Abstract
Residual lignin affects the physical and chemical performance of lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers (LCNFs). In this work, LCNFs were prepared from sugarcane bagasse powder (SBP) through p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-TsOH) hydrolysis and the subsequent homogenization treatment. By adjusting the concentration of p-TsOH and hydrolysis temperature, LCNFs with lignin content of 4.69–17.53% were obtained, and the effects of lignin content on the chemical structure, crystallinity, size, hydrophobicity and thermal stability of LCNFs were systematically studied. With the increase of lignin content, the diameters and average water contact angles of LCNFs were increased (from 169.65 to 781.56 nm and 39.74–86.16°, respectively), while the crystallinities were decreased. The thermal stabilities of LCNFs were decided both by lignin content and the crystallinity. The by-product lignin nanoparticles (LNPs) with an average diameter of 50–500 nm were generated with LCNFs, further improving the resource utilization value of SBP. This study provides theoretical and experimental basis for the subsequent processing of films with different hydrophobic properties and materials with higher mechanical properties and thermal stability.
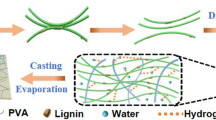
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LCNFs:
-
Lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers
- SBP:
-
Sugarcane bagasse powder
- p-TsOH:
-
p-Toluenesulfonic acid
- LNPs:
-
Lignin nanoparticles
- CNCs:
-
Cellulose nanocrystals
- CNFs:
-
Cellulose nanofibers
References
Abe K (2016) Nanofibrillation of dried pulp in NaOH solutions using bead milling. Cellulose 23(2):1257–1261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0891-4
Alemdar A, Sain M (2008) Isolation and characterization of nanofibers from agricultural residues-Wheat straw and soy hulls. Bioresour Technol 99(6):1664–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.029
Astner AF, Young TM, Bozell JJ (2015) Lignin yield maximization of mixed biorefinery feedstocks by organosolv fractionation using Taguchi Robust Product Design. Biomass Bioenerg 73:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.12.021
Bian HY, Chen LH, Dai HQ, Zhu JY (2017a) Integrated production of lignin containing cellulose nanocrystals (LCNC) and nanofibrils (LCNF) using an easily recyclable di-carboxylic acid. Carbohyd Polym 167:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.050
Bian HY, Chen LH, Gleisner R, Dai HQ, Zhu JY (2017b) Producing wood-based nanomaterials by rapid fractionation of wood at 80 °C using a recyclable acid hydrotrope. Green Chem 19(14):3370–3379. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7gc00669a
Bian HY, Dong ML, Chen LD, Zhou XL, Wang RB, Jiao L, Ji XX, Dai HQ (2020) On-demand regulation of lignocellulosic nanofibrils based on rapid fractionation using acid hydrotrope: kinetic study and characterization. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(25):9569–9577. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02968
Chen WS, Yu HP, Liu YX (2011) Preparation of millimeter-long cellulose I nanofibers with diameters of 30–80 nm from bamboo fibers. Carbohyd Polym 86(2):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.04.061
Chen LH, Wang QQ, Hirth K, Baez C, Agarwal UP, Zhu JY (2015) Tailoring the yield and characteristics of wood cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) using concentrated acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 22(3):1753–1762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0615-1
Chen LH, Zhu JY, Baez C, Kitin P, Elder T (2016) Highly thermal-stable and functional cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils produced using fully recyclable organic acids. Green Chem 18(13):3835–3843. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6gc00687f
Chen LH, Dou JZ, Ma QL, Li N, Wu RC, Bian HY, Yelle DJ, Vuorinen T, Fu SY, Pan XJ (2017) Rapid and near-complete dissolution of wood lignin at ≤80°C by a recyclable acid hydrotrope. Sci Adv 3(9):e1701735. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1701735
Chirayil CJ, Joy J, Mathew L, Mozetic M, Koetz J, Thomas S (2014) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibrils from Helicteres isora plant. Ind Crop Prod 59:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.04.020
Dong ML, Wu C, Chen LD, Zhou XL, Yang WS, Xiao HN, Ji XX, Dai HQ, Hu CQ, Bian HY (2021) Benzenesulfonic acid-based hydrotropic system for achieving lignocellulose separation and utilization under mild conditions. Bioresour Technol 337:125379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125379
Du HS, Liu C, Mu XD, Gong WB, Lv D, Hong YM, Si CL, Li B (2016) Preparation and characterization of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals via a sustainable approach of FeCl3-catalyzed formic acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 23(4):2389–2407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0963-5
Espinosa E, Bascon-Villegas I, Rosal A, Perez-Rodriguez F, Chinga-Carrasco G, Rodriguez, (2019) PVA/(ligno)nanocellulose biocomposite films. Effect of residual lignin content on structural, mechanical, barrier and antioxidant properties. Int J Biol Macromol 141:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.262
Espinosa E, Rol F, Bras J, Rodriguez A (2020) Use of multi-factorial analysis to determine the quality of cellulose nanofibers: effect of nanofibrillation treatment and residual lignin content. Cellulose 27(18):10689–10705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03136-3
Ewulonu Chinomso M, Liu Xuran, Min Wu, Yong Huang (2019) Lignin-containing cellulose nanomaterials: a promising new nanomaterial for numerous applications. J Bioresour Bioprod 4(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.21967/jbb.v4i1.186
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
García A, Gandini A, Labidi J, Belgacem N, Bras J (2016) Industrial and crop wastes: a new source for nanocellulose biorefinery. Ind Crop Prod 93:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.06.004
Gonçalves AR, Benar P, Costa SM, Ruzene DS, Moriya RY, Luz SM, Ferretti LP (2005) Integrated processes for use of pulps and lignins obtained from sugarcane bagasse and straw: a review of recent efforts in Brazil. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 123(1–3):0821–0826. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:123:1-3:0821
Henschen J, Li DF, Ek M (2019) Preparation of cellulose nanomaterials via cellulose oxalates. Carbohydr Polym 213:208–2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.056
Jiang Y, Liu XY, Yang Q, Song XP, Qin CR, Wang SF, Li KC (2018) Effects of residual lignin on mechanical defibrillation process of cellulosic fiber for producing lignocellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 25(11):6479–6494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2042-6
Khoo RZ, Chow WS, Ismail H (2018) Sugarcane bagasse fiber and its cellulose nanocrystals for polymer reinforcement and heavy metal adsorbent: a review. Cellulose 25(8):4303–4330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1879-z
Kumar A, Negi YS, Choudhary V, Bhardwaj NK (2014) Characterization of cellulose nanocrystals produced by acid-hydrolysis from sugarcane bagasse as agro-waste. J Mater Phys Chem 2(1):1–8
Lan TQ, Liu HR, Li H, Qin YY, Yue GJ (2020) Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing nanofibrillated cellulose. Bioresources 15(3):4689–4698
Li YN, Liu YZ, Chen WS, Wang QW, Liu YX, Li J, Yu HP (2016) Facile extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from wood using ethanol and peroxide solvothermal pretreatment followed by ultrasonic nanofibrillation. Green Chem 18(4):1010–1018. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc02576a
Lin XH, Chen LH, Li HY, Lv YC, Liu YF, Lu XB, Liu MH (2021) Mild depolymerization of the sinocalamus oldhami alkali lignin to phenolic monomer with base and activated carbon supported nickel-tungsten carbide catalyst composite system. Bioresour Technol 333:125136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125136
Liu YF, Wang HS, Yu G, Yu QX, Li B, Mu XD (2014) A novel approach for the preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose by using phosphotungstic acid. Carbohyd Polym 110:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.040
Liu XR, Li YD, Ewulonu CM, Ralph J, Xu F, Zhang QL, Wu M, Huang Y (2019) Mild alkaline pretreatment for isolation of native-like lignin and lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers (LCNF) from crop waste. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 7(16):14135–14142. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02800
Liu K, Du HS, Zheng T, Liu W, Zhang M, Liu HY, Zhang XY, Si CL (2021) Lignin-containing cellulose nanomaterials: preparation and applications. Green Chem: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC02841C
Luo X, Gleisner R, Tian S, Negron J, Zhu W, Horn E, Pan XY, Zhu JY (2010) Evaluation of mountain beetle-infested lodgepole pine for cellulosic ethanol production by sulfite pretreatment to overcome recalcitrance of lignocellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 49(17):8258–8266. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie1003202
Mandal A, Chakrabarty D (2011) Isolation of nanocellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and its characterization. Carbohydr Polym 86(3):1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.030
Marino MA, Rezende CA, Tasic L (2018) A multistep mild process for preparation of nanocellulose from orange bagasse. Cellulose 25(10):5739–5750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1977-y
Nair SS, Yan N (2015) Effect of high residual lignin on the thermal stability of nanofibrils and its enhanced mechanical performance in aqueous environments. Cellulose 22(5):3137–3150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0737-5
Nair SS, Kuo PY, Chen HY, Yan N (2017) Investigating the effect of lignin on the mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of cellulose nanofibril reinforced epoxy composite. Ind Crop Prod 100:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.02.032
Oksman K, Etang JA, Mathew AP, Jonoobi M (2011) Cellulose nanowhiskers separated from a bio-residue from wood bioethanol production. Biomass Bioenerg 35(1):146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.08.021
Paakko M, Vapaavuori J, Silvennoinen R, Kosonen H, Ankerfors M, Lindstrom T, Berglund LA, Ikkala O (2008) Long and entangled native cellulose I nanofibers allow flexible aerogels and hierarchically porous templates for functionalities. Soft Matter 4(12):2492–2499. https://doi.org/10.1039/b810371b
Poletto M, Zattera AJ, Forte MMC, Santana RMC (2012) Thermal decomposition of wood: Influence of wood components and cellulose crystallite size. Bioresour Technol 109:148–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.122
Reid MS, Villalobos M, Cranston ED (2017) Benchmarking cellulose nanocrystals: from the laboratory to industrial production. Langmuir 33(7):1583–1598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03765
Rojo E, Peresin MS, Sampson WW, Hoeger IC, Vartiainen J, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2015) Comprehensive elucidation of the effect of residual lignin on the physical, barrier, mechanical and surface properties of nanocellulose films. Green Chem 17(3):1853–1866. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc02398f
Sato K, Tominaga Y, Imai Y (2020) Nanocelluloses and related materials applicable in thermal management of electronic devices: a review. Nanomaterials 10(3):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030448
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Shao ZL, Li KH (2006) The effect of fiber surface lignin on interfiber bonding. J Wood Chem Technol 26(3):231–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/02773810601023438
Sirviö JA, Ismail MY, Zhang KT, Tejesvi MV, Ämmälä A (2020) Transparent lignin-containing wood nanofiber films with UV-blocking, oxygen barrier, and anti-microbial properties. J Mater Chem 8(16):7935–7946. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta13182e
Somerville C, Bauer S, Brininstool G, Facette HT, Milne J, Osborne E, Paredez A, Persson S, Raab T (2004) Toward a systems approach to understanding plant-cell walls. Science 306(5705):2206–2211. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102765
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak JJ (2010) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: water interactions and physical properties for packaging applications. Cellulose 17(4):835–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9424-8
Tonoli GHD, Teixeira EM, Correa AC, Marconcini JM, Caixeta LA, Pereira-da-Silva MA, Mattoso LHC (2012) Cellulose micro/nanofibres from Eucalyptus kraft pulp: preparation and properties. Carbohyd Polym 89(1):80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.052
Wang QQ, Zhu JY, Gleisner R, Kuster TA, Baxa U, McNeil SE (2012) Morphological development of cellulose fibrils of a bleached eucalyptus pulp by mechanical fibrillation. Cellulose 19(5):1631–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9745-x
Wang RB, Chen LH, Zhu JY, Yang RD (2017) Tailored and integrated production of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) with nanofibrils (CNF) through maleic acid hydrolysis. ChemNanoMat 3(5):328–335. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.201700015
Wu CL, McClements DJ, He MY, Zheng L, Tian T, Teng F, Li Y (2021) Preparation and characterization of okara nanocellulose fabricated using sonication or high-pressure homogenization treatments. Carbohydr Polym 255:117364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117364
Xu Y, Yang S, Zhao PT, Wu M, Song XP, Ragauskas AJ (2021) Effect of endoglucanase and high-pressure homogenization post-treatments on mechanically grinded cellulose nanofibrils and their film performance. Carbohydr Polym 253:117253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117253
Yang HP, Yan R, Chen HP, Lee DH, Zheng CG (2007) Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86:1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013
Zhang LL, Lu HL, Yu J, Wang ZG, Fan YM, Zhou XF (2017) Dissolution of lignocelluloses with a high lignin content in a N-Methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate solvent system via simple glycerol-swelling and mechanical pretreatments. J Agric Food Chem 65(44):9587–9594. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03429
Zhuo X, Liu C, Pan RT, Dong XY, Li YF (2017) Nanocellulose mechanically isolated from amorpha fruticosa linn. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(5):4414–4420. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00478
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2020J01506) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22008035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yifan Liu: conducted major parts of the study and drafted the manuscript. Beiqiu Chen: performed the chemical reactions and physicochemical properties measurements. Yuancai Lv: analyzed most of the characterizations. Xiaoxia Ye: completed most of the figures and contributed the major revisions of the manuscript. Chunxiang Lin: developed the concept of the study and contributed the major revisions of the manuscript. Minghua Liu: contributed to the interpretation and provided experimental conditions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. This manuscript does not involve human subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chen, B., Lv, Y. et al. Insight into the performance of lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers (LCNFs) via lignin content regulation by p-toluenesulfonic acid delignification. Cellulose 29, 2273–2287 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04432-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04432-w