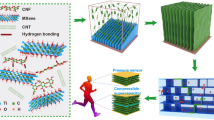
Abstract
Bacterial cellulose (BC)/polypyrrole (PPy) nanofibrous composites have been extensively studied in supercapacitors owing to their large specific surface area and excellent tensile strength. However, the inferior cycling stability due to structural pulverization of PPy impedes their potential applications. Herein, nanofibrous composite membranes of MXene, PPy and oxidized BC (TOBC) were prepared for flexible supercapacitor electrodes. The C6 primary hydroxyl groups of BC nanofibers were oxidized into aldehyde or carboxyl groups. Due to the enhanced interaction of TOBC with PPy and MXene, the TOBC nanofibers were horizontally wrapped on the MXene nanosheets and PPy was homogeneously deposited on the TOBC nanofibers. The flexible solid-state supercapacitors fabricated with the MXene@TOBC@PPy (TMP) electrodes achieved an areal specific capacitance of 928.9 mF cm−2 at 0.7 mA cm−2 and a capacitance retention of 85.5% after 5000 cycles. Therefore, the TMP electrodes could be a promising electrode material for flexible supercapacitors.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Amorim JDPD, Souza KCD, Duarte CR, Duarte IDS, Sarubbo LA (2020) Plant and bacterial nanocellulose: production, properties and applications in medicine, food, cosmetics, electronics and engineering. A review. Environ Chem Lett 18:851–869
Anasori B, Lukatskaya MR, Gogotsi Y (2017) 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat Rev Mater 2:16098. https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2016.98
Boota M, Gogotsi Y (2018) MXene—conducting polymer asymmetric pseudocapacitors. Adv Energy Mater 9:1802917. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201802917
Cao WT, Chen FF, Zhu YJ, Zhang YG, Jiang YY, Ma MG, Chen F (2018) Binary strengthening and toughening of MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite paper with nacre-inspired structure and superior electromagnetic interference shielding properties. ACS Nano 12:4583–4593. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00997
Chen Y, Chen S, Wang B, Yao J, Wang H (2017) TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers-supported gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic properties. Carbohydr Polym 160:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.020
Chen S, Qiu L, Cheng HM (2020) Carbon-based fibers for advanced electrochemical energy storage devices. Chem Rev 120:2811–2878. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00466
Fang D, Zhou J, Sheng L, Tang W, Tang J (2020) Juglone bonded carbon nanotubes interweaving cellulose nanofibers as self-standing membrane electrodes for flexible high energy supercapacitors. Chem Eng J 396:125325
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Geng L, Zhu P, Wei Y, Guo R, Xiang C, Cui C, Li Y (2019) A facile approach for coating Ti3C2Tx on cotton fabric for electromagnetic wave shielding. Cellulose 26:2833–2847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02284-5
Ghidiu M, Lukatskaya MR, Zhao MQ, Gogotsi Y, Barsoum MW (2014) Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide “clay” with high volumetric capacitance. Nature 516:78–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13970
Guan F, Chen S, Sheng N, Chen Y, Yao J, Pei Q, Wang H (2019) Mechanically robust reduced graphene oxide/bacterial cellulose film obtained via biosynthesis for flexible supercapacitor. Chem Eng J 360:829–837
He W et al (2019) Construction of Longan–like hybrid structures by anchoring nickel hydroxide on yolk–shell polypyrrole for asymmetric supercapacitors. Nano Energy 56:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.11.048
Hu H, Hua T (2017) An easily manipulated protocol for patterning of MXenes on paper for planar micro-supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 5:19639–19648. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta04735e
Huang C et al (2020) TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofiber membranes as high-performance separators for lithium-ion batteries. Carbohydr Polym 230:115570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115570
Isogai A (2004) TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. The effffect of oxidation conditions on chemical and crystal structures of the water-insoluble fractions. Biomacromol 5:1983–1989
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85
Jian X et al (2019) Three-dimensional carambola-like MXene/polypyrrole composite produced by one-step co-electrodeposition method for electrochemical energy storage. Electrochim Acta 318:820–827
Jin X et al (2020) Flame-retardant poly(vinyl alcohol)/MXene multilayered films with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal conductive performances. Chem Eng J 380:122475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122475
Liu J, Liu Z, Zhang HB, Chen W, Zhao Z, Wang QW, Yu ZZ (2019) Ultrastrong and highly conductive MXene-based films for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Electron Mater 6:1901094. https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.201901094
Lozano-Castelló D, Cazorla-Amorós D, Linares-Solano A, Shiraishi S, Kurihara H, Oya A (2003) Influence of pore structure and surface chemistry on electric double layer capacitance in non-aqueous electrolyte. Carbon 41:1765–1775
Lukatskaya MR et al (2013) Cation intercalation and high volumetric capacitance of two-dimensional titanium carbide. Science 341:1502–1505. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241488
Lukatskaya MR et al (2017) Ultra-high-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage in two-dimensional transition metal carbides. Nat Energy 2:17105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2017.105
Luo H et al (2018) Constructing 3D bacterial cellulose/graphene/polyaniline nanocomposites by novel layer-by-layer in situ culture toward mechanically robust and highly flexible freestanding electrodes for supercapacitors. Chem Eng J 334:1148–1158
Lv J et al (2019) High-performance polypyrrole coated knitted cotton fabric electrodes for wearable energy storage. Org Electron 74:59–68
Lv P, Song L, Li Y, Pang H, Liu W (2021) Hybrid ternary rice paper/polypyrrole ink/pen ink nanocomposites as components of flexible supercapacitors. Int J Hydrog Energy 46:13219–13229
Ma L, Liu R, Niu H, Wang F, Liu L, Huang Y (2016) Freestanding conductive film based on polypyrrole/bacterial cellulose/graphene paper for flexible supercapacitor: large areal mass exhibits excellent areal capacitance. Electrochim Acta 222:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.10.195
Ma L, Bi Z, Xue Y, Zhang W, Huang Q, Zhang L, Huang Y (2020) Bacterial cellulose: an encouraging eco-friendly nano-candidate for energy storage and energy conversion. J Mater Chem A 8:5812–5842
Manan S, Ullah MW, Ul-Islam M, Shi Z, Gauthier M, Yang G (2022) Bacterial cellulose: Molecular regulation of biosynthesis, supramolecular assembly, and tailored structural and functional properties. Prog Mater Sci 129:100972
Mu X et al (2019) Revealing the pseudo-intercalation charge storage mechanism of MXenes in acidic electrolyte. Adv Funct Mater 29:1902953. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201902953
Naguib M, Mochalin VN, Barsoum MW, Gogotsi Y (2014) 25th anniversary article: MXenes: a new family of two-dimensional materials. Adv Mater 26:992–1005. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201304138
Naskar P, Maiti A, Chakraborty P, Kundu D, Biswas B, Banerjee A (2021) Chemical supercapacitors: a review focusing on metallic compounds and conducting polymers. J Mater Chem A 9:1970–2017. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta09655e
Nyholm L, Nystrom G, Mihranyan A, Stromme M (2011) Toward flexible polymer and paper-based energy storage devices. Adv Mater 23:3751–3769. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201004134
Okita Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2010) Entire surface oxidation of various cellulose microfibrils by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Biomacromol 11:1696–1700
Peng S, Fan L, Rao W, Bai Z, Xu W, Xu J (2017a) Bacterial cellulose membranes coated by polypyrrole/copper oxide as flexible supercapacitor electrodes. J Mater Sci 52:1930–1942
Peng S, Fan L, Wei C, Liu X, Zhang H, Xu W, Xu J (2017b) Flexible polypyrrole/copper sulfide/bacterial cellulose nanofibrous composite membranes as supercapacitor electrodes. Carbohyd Polym 157:344–352
Sheng N et al (2019) Polypyrrole@TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose/reduced graphene oxide macrofibers for flexible all-solid-state supercapacitors. Chem Eng J 368:1022–1032
Simon P, Gogotsi Y (2020) Perspectives for electrochemical capacitors and related devices. Nat Mater 19:1151–1163. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0747-z
Song Q, Zhan Z, Chen B, Zhou Z, Lu C (2020) Biotemplate synthesis of polypyrrole@bacterial cellulose/MXene nanocomposites with synergistically enhanced electrochemical performance. Cellulose 27:7475–7488
Sun Y, Yang Y, Fan L, Zheng W, Ye D, Xu J (2022) Polypyrrole/SnCl2 modified bacterial cellulose electrodes with high areal capacitance for flexible supercapacitors. Carbohyd Polym 292:119679
Tsuguyuki Saito SK, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromol 8:2485–2491
Wang F, Kim H-J, Park S, Kee C-D, Kim S-J, Oh I-K (2016) Bendable and flexible supercapacitor based on polypyrrole-coated bacterial cellulose core-shell composite network. Compos Sci Technol 128:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.03.012
Wu Y, Hu H, Yuan C, Song J, Wu M (2020) Electrons/ions dual transport channels design: Concurrently tuning interlayer conductivity and space within re-stacked few-layered MXenes film electrodes for high-areal-capacitance stretchable micro-supercapacitor-arrays. Nano Energy 74:14812
Xu J, Zhu L, Bai Z, Liang G, Liu L, Fang D, Xu W (2013) Conductive polypyrrole–bacterial cellulose nanocomposite membranes as flexible supercapacitor electrode. Org Electron 14:3331–3338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2013.09.042
Xu T et al (2021) Advanced nanocellulose-based composites for flexible functional energy storage devices. Adv Mater 33:2101368. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202101368
Yang L, Lin F, Zabihi F, Yang S, Zhu M (2021) High specific capacitance cotton fiber electrode enhanced with PPy and MXene by in situ hybrid polymerization. Int J Biol Macromol 181:1063–1071
Yao J et al (2018) Hierarchical core-sheath polypyrrole@carbon nanotube/bacterial cellulose macrofibers with high electrochemical performance for all-solid-state supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 283:1578–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.086
Zhang N, Zang G-L, Shi C, Yu H-Q, Sheng G-P (2016) A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) removal. J Hazard Mater 316:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.018
Zhang C, Xu S, Cai D, Cao J, Wang L, Han W (2019) Planar supercapacitor with high areal capacitance based on Ti3C2/Polypyrrole composite film. Electrochim Acta 330:135277
Zhang J, Chen Q, Zhang H, Hou Y, Guo J (2020) High-performance polypyrrole coated filter paper electrode for flexible all-solid-state supercapacitor. J Electrochem Soc 167:140533
Zhao Z, Xia K, Hou Y, Zhang Q, Ye Z, Lu J (2021) Designing flexible, smart and self-sustainable supercapacitors for portable/wearable electronics: from conductive polymers. Chem Soc Rev 50:12702–12743. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cs00800e
Zhou J, Yuan Y, Tang J, Tang W (2019) Metal-organic frameworks governed well-aligned conducting polymer/bacterial cellulose membranes with high areal capacitance. Energy Storage Mater 23:594–601
Zhu M et al (2016) Highly flexible, freestanding supercapacitor electrode with enhanced performance obtained by hybridizing polypyrrole chains with MXene. Adv Energy Mater 6:1600969. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201600969
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Analytical & Testing Center of WTU for SEM.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51703170).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by LF, WZ, YY, YS and SP. The first draft and revision of the manuscript was written by LF, JX and GY. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Zheng, W., Yang, Y. et al. Bacterial cellulose composites (MXene@TOBC@PPy) for flexible supercapacitors with improved electrochemical performance. Cellulose 30, 6507–6521 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05272-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05272-y