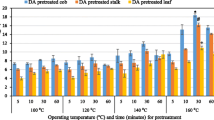
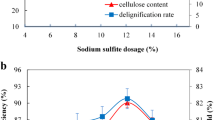
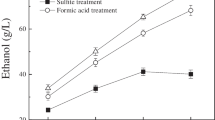
Abstract
As a cheap, biodegradable, and nontoxic chemical, choline chloride (ChCl) is widely used in animal feed. In this study, acid and alkali catalyzed ChCl pretreatments of corn stover (CS) were investigated. Compared with single aqueous ChCl pretreatment, H2SO4 acidified aqueous ChCl pretreatment was more effective in removing lignin (69.5%) and xylan (84.9%). NaOH alkalified aqueous ChCl pretreatment demonstrated better performance of delignification (76.8%) but weaker capability of removing xylan (46.2%) than acidified aqueous ChCl pretreatment. Following enzymatic digestibility of pretreated CS, glucose yield from acidified ChCl pretreatment was 72.1%, significantly lower than that of alkalified ChCl pretreatment (89.4%). However, the highest glucose yield of 98.6% resulted from solitary alkali pretreatment. Correlation studies between change in physico-chemical properties of pretreated solids and corresponding enzymatic digestibility indicated high delignification and bigger cellulose crystallite size were mainly responsible for high enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency. Additionally, the properties of extracted lignin from single and combined pretreatments with ChCl and alkali or acid were analyzed. Acidified ChCl pretreatment increased, whereas alkaline ChCl pretreatment decreased molecular weight and phenolic hydroxyl groups of separated lignin in comparison to individual acid and alkali pretreatment. These findings would provide useful information in understanding biomass pretreatments with aqueous ChCl.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and material presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Asikkala J, Tamminen T, Argyropoulos DS (2012) Accurate and reproducible determination of lignin molar mass by acetobromination. J Agric Food Chem 60(36):8968–8973. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf303003d
Becker J, Wittmann C (2019) A field of dreams: lignin valorization into chemicals, materials, fuels, and health-care products. Biotechnol Adv 37(6):107360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.02.016
Cai Q, Fan Z, Chen J, Guo W, Ma F, Sun S, Hu L, Zhou Q (2018) Dissolving process of bamboo powder analyzed by FT-IR spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 1171:639–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.06.066
Castro RCdA, Fonseca BG, dos Santos HTL, Ferreira IS, Mussatto SI, Roberto IC (2017) Alkaline deacetylation as a strategy to improve sugars recovery and ethanol production from rice straw hemicellulose and cellulose. Ind Crop Prod 106:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.08.053
Chen Z, Reznicek WD, Wan C (2018) Aqueous choline chloride: a novel solvent for switchgrass fractionation and subsequent hemicellulose conversion into furfural. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(5):6910–6919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00728
da Costa Lopes AM, Gomes JRB, Coutinho JAP, Silvestre AJD (2020) Novel insights into biomass delignification with acidic deep eutectic solvents: a mechanistic study of β-O-4 ether bond cleavage and the role of the halide counterion in the catalytic performance. Green Chem 22(8):2474–2487. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC02569C
Das N, Jena PK, Padhi D, Kumar Mohanty M, Sahoo G (2021) A comprehensive review of characterization, pretreatment and its applications on different lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01294-3
de Menezes FF, Rencoret J, Nakanishi SC, Nascimento VM, Silva VFN, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, de Moraes Rocha GJ (2017) Alkaline pretreatment severity leads to different lignin applications in sugar cane biorefineries. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(7):5702–5712. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00265
El Hage R, Brosse N, Chrusciel L, Sanchez C, Sannigrahi P, Ragauskas A (2009) Characterization of milled wood lignin and ethanol organosolv lignin from miscanthus. Polym Degrad Stab 94(10):1632–1638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.07.007
El Mansouri N-E, Salvadó J (2007) Analytical methods for determining functional groups in various technical lignins. Ind Crop Prod 26(2):116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2007.02.006
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD (2020) Increment in evolution of cellulose crystallinity analysis. Cellulose 27(10):5445–5448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03172-z
Ghose T (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59(2):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198759020257
Karimi K, Taherzadeh MJ (2016) A critical review of analytical methods in pretreatment of lignocelluloses: composition, imaging, and crystallinity. Bioresour Technol 200:1008–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.022
Kim JS, Lee YY, Kim TH (2016) A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 199:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.085
Knill CJ, Kennedy JF (2003) Degradation of cellulose under alkaline conditions. Carbohydr Polym 51(3):281–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(02)00183-2
Korányi TI, Fridrich B, Pineda A, Barta K (2020) Development of “Lignin-First” approaches for the valorization of lignocellulosic biomass. Molecules 25(12):2815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122815
Kucharska K, Rybarczyk P, Hołowacz I, Łukajtis R, Glinka M, Kamiński M (2018) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials as substrates for fermentation processes. Molecules 23(11):2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112937
Kumar B, Verma P (2020) Biomass-based biorefineries: an important architype towards a circular economy. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119622
Kumar V, Yadav SK, Kumar J, Ahluwalia V (2020) A critical review on current strategies and trends employed for removal of inhibitors and toxic materials generated during biomass pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 299:122633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122633
Kupina S, Fields C, Roman MC, Brunelle SL (2018) Determination of total phenolic content using the folin-C assay: single-laboratory validation, first action 2017.13. J AOAC Int 101(5):1466–1472. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.18-0031
Li Y, Qi B, Wan Y (2020) Separation of monosaccharides from pretreatment inhibitors by nanofiltration in lignocellulosic hydrolysate: fouling mitigation by activated carbon adsorption. Biomass Bioenerg 136:105527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105527
Li Z, Cai Z, Zeng Q, Zhang T, France LJ, Song C, Zhang Y, He H, Jiang L, Long J, Li X (2018) Selective catalytic tailoring of the H unit in herbaceous lignin for methyl p-hydroxycinnamate production over metal-based ionic liquids. Green Chem 20(16):3743–3752. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC01252K
Loow Y-L, New EK, Yang GH, Ang LY, Foo LYW, Wu TY (2017) Potential use of deep eutectic solvents to facilitate lignocellulosic biomass utilization and conversion. Cellulose 24(9):3591–3618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1358-y
Mellmer MA, Sanpitakseree C, Demir B, Ma K, Elliott WA, Bai P, Johnson RL, Walker TW, Shanks BH, Rioux RM, Neurock M, Dumesic JA (2019) Effects of chloride ions in acid-catalyzed biomass dehydration reactions in polar aprotic solvents. Nat Commun 10(1):1132. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09090-4
Satlewal A, Agrawal R, Bhagia S, Sangoro J, Ragauskas AJ (2018) Natural deep eutectic solvents for lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment: recent developments, challenges and novel opportunities. Biotechnol Adv 36(8):2032–2050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.08.009
Serrano L, Esakkimuthu ES, Marlin N, Brochier-Salon M-C, Mortha G, Bertaud F (2018) Fast, easy, and economical quantification of lignin phenolic hydroxyl groups: comparison with classical techniques. Energy Fuels 32(5):5969–5977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b00383
Shuai L, Luterbacher J (2016) Organic solvent effects in biomass conversion reactions. Chemsuschem 9(2):133–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201501148
Sluiter A, Hames B, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass—NREL/TP-510–42618. Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP)
Sporck D, Reinoso FA, Rencoret J, Gutiérrez A, José C, Ferraz A, Milagres AM (2017) Xylan extraction from pretreated sugarcane bagasse using alkaline and enzymatic approaches. Biotechnol Biofuels 10(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0981-z
Trajano HL, Engle NL, Foston M, Ragauskas AJ, Tschaplinski TJ, Wyman CE (2013) The fate of lignin during hydrothermal pretreatment. Biotechnol Biofuels 6(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-110
Uma Maheswari C, Obi Reddy K, Muzenda E, Guduri BR, Varada Rajulu A (2012) Extraction and characterization of cellulose microfibrils from agricultural residue—Cocos nucifera L. Biomass Bioenerg 46:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.06.039
Xu L, Zhang S-J, Zhong C, Li B-Z, Yuan Y-J (2020) Alkali-based pretreatment-facilitated lignin valorization: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 59(39):16923–16938. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c01456
Yan L, Pu Y, Bowden M, Ragauskas AJ, Yang B (2016) Physiochemical characterization of lignocellulosic biomass dissolution by flowthrough pretreatment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(1):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01021
Yang H, Yoo CG, Meng X, Pu Y, Muchero W, Tuskan GA, Tschaplinski TJ, Ragauskas AJ, Yao L (2020) Structural changes of lignins in natural populus variants during different pretreatments. Bioresour Technol 295:122240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122240
Yao K, Wu Q, An R, Meng W, Ding M, Li B, Yuan Y (2018) Hydrothermal pretreatment for deconstruction of plant cell wall: part I. Effect on lignin-carbohydrate complex. AIChE J 64(6):1938–1953. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.16114
Yu W, Wang C, Yi Y, Wang H, Yang Y, Zeng L, Tan Z (2021) Direct pretreatment of raw ramie fibers using an acidic deep eutectic solvent to produce cellulose nanofibrils in high purity. Cellulose 28(1):175–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03538-3
Yuan Z, Kapu NS, Beatson R, Chang XF, Martinez DM (2016) Effect of alkaline pre-extraction of hemicelluloses and silica on kraft pulping of bamboo (Neosinocalamus affinis Keng). Ind Crop Prod 91:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.06.019
Zakis GF (1994) Functional analysis of lignins and their derivatives. Tappi Press, Atlanta, GA, USA
Zeng YN, Zhao S, Yang SH, Ding SY (2014) Lignin plays a negative role in the biochemical process for producing lignocellulosic biofuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 27:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.008
Zhang L, Yan L, Wang Z, Laskar DD, Swita MS, Cort JR, Yang B (2015) Characterization of lignin derived from water-only and dilute acid flowthrough pretreatment of poplar wood at elevated temperatures. Biotechnol Biofuels 8(1):203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0377-x
Zhao C, Huang J, Yang L, Yue F, Lu F (2019) Revealing structural differences between alkaline and kraft lignins by HSQC NMR. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(14):5707–5714. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00499
Zhao X, Zhang L, Liu D (2012) Biomass recalcitrance. Part I: the chemical compositions and physical structures affecting the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 6(4):465–482. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1331
Zoghlami A, Paës G (2019) Lignocellulosic biomass: understanding recalcitrance and predicting hydrolysis. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00874
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB1501701) and the Science and Technology Service Network Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KFJ-STS-QYZX-096).
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB1501701) and the Science and Technology Service Network Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KFJ-STS-QYZX-096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BQ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-original draft; ZW: Investigation; JL: Writing-review & editing; YW: Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, B., Wang, Z., Luo, J. et al. Pretreatment of corn stover by acidic and basic choline chloride solutions for enzymatic hydrolysis. Cellulose 28, 10127–10141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04163-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04163-4