Abstract
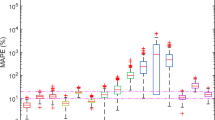
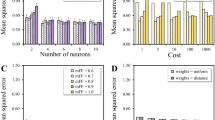
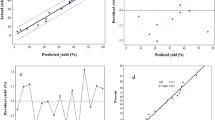
Extraction of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) from diverse cellulose sources is a promising and sustainable approach to produce nanocomposites. However, the traditional batch experiments are time/labor-consuming. Hence, three machine learning (ML) algorithms, i.e., decision regression tree, random forest, and artificial neural networks were applied to develop ML models. The dataset collected from published literature was used to train the ML models applicable to a wide range of cellulose source and reaction conditions. Among the three ML models, the random forest algorithm was the best one (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 5.52) for the yield prediction, and the decision regression tree provided the highest accuracy (R2 = 0.86, RSME = 6.03) for the crystallinity prediction. The concentration of reagent and cellulose source was identified as the most important feature in yield and crystallinity prediction, respectively. The partial dependence analysis showed the impact of each input feature and their combined effects on the yield and crystallinity. This study may provide new perspectives and opportunities to understand and improve the preparation of CNCs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbor VB, Cicek N, Sparling R, Berlin A, Levin DB (2011) Biomass pretreatment: fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol Adv 29:675–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.05.005
Bondeson D, Mathew A, Oksman K (2006) Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 13:171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-006-9061-4
Camarero Espinosa S, Kuhnt T, Foster EJ, Weder C (2013) Isolation of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals by phosphoric acid hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 14:1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400219u
Cao X, Ding B, Yu J, Al-Deyab SS (2012) Cellulose nanowhiskers extracted from TEMPO-oxidized jute fibers. Carbohyd Polym 90:1075–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.06.046
Chen L, Wang Q, Hirth K, Baez C, Agarwal UP, Zhu JY (2015) Tailoring the yield and characteristics of wood cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) using concentrated acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 22:1753–1762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0615-1
Chen L, Zhu JY, Baez C, Kitin P, Elder T (2016) Highly thermal-stable and functional cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils produced using fully recyclable organic acids. Green Chem 18:3835–3843. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC00687F
Cheng M, Qin Z, Liu Y, Qin Y, Li T, Chen L, Zhu M (2014) Efficient extraction of carboxylated spherical cellulose nanocrystals with narrow distribution through hydrolysis of lyocell fibers by using ammonium persulfate as an oxidant. J Mater Chem A 2:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA13653A
Cheng M, Qin Z, Hu J, Liu Q, Wei T, Li W, Ling Y, Liu B (2020) Facile and rapid one–step extraction of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals by H2SO4/HNO3 mixed acid hydrolysis. Carbohyd Polym 231:115701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115701
Coelho CCS, Michelin M, Cerqueira MA, Gonçalves C, Tonon RV, Pastrana LM, Freitas-Silva O, Vicente AA, Cabral LMC, Teixeira JA (2018) Cellulose nanocrystals from grape pomace: production, properties and cytotoxicity assessment. Carbohyd Polym 192:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.023
Correia DM, Lizundia E, Meira RM, Rincón-Iglesias M, Lanceros-Méndez S (2020) Cellulose nanocrystal and water-soluble cellulose derivative based electromechanical bending actuators. Materials 13:2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102294
Deepa B, Abraham E, Cordeiro N, Mozetic M, Mathew AP, Oksman K, Faria M, Thomas S, Pothan LA (2015) Utilization of various lignocellulosic biomass for the production of nanocellulose: a comparative study. Cellulose 22:1075–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0554-x
Ditzel FI, Prestes E, Carvalho BM, Demiate IM, Pinheiro LA (2017) Nanocrystalline cellulose extracted from pine wood and corncob. Carbohyd Polym 157:1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.036
Dong XM, Revol J-F, Gray DG (1998) Effect of microcrystallite preparation conditions on the formation of colloid crystals of cellulose. Cellulose 5:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009260511939
Dugan JM, Gough JE, Eichhorn SJ (2013) Bacterial cellulose scaffolds and cellulose nanowhiskers for tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 8:287–298. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.12.211
Fan J-s, Li Y-h (2012) Maximizing the yield of nanocrystalline cellulose from cotton pulp fiber. Carbohyd Polym 88:1184–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.01.081
García-García D, Balart R, Lopez-Martinez J, Ek M, Moriana R (2018) Optimizing the yield and physico-chemical properties of pine cone cellulose nanocrystals by different hydrolysis time. Cellulose 25:2925–2938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1760-0
Guiao KS, Tzoganakis C, Mekonnen TH (2022) Thermo-mechano-chemical deconstruction of cellulose for cellulose nanocrystal production by reactive processing. Carbohyd Polym 291:119543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119543
Hamad WY, Hu TQ (2010) Structure–process–yield interrelations in nanocrystalline cellulose extraction. Can J Cheml Eng 88:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20298
Iskak NAM, Julkapli NM, Hamid SBA (2017) Understanding the effect of synthesis parameters on the catalytic ionic liquid hydrolysis process of cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 24:2469–2481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1273-2
Ji H, Xiang Z, Qi H, Han T, Pranovich A, Song T (2019) Strategy towards one-step preparation of carboxylic cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils with high yield, carboxylation and highly stable dispersibility using innocuous citric acid. Green Chem 21:1956–1964. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03493A
Jonoobi M, Oladi R, Davoudpour Y, Oksman K, Dufresne A, Hamzeh Y, Davoodi R (2015) Different preparation methods and properties of nanostructured cellulose from various natural resources and residues: a review. Cellulose 22:935–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0551-0
Kargarzadeh H, Ahmad I, Abdullah I, Dufresne A, Zainudin SY, Sheltami RM (2012) Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 19:855–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9684-6
Kontturi E, Meriluoto A, Penttilä PA, Baccile N, Malho J-M, Potthast A, Rosenau T, Ruokolainen J, Serimaa R, Laine J, Sixta H (2016) Degradation and crystallization of cellulose in hydrogen chloride vapor for high-yield isolation of cellulose nanocrystals. Angew Chem Int Edit 55:14455–14458. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201606626
Leung ACW, Hrapovic S, Lam E, Liu Y, Male KB, Mahmoud KA, Luong JHT (2011) Characteristics and properties of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals prepared from a novel one-step procedure. Small 7:302–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201001715
Li J, Pan L, Suvarna M, Tong YW, Wang X (2020) Fuel properties of hydrochar and pyrochar: prediction and exploration with machine learning. Appl Energ 269:115166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115166
Li J, Zhang W, Liu T, Yang L, Li H, Peng H, Jiang S, Wang X, Leng L (2021) Machine learning aided bio-oil production with high energy recovery and low nitrogen content from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass with experiment verification. Chem Eng J 425:130649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130649
Li J, Zhu X, Li Y, Tong YW, Ok YS, Wang X (2021) Multi-task prediction and optimization of hydrochar properties from high-moisture municipal solid waste: application of machine learning on waste-to-resource. J Clean Prod 278:123928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123928
Liu Y, Wang H, Yu G, Yu Q, Li B, Mu X (2014) A novel approach for the preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose by using phosphotungstic acid. Carbohyd Polym 110:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.040
Liu C, Li B, Du H, Lv D, Zhang Y, Yu G, Mu X, Peng H (2016) Properties of nanocellulose isolated from corncob residue using sulfuric acid, formic acid, oxidative and mechanical methods. Carbohyd Polym 151:716–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.025
Liu Y, Guo B, Xia Q, Meng J, Chen W, Liu S, Wang Q, Liu Y, Li J, Yu H (2017a) Efficient cleavage of strong hydrogen bonds in cotton by deep eutectic solvents and facile fabrication of cellulose nanocrystals in high yields. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:7623–7631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00954
Liu Z, Li X, Xie W, Deng H (2017b) Extraction, isolation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose from industrial kelp (Laminaria japonica) waste. Carbohyd Polym 173:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.079
Louie SG, Chan Y-H, da Jornada FH, Li Z, Qiu DY (2021) Discovering and understanding materials through computation. Nat Mater 20:728–735. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-021-01015-1
Lu Z, Fan L, Zheng H, Lu Q, Liao Y, Huang B (2013) Preparation, characterization and optimization of nanocellulose whiskers by simultaneously ultrasonic wave and microwave assisted. Bioresour Technol 146:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.047
Lu Q, Cai Z, Lin F, Tang L, Wang S, Huang B (2016) Extraction of cellulose nanocrystals with a high yield of 88% by simultaneous mechanochemical activation and phosphotungstic acid hydrolysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:2165–2172. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01620
Lu Q, Lu L, Li Y, Yan Y, Fang Z, Chen X, Huang B (2019) High-yield synthesis of functionalized cellulose nanocrystals for nano-biocomposites. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:2036–2043. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00048
Mao J, Heck B, Reiter G, Laborie M-P (2015) Cellulose nanocrystals’ production in near theoretical yields by 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate ([Bmim]HSO4)–mediated hydrolysis. Carbohyd Polym 117:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.001
Martínez-Sanz M, Lopez-Rubio A, Lagaron JM (2011) Optimization of the nanofabrication by acid hydrolysis of bacterial cellulose nanowhiskers. Carbohyd Polym 85:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.02.021
Meesupthong R, Yingkamhaeng N, Nimchua T, Pinmanee P, Mussatto SI, Li B, Sukyai P (2021) Xylanase pretreatment of energy cane enables facile cellulose nanocrystal isolation. Cellulose 28:799–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03559-y
Mondal S (2017) Preparation, properties and applications of nanocellulosic materials. Carbohyd Polym 163:301–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.050
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00108B
Nozaki APM, Lona LMF (2021) Comparison between cellulose nanocrystal and microfibrillated cellulose as reinforcement of poly(vinyl acetate) composites obtained by either in situ emulsion polymerization or a simple mixing technique. Cellulose 28:2273–2286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03691-3
Oliveira FBd, Bras J, Pimenta MTB, Curvelo AAdS, Belgacem MN (2016) Production of cellulose nanocrystals from sugarcane bagasse fibers and pith. Ind Crop Prod 93:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.064
Rhim J-W, Reddy JP, Luo X (2015) Isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from onion skin and their utilization for the preparation of agar-based bio-nanocomposites films. Cellulose 22:407–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0517-7
Robles E, Fernández-Rodríguez J, Barbosa AM, Gordobil O, Carreño NLV, Labidi J (2018) Production of cellulose nanoparticles from blue agave waste treated with environmentally friendly processes. Carbohyd Polym 183:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.015
Sacui IA, Nieuwendaal RC, Burnett DJ, Stranick SJ, Jorfi M, Weder C, Foster EJ, Olsson RT, Gilman JW (2014) Comparison of the properties of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils isolated from bacteria, tunicate, and wood processed using acid, enzymatic, mechanical, and oxidative methods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:6127–6138. https://doi.org/10.1021/am500359f
Sadeghifar H, Filpponen I, Clarke SP, Brougham DF, Argyropoulos DS (2011) Production of cellulose nanocrystals using hydrobromic acid and click reactions on their surface. J Mater Sci 46:7344–7355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5696-0
Sai Prasanna N, Mitra J (2020) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from Cucumis sativus peels. Carbohyd Polym 247:116706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116706
Salminen R, Reza M, Pääkkönen T, Peyre J, Kontturi E (2017) TEMPO-mediated oxidation of microcrystalline cellulose: limiting factors for cellulose nanocrystal yield. Cellulose 24:1657–1667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1228-7
Seta FT, An X, Liu L, Zhang H, Yang J, Zhang W, Nie S, Yao S, Cao H, Xu Q, Bu Y, Liu H (2020) Preparation and characterization of high yield cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) derived from ball mill pretreatment and maleic acid hydrolysis. Carbohyd Polym 234:115942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115942
Shojaeiarani J, Bajwa DS, Chanda S (2021) Cellulose nanocrystal based composites: a review. Compos Part C Open Access 5:100164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomc.2021.100164
Sirviö JA, Visanko M, Liimatainen H (2016) Acidic deep eutectic solvents as hydrolytic media for cellulose nanocrystal production. Biomacromolecules 17:3025–3032. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00910
Song K, Ji Y, Wang L, Wei Y, Yu Z (2018) A green and environmental benign method to extract cellulose nanocrystal by ball mill assisted solid acid hydrolysis. J Clean Prod 196:1169–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.128
Tan XY, Abd Hamid SB, Lai CW (2015) Preparation of high crystallinity cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) by ionic liquid solvolysis. Biomass Bioenerg 81:584–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.08.016
Tang L-r, Huang B, Ou W, Chen X-r, Chen Y-d (2011) Manufacture of cellulose nanocrystals by cation exchange resin-catalyzed hydrolysis of cellulose. Bioresour Technol 102:10973–10977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.070
Tang Q, Chen Y, Yang H, Liu M, Xiao H, Wu Z, Chen H, Naqvi SR (2020) Prediction of bio-oil yield and hydrogen contents based on machine learning method: effect of biomass compositions and pyrolysis conditions. Energy Fuels 34:11050–11060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c01893
Tang Y, Yang H, Vignolini S (2022) Recent progress in production methods for cellulose nanocrystals: leading to more sustainable processes. Adv Sustain Syst 6:2100100. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202100100
Tao H, Wu T, Aldeghi M, Wu TC, Aspuru-Guzik A, Kumacheva E (2021) Nanoparticle synthesis assisted by machine learning. Nat Rev Mater 6:701–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-021-00337-5
Trache D, Hussin MH, Haafiz MKM, Thakur VK (2017) Recent progress in cellulose nanocrystals: sources and production. Nanoscale 9:1763–1786. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR09494E
Vanderfleet OM, Osorio DA, Cranston ED (2018) Optimization of cellulose nanocrystal length and surface charge density through phosphoric acid hydrolysis. Philos Trans Royal Soc 376:20170041. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2017.0041
Wang QQ, Zhu JY, Reiner RS, Verrill SP, Baxa U, McNeil SE (2012) Approaching zero cellulose loss in cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) production: recovery and characterization of cellulosic solid residues (CSR) and CNC. Cellulose 19:2033–2047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9765-6
Wang Q, Zhao X, Zhu JY (2014) Kinetics of strong acid hydrolysis of a bleached kraft pulp for producing cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs). Ind Eng Chem Res 53:11007–11014. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie501672m
Wang R, Chen L, Zhu JY, Yang R (2017) Tailored and integrated production of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) with nanofibrils (CNF) through maleic acid hydrolysis. ChemNanoMat 3:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.201700015
Wang J, Liu X, Jin T, He H, Liu L (2019) Preparation of nanocellulose and its potential in reinforced composites: a review. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 30:919–946. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2019.1612726
Wang H, Xie H, Du H, Wang X, Liu W, Duan Y, Zhang X, Sun L, Zhang X, Si C (2020) Highly efficient preparation of functional and thermostable cellulose nanocrystals via H2SO4 intensified acetic acid hydrolysis. Carbohyd Polym 239:116233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116233
Wang J, Xu J, Zhu S, Wu Q, Li J, Gao Y, Wang B, Li J, Gao W, Zeng J, Chen K (2021) Preparation of nanocellulose in high yield via chemi-mechanical synergy. Carbohyd Polym 251:117094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117094
Yang D, Peng X-W, Zhong L-X, Cao X-F, Chen W, Sun R-C (2013) Effects of pretreatments on crystalline properties and morphology of cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 20:2427–2437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9997-0
Yu H, Qin Z, Liang B, Liu N, Zhou Z, Chen L (2013) Facile extraction of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals with a high yield of 93% through hydrochloric acid hydrolysis under hydrothermal conditions. J Mater Chem A 1:3938–3944. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA01150J
Yu H-Y, Zhang D-Z, Lu F-F, Yao J (2016) New approach for single-step extraction of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals for their use as adsorbents and flocculants. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:2632–2643. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00126
Yu H, Abdalkarim SYH, Zhang H, Wang C, Tam KC (2019) Simple process to produce high-yield cellulose nanocrystals using recyclable citric/hydrochloric acids. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:4912–4923. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05526
Zhang Z, Friedrich K (2003) Artificial neural networks applied to polymer composites: a review. Compos Sci Technol 63:2029–2044. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00106-4
Zhang K, Sun P, Liu H, Shang S, Song J, Wang D (2016) Extraction and comparison of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals from bleached sugarcane bagasse pulp using two different oxidation methods. Carbohyd Polym 138:237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.038
Zhang H, Chen Y, Wang S, Ma L, Yu Y, Dai H, Zhang Y (2020) Extraction and comparison of cellulose nanocrystals from lemon (Citrus limon) seeds using sulfuric acid hydrolysis and oxidation methods. Carbohyd Polym 238:116180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116180
Zhu JY, Agarwal UP (2023) Nanocellulose: native state, production, and characterization. In: Hu L, Jiang F, Chen C (eds) Emerging nanotechnologies in nanocellulose. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Zhu X, Tsang DCW, Wang L, Su Z, Hou D, Li L, Shang J (2020) Machine learning exploration of the critical factors for CO2 adsorption capacity on porous carbon materials at different pressures. J Clean Prod 273:122915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122915
Zhu JY, Agarwal UP, Ciesielski PN, Himmel ME, Gao R, Deng Y, Morits M, Österberg M (2021) Towards sustainable production and utilization of plant-biomass-based nanomaterials: a review and analysis of recent developments. Biotechnol Biofuels 14:114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-01963-5
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2020MB041); National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51703110); and Shandong Province Key Research and Development Plan of China (Public Welfare Project 2019 GGX102068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by WH, DQ, LY, and CS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by WH and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Du, Q., Liu, Y. et al. Prediction and analysis of preparation of cellulose nanocrystals with machine learning. Cellulose 30, 6273–6287 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05260-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05260-2