterization, stability, mucoadhesive properties and antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocoll 94:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.03.042
Peng HL, Xiong H, Li JH, Xie MY, Liu YZ, Bai CQ, Chen LX (2010) Vanillin cross-linked chitosan microspheres for controlled release of resveratrol. Food Chem 121(1):23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.085
Pi C, Yuan JY, Liu H, Zuo Y, Feng T, Zhan CL, Wu J, Ye Y, Zhao L, Wei YM (2018) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of curcumin loaded hollow microspheres prepared with ethyl cellulose and citric acid. Int J Biol Macromol 115:1046–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.171
Rogers TL, Wallick D (2012) Reviewing the use of ethylcellulose, methylcellulose and hypromellose in microencapsulation. Part 1: materials used to formulate microcapsules. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 38(2):129–157. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2011.590990
Sanna V, Roggio AM, Pala N, Marceddu S, Lubinu G, Mariani A, Sechi M (2015) Effect of chitosan concentration on PLGA microcapsules for controlled release and stability of resveratrol. Int J Biol Macromol 72:531–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.08.053
Sessa M, Tsao R, Liu RH, Ferrari G, Donsi F (2011) Evaluation of the stability and antioxidant activity of nanoencapsulated resveratrol during in vitro digestion. J Agric Food Chem 59(23):12352–12360. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2031346
Shao J, Li X, Lu X, Jiang C, Hu Y, Li Q, You Y, Fu Z (2009) Enhanced growth inhibition effect of Resveratrol incorporated into biodegradable nanoparticles against glioma cells is mediated by the induction of intracellular reactive oxygen species levels. Colloids Surf B 72(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.03.010
Shin TH, Ho MJ, Kim SR, Im SH, Kim CH, Lee S, Kang MJ, Choi YW (2018) Formulation and in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation of ethyl cellulose-coated sustained release multiple-unit system of tacrolimus. Int J Biol Macromol 109:544–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.111
Signorelli P, Ghidoni R (2005) Resveratrol as an anticancer nutrient: molecular basis, open questions and promises. J Nutr Biochem 16(8):449–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.01.017
Simoes MG, Coimbra P, Carreira AS, Figueiredo MM, Gil MH, Simoes PN (2020) Eugenol-loaded microspheres incorporated into textile substrates. Cellulose 27(7):4109–4121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03010-2
Soto-Valdez H, Auras R, Peralta E (2011) Fabrication of poly(lactic acid) films with resveratrol and the diffusion of resveratrol into ethanol. J Appl Polym Sci 121(2):970–978. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.33687
Summerlin N, Soo E, Thakur S, Qu Z, Jambhrunkar S, Popat A (2015) Resveratrol nanoformulations: challenges and opportunities. Int J Pharm 479(2):282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.01.003
Svajger U, Jeras M (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol and its potential use in therapy of immune-mediated diseases. Int Rev Immunol 31(3):202–222. https://doi.org/10.3109/08830185.2012.665108
Wang XG, Yin H, Chen ZF, Xia L (2020) Epoxy resin/ethyl cellulose microcapsules prepared by solvent evaporation for repairing microcracks: particle properties and slow-release performance. Mater Today Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100854
Wu JM, Hsieh TC (2011) Resveratrol: a cardioprotective substance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1215:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05854.x
Yang X, Li X, Ren JY (2014) From French paradox to cancer treatment: anti-cancer activities and mechanisms of resveratrol. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 14(6):806–825. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520614666140521121722
Yap SF, Adams MJ, Seville JPK, Zhang ZB (2008) Single and bulk compression of pharmaceutical excipients: evaluation of mechanical properties. Powder Technol 185(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2007.09.005
Zhang Y, Yu YF, Shi XX, Zhao SC, Chen AB, Huang DW, Niu DJ, Qin Z (2013) Study on the preparation of genipin crosslinked chitosan microspheres of resveratrol and in vitro release. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0175-8
Zhou J, Cheng WH, Liu TT, Li JX, Li XZ (2019) Preparation, characterization, and in vitro antioxidant activity of pH-sensitive resveratrol microcapsule in simulated intestinal fluids. Int J Food Prop 22(1):804–814. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2019.1610432
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank National Natural Science Foundation of China (22068018) and Yunnan Ten Thousand Talents Plan Young & Elite Talents Project for funding.
Funding
The study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (22068018) and Yunnan Ten Thousand Talents Plan Young & Elite Talents Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing -Review & Editing. MG: Investigation. XP: Investigation. YL: Investigation. MJ: Investigation. TS: Investigation. YS: Investigation. YH: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
No ethics approval was required in this work.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish the data in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Gao, M., Pan, X. et al. Preparation of resveratrol-loaded ethyl cellulose microspheres via foam-transfer and its application performances. Cellulose 30, 6401–6421 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05274-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05274-w