Abstract
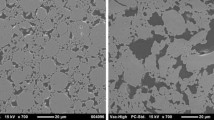
Natural biomaterials with intrinsic biomineralization potential are of utmost interest in bone tissue engineering (BTE) applications. Here, we report the biomimetic mineralization potential of a natural fiber derived from Cissus quadrangularis (CQ) stem, CQF, with inherent biomineralization and osteoinductive potential and is proposed for regenerative BTE. CQF has an organized microstructure characterized by an array of submicron size fibrils (SEM analysis) saturated with –OH groups of cellulose on the surface (FTIR spectrum), which provides a better platform for cell adhesion/proliferation and play a key role in the early nucleation of calcium phosphate, the inorganic phase of bone. A single unit of CQF has a tensile strength of 89.75 ± 5.25 MPa, which is in line with the mechanical property requirement of bone. CQF depicts signs of surface erosion (SEM analysis) with a weight loss of 11% after 30 days incubation in physiological conditions, supporting its intended stability required during the bone regeneration phase. CQF demonstrated excellent cytocompatibility (MTT assay and cell adhesion) and elicited primary nucleation and growth of apatite crystals (Ca/P 1.30; day 7), progressed further to secondary growth (Ca/P 1.51; day 14) upon incubation in simulated body fluid (SBF; 1.5X). Biomineralization of CQF was further confirmed by Alizarin Red S staining (day 14) in MG-63 cells. The osteoinductive potential of CQF was validated by quantifying early osteoblast differentiation marker alkaline phosphatase activity in Rat Bone marrow Mesenchymal Cells (BMC). The results, therefore, confer that CQF could be proposed for regenerative BTE.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber AH, Lu D, Pugno NM (2015) Extreme strength observed in limpet teeth. J R Soc Interface 12:5. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2014.1326
Bodo M, Lilli C, Bellucci C et al (2002) Basic fibroblast growth factor autocrine loop controls human osteosarcoma phenotyping and differentiation basic fibroblast growth factor autocrine loop controls human osteosarcoma phenotyping and differentiation. J Mol Med 8:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402020
Dimitriou R, Jones E, Mc Gonagle D, Giannoudis PV (2011) Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions. BMC Med 9:66–76
Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE (2006) Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044
García-gareta E, Coathup MJ, Blunn GW (2015) Osteoinduction of bone grafting materials for bone repair and regeneration. Bone 81:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2015.07.007
Ghasemi T, Shahroudi A, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Mousavian A (2018) Current concepts in scaffolding for bone tissue engineering. Arch Bone Jt Surg. https://doi.org/10.22038/ABJS.2018.26340.1713
Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Peister A, Prockop DJ (2004) An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal Biochem 329:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2004.02.002
Guerado E, Caso E (2017) Challenges of bone tissue engineering in orthopaedic patients. World J Orthop 8:87. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i2.87
Indran S, Raj RE (2015) Characterization of new natural cellulosic fiber from Cissus quadrangularis stem. Carbohydr Polym 117:392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.072
Jayaramudu J, Guduri BR, Rajulu AV (2010) Characterization of new natural cellulosic fabric Grewia tilifolia. Carbohydr Polym 79:847–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.10.046
Jiang T, Nukavarapu SP, Deng M et al (2010) Chitosan-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microsphere-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: In vitro degradation and in vivo bone regeneration studies. Acta Biomater 6:3457–3470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2010.03.023
Johnathan NG, Spiller K, Bernhard J, Novakovic GV (2017) Biomimetic approaches for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B 23:480–493. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.teb.2016.0289
Kalita H, Hazarika A, Kandimalla R et al (2018) Development of banana (Musa balbisiana) pseudo stem fiber as a surgical bio-tool to avert post-operative wound infections -. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra04470h
Kandimalla R, Kalita S, Choudhury B et al (2016) Fiber from ramie plant ( Boehmeria nivea ): A novel suture biomaterial. Mater Sci Eng C 62:816–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.02.040
Kerativitayanan P, Tatullo M, Khariton M et al (2017) Nanoengineered osteoinductive and elastomeric scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00029
Kim HD, Amirthalingam S, Kim SL et al (2017) Biomimetic materials and fabrication approaches for bone tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 1700612:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201700612
Kommula VP, Rajulu V, Reddy KO et al (2013) International journal of polymer analysis and characterization physico-chemical, tensile, and thermal characterization of napier grass ( Native African ) fiber strands. Int J Polym Anal Ch. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2013.784935
Kothari SC, Shivarudraiah P, Venkataramaiah SB et al (2011) Safety assessment of Cissus quadrangularis extract (CQR-300): subchronic toxicity and mutagenicity studies. Food Chem Toxicol 49:3343–3357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.09.029
Kukubo T, Takadama H (2006) How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity. Biomater 27:2907–2915
Lindman B, Karlström G, Stigsson L (2010) On the mechanism of dissolution of cellulose. J Mol Liq 156:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2010.04.016
Linn KF, He S, Y Song C Wang, (2016) Low temperature additive manufacturing biomimic three-dimensional hydroxyapatite / collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00815
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mate GS, Naikwade NS, Magdum CS, et al (2008) Evaluation of anti-nociceptive activity of Cissus quadrangularis on albino mice. Int. J. Green Pharm 118–121
Mayandi K, Rajini N, Pitchipoo P et al (2015a) Mechanical performance of Cissus quadrangularis / polyester composite. Mater Today Commun 4:222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2015.08.001
Mayandi K, Rajini N, Pitchipoo P et al (2015b) A comparative study on characterisations of Cissus quadrangularis and Phoenix reclinata natural fibres. J Reinf Plast Compos. https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684415570045
Mayandi K, Rajini N, Pitchipoo P, Arumugaprabhu V (2015c) Effect of alkali treatment on tensile and physicochemical characterization of Cissus quadrangularis fiber. Appl Mech Mater 814:172–178. https://doi.org/10.4028/scientific.net/AMM.813-814.172
Morgan DML (1998) Tetrazolium (MTT) assay for cellular viability and activity. Methods Mol Biol 79:179–183
Murphy CM, O ’brien FJ, Little DG, Schindeler A (2013) Cell-scaffold interactions in the bone tissue engineering triad. Eur Cells Mater 26:120–132. https://doi.org/10.22203/eCM.v026a09
Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A, Maffulli N (2014) Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res 9:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-9-18
Pascual AMD, Vicente ALD (2017) Multifunctional Poly (Glycolic Acid-Co- Propylene Fumarate) electrospun fibers reinforced with grapheme oxide and hydroxyapatite nano rods. J Mater Chem B 5:4084–4096
Qu H, Fu ZH and YS (2019) RSC advances biomaterials for bone tissue engineering scaffolds. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra05214c
Sailaja GS, Sreenivasan K, Yokogawa Y et al (2009) Bioinspired mineralization and cell adhesion on surface functionalized poly(vinyl alcohol) films. Acta Biomater 5:1647–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2008.12.005
Sain M, Panthapulakkal S (2006) Bioprocess preparation of wheat straw fibers and their characterization. Ind Crop Prod 23:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2005.01.006
Sakkas A, Wilde F, Heufelder M et al (2017) Autogenous bone grafts in oral implantology—is it still a “gold standard”? A consecutive review of 279 patients with 456 clinical procedures. Int J Implant Dent. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-017-0084-4
Shin K, Acri T, Geary S, Salem AK (2017) Biomimetic mineralization of biomaterials using simulated body fluids for bone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Tissue Eng Part A 23:1169–1180. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2016.0556
Shirwaikar A, Khan S, Malini S (2003) Antiosteoporotic effect of ethanol extract of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. on ovariectomized rat. J Ethnopharmacol 89:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2003.08.004
Singh YP, Moses C (2018) Hierarchically Structured Seamless Silk Scaffolds for Osteochondral Interface Tissue Engineering. J Mater Chem B 6:5671–5689. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tb01344f
Singh G, Rawat P, Maurya R (2007) Constituents of Cissus quadrangularis. Nat Prod Res 21:522–528. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786410601130471
Song J, Saiz E, Bertozzi CR (2003) A new approach to mineralization of biocompatible hydrogel scaffolds: an efficient process toward 3-dimensional bonelike composites. J Am Chem Soc 1236–1243
Stohs SJ, Ray SD (2012) A review and evaluation of the efficacy and safety of Cissus quadrangularis extracts. Phytother. Res
Sun F, Chen J, Jin S et al (2018) Development of Biomimetic Trilayer Fibrous Membranes For Guided Bone Regeneration. J Mater Chem B 7:665–675. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8tb02435a
Tanahashi M, Yao T, Kokubo T et al (1995) Apatite coated on organic polymers by biomimetic process: improvement in its adhesion to substrate by glow-discharge treatment. J Biomed Mater Res 29:349–357
Thein-Han WW RDKM (2009) Biomaterials Biomimetic chitosan – nanohydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 5:1182–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2008.11.025
Uff CR, Scott AD, Pockley AG, Robin KS (1995) Influence of soluble suture factors on in vitro macrophage function. Biomater 16:355–360
Yahia S, Khalil IA, El-sherbiny IM (2019) Sandwich-like nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:28610–28620. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b06359
Yang J, Long T, He N et al (2014) Fabrication of a chitosan/bioglass three dimensional porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering applications. J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med 2:6611–6618. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00940A
Acknowledgements
Praseetha R. Nair gratefully acknowledges the Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment- Women Scientist Division, Back to Lab scheme, Kerala, India. The authors are very much grateful to Dr. Padma Nambisan, Professor (Rtd.), Department of Biotechnology, CUSAT for the constant motivational support throughout this work. The authors are extremely thankful to the Department of Biotechnology, CUSAT for providing the cell culture and animal house facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Praseetha R. Nair has performed the experiment, analyzed the data and written the manuscript. S. Sreeja has executed biological experiments and interpreted the results. G.S. Sailaja has conceived the idea, supervised the work and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The animals for BMC isolation were purchased from Kerala Agricultural University, Mannuthy, Kerala, India and housed in separate cages. The animals (Quarantine period – 2 weeks; 12 h in dark and 12 h in light) were fed with standard food and water ad libitum. All the animal care was taken follwing Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (363/GO/Re/S/01/CPCSEA, 28/12/2017/10) and CPCSEA guidelines. All efforts are undertaken to avoid animal suffering.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, P.R., Sreeja, S. & Sailaja, G.S. Cissus quadrangularis stem derived fiber: a natural osteoinductive substrate for regenerative bone tissue engineering. Cellulose 29, 413–426 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04288-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04288-6