Abstract
Nano-hydroxyapatite/bamboo fiber (n-HA/BF) composite membranes were obtained by a simple casting technology. The mechanism of the membrane formation and the effects of different pre-drying conditions, drying methods and n-HA addition amounts on the properties of the n-HA/BF composite membranes were investigated by Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), contact angle, Electromechanical universal tester, in vitro soaking in simulated body fluid (SBF) and in vitro cell culture experiment. The results demonstrated that different preparation conditions did not affect the dispersity of n-HA nanoparticles in BF matrix, but determined the membrane appearances, owing to the different changes of hydrogen bond under different pre-drying temperatures. Moreover, the hydrophilicity of the composite membranes could be improved when the membranes were prepared at 70 °C and freeze-drying as well as n-HA high addition content, and the mechanical properties of the composite membranes depended on n-HA addition content. In vitro soaking behavior indicated that the corrosion properties and bone-like apatite deposition could be controlled by different preparation conditions. The cell proliferation results showed that the n-HA/BF composite membranes obtained in different preparation conditions were all non-toxic. The obtained results showed that the casting technique could be used to prepare n-HA/BF composite membranes, and the properties of the composite membranes could be controlled by adopting different preparation conditions, which would have a great potential for guide bone tissue regeneration (GBR) membranes, and the study would provide a new way for BF application in biomedical fields.
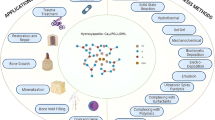
Graphical abstract
In this manuscript, nano-hydroxyapatite/BF (n-HA/BF) composite membranes were prepared by casting method, and the membrane forming mechanism and the effects of different pre-drying conditions, drying methods and n-HA amounts on the corresponding n-HA/BF membrane were investigated. Results demonstrated that the morphologies of membrane was determined by the different preparation conditions owing to different hydrogen bond changes. Moreover, the hydrophilicity, the mechanical properties, the degradability and bone-like apatite deposition could be controlled by different preparation conditions, and all the n-HA/BF composite membranes were all non-toxic. The obtained results indicated that the n-HA/BF composite membrane with 20% n-HA prepared at room temperature has a great potential as guide bone tissue regeneration (GBR) membrane, which would provide a new application for BF in biomedical field.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai CC, Liu L, Goh JCH (2021) Pore size modulates in vitro osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in fibronectin/gelatin coated silk fibroin scaffolds. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 124:112088
Bee SL, Hamid ZAA (2019) Characterization of chicken bone waste-derived hydroxyapatite and its functionality on chitosan membrane for guided bone regeneration. Compos Part B-Eng 163:562–573
Bierhalz ACK, Moraes AM (2017) Composite membranes of alginate and chitosan reinforced with cotton or linen fibers incorporating epidermal growth factor. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 76:287–294
Castro AGB, Diba M, Kersten M, Jansen JA, van den Beucken JJJP, Yang F (2018) Development of a PCL-silica nanoparticles composite membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 85:154–161
Chesley M, Kennard R, Roozbahani S, Kim SM, Kukk K, Mason M (2020) One-step hydrothermal synthesis with in situ milling of biologically relevant hydroxyapatite. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 113:110962
Chingakham C, Manaf O, Sujith A, Sajith V (2020) Hydrophobic nano-bamboo fiber-reinforced acrylonitrile butadiene styrene electrospun membrane for the filtration of crude biodiesel. Appl Nanosci 10:795–806
Cai J, Zhou R, Li TT, He JR, Wang GZ, Wang HB, Xiong HG (2018) Bamboo cellulose-derived cellulose acetate for electrospun nanofibers: synthesis, characterization and kinetics. Cellulose 25:391–398
Dhinasekaran D, Vimalraj S, Rajendran AR, Saravannan S, Purushothaman B, Subramaniam B (2021) Bio-inspired multifunctional collagen/electrospun bioactive glass membranes for bone tissue engineering applications. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 126:111856
Fong MK, Rahman MNA, Arifin AMT, Haq RHA, Hassan MF, Taib I (2021) Characterization, thermal and biological properties of PCL/PLA/PEG/N-HA composites. Biointerface Res App 11:9017–9026
Guimaraes M, Botaro VR, Novack KM, Teixeira FG, Tonoli GHD (2015) Starch/PVA-based nanocomposites reinforced with bamboo nanofibrils. Ind Crops Prod 70:72–83
Hivechi A, Bahrami SH, Siegel RA, Siehr A, Sahoo A, Milan PB, Joghataei MT, Amoupour M, Simorgh S (2021) Cellulose nanocrystal effect on crystallization kinetics and biological properties of electrospun polycaprolactone. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 121:111855
Hoornaert A, d’Arros C, Heymann MF, Layrolle P (2016) Biocompatibility, resorption and biofunctionality of a new synthetic biodegradable membrane for guided bone regeneration. Biomed Mater 11:045012
Hoseini SJ, Darroudi M, Oskuee RK, Gholami L, Zak A (2015) Honey-based synthesis of ZnO nanopowders and their cytotoxicity effects. Adv Powder Technol 26:991–996
Jiang LY, Li Y, Xiong CD, Su SP (2017) Preparation and characterization of a novel degradable nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(lactic-co-glycolic) composite reinforced with bamboo fiber. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 75:1014–1018
Jiang LY, Li Y, Ma BL, Ding HJ, Su SP, Xiong CD (2018) Effect of bamboo fiber length on mechanical properties, crystallization behavior, and in vitro degradation of bamboo fiber/nanohydroxyapatite/poly (lactic-co-glycolic) composite. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:4585–4591
Jiang LY, Ma BL, Li Y, Ding HJ, Su SP, Xiong CD (2019) Effect of bamboo fiber on the degradation behavior and in vitro cytocompatibility of the nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (n-HA/PLGA) composite. Cellulose 26:1099–1110
Khalil HPSA, Bhat IUH, Jawaid M, Zaidon A, Hermawan D, Hadi YS (2012) Bamboo Fibre Reinforced Biocomposites: a review. Mater Des 42:353–368
Lee BS, Lee CC, Lin HP, Shih WA, Hsieh WL, Lai CH, Takeuchi Y, Chen YW (2016) Functional chitosan membrane with grafted epigallocatechin-3-gallate and lovastatin enhances periodontal tissue regeneration in dogs. Carbohyd Polym 151:790–802
Li BW, Liu YH, Zhou YS, You PY, Wang M, Tang L, Deng Y (2020) Development of a novel extracellular matrix membrane with an asymmetric structure for guided bone regeneration. Mater Lett 274:127926
Li S, Wang TY, Hu JQ, Wang B, Li YZ, Wang LC, Li G, Zhang JL, Zhou ZG (2021) Effect of hydroxyapatite content and particle size on the mechanical behaviors and osteogenesis in vitro of polyetheretherketone-hydroxyapatite composite. Polym Compos 42:6512–6522
Li WW, Ma GW, Brazile B, Li N, Dai W, Butler JR, Claude AA, Wertheim JA, Liao J, Wang B (2015a) Investigating the potential of Amnion-based scaffolds as a barrier membrane for guided bone regeneration. Langmuir 31:8642–8653
Li Y, Jiang LY, Xiong CD, Peng WJ (2015b) Effect of different surface treatment for bamboo fiber on the crystallization behavior and mechanical property of bamboo fiber/nanohydroxyapatite/poly(lactic-co- glycolic) composite. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:12017–12024
Liu D, Song J, Anderson DP, Chang PR, Hua Y (2012) Bamboo fiber and its reinforced composites: structure and properties. Cellulose 19:1449–1480
Long HB, Wu ZQ, Dong QQ, Shen YT, Zhou WY, Luo Y, Zhang CQ, Dong XM (2019) Effect of polyethylene glycol on mechanical properties of bamboo fiber-reinforced polylactic acid composites. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47709
Ma BL, Jiang LY, Tang CY, Tang S, Su SP, Shu Y (2020) Preparation and properties of biomimetic hydroxyapatite-based nanocomposite utilizing bamboo fiber. Cellulose 27:2069–2083
Ma FB, Xia XY, Tang B (2019) Strontium chondroitin sulfate/silk fibroin blend membrane containing microporous structure modulates macrophage responses for guided bone regeneration. Carbohyd Polym 213:266–275
Macuvele DLP, Nones J, Matsinhe JV, Lima MM, Soares C, Fiori MA, Riella HG (2017) Advances in ultra high molecular weight polyethylene/hydroxyapatite composites for biomedical applications: a brief review. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 76:1248–1262
Niu XL, Wang LF, Xu MJ, Qin M, Zhao LQ, Wei Y, Hu YC, Lian XJ, Liang ZW, Chen S, Chen WY, Huang D (2021) Electrospun polyamide-6/chitosan nanofibers reinforced nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-6 composite bilayered membranes for guided bone regeneration. Carbohyd Polym 260:117769
Oksana Z, Wu XF, Zhou ZP, Ted A, Jivan T, John H (2020) A comparative experimental study of the hygroscopic and mechanical behaviors of electrospun nanofiber membranes and solution-cast films of polybenzimidazole. J Appl Polym Sci 137:e49639
Phuong HAL, Ayob NAI, Blanford CF, Rawi NFM, Szekely G (2019) Nonwoven membrane supports from renewable resources: bamboo fiber reinforced poly (Lactic Acid) composites. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:11885–11893
Priyadarshini B, Vijayalakshmi U (2018) Development of cerium and silicon co-doped hydroxyapatite nanopowder and its in vitro biological studies for bone regeneration applications. Adv Powder Technol 29:2792–2803
Prajatelistia E, Sanandiya ND, Nurrochman A, Marseli F, Choy S, Hwang DS (2021) Biomimetic Janus chitin nanofiber membrane for potential guided bone regeneration application. Carbohyd Polym 251:117032
Shakeri A, Khakdan F, Soheili V, Sahebkar A, Rassam G, Asili J (2014) Chemical composition, antibacterial activity, and cytotoxicity of essential oil from Nepeta ucrainica L. spp. Kopetdaghensis. Ind Crops Prod 58:315–321
Soares P, Laurindo CAH, Torres RD, Kuromoto NK, Peitl O, Zanotto ED (2012) Effect of a bioactive glass-ceramic on the apatite nucleation on titanium surface modified by micro-arc oxidation. Cellulose 206:4601–4605
Tang S, Jiang LY, Ma BL, Tang CY, Wen Y, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Su SP (2020) Preparation and characterization of bamboo fiber/chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite composite membrane by ionic crosslinking. Cellulose 27:5089–5100
Yadav S, Gangwar S (2020) The effectiveness of functionalized nano-hydroxyapatite filler on the physical and mechanicalproperties of novel dental restorative composite. Cellulose 69:907–918
Ye HL, Zhu JJ, Deng D, Jin SE, Li JD, Man Y (2019) Enhanced osteogenesis and angiogenesis by PCL/chitosan/Sr-doped calcium phosphate electrospun nanocomposite membrane for guided bone. J Biomat Sci-Polym E 30:1505–1522
Yu L, Cai Y, Wang H, Pan LB, Li JY, Chen S, Liu Z, Han FX, Li B (2020) Biomimetic bone regeneration using angle-ply collagen membrane-supported cell sheets subjected to mechanical conditioning. Acta Biomater 112:75–86
Zhu J, Tang D, Lu ZH, Xin ZY, Song J, Meng JM, Lu JR, Li Z, Li JS (2020) Ultrafast bone-like apatite formation on highly porous poly(l-lactic acid)-hydroxyapatite fibres. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 116:11168
Zuo YF, Li WH, Li P, Liu WJ, Li XG, Wu YQ (2018) Preparation and characterization of polylactic acid-g-bamboo fiber based on in-situ solid phase polymerization. Ind Crops Prod 123:646–653
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the support of the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (2020JJ4430), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Changsha City under Grant (kq2202238).
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (2020JJ4430), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Changsha City under Grant (kq2202238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conficts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Jiang, Z., Ma, B. et al. Effect of different preparation conditions on the properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/bamboo fiber composite membrane. Cellulose 29, 9361–9374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04850-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04850-w