Abstract
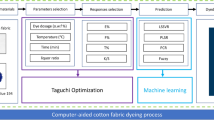
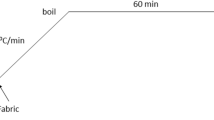
The textile bleaching process that involves hot hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) solution is commonly practised in cotton fabric manufacture. The purpose of the bleaching process is to remove color from the cotton, achieving a permanent white before proceeding to dyeing or shape matching. Normally, the visual ratings of whiteness on the cotton are measured based on whiteness index (WI). However, it is found that there is little research on chemical predictive modelling of the cotton fabric’s WI compared to experimental study. Analytics using predictive modelling can forecast the outcomes, leading to better-informed cotton quality assurance and control decisions. Up to date, there is limited study applying least square support vector regression (LSSVR) model in the textile domain. Hence, the present study aims to develop a multi-output LSSVR (MLSSVR) model using bleaching process variables and results obtained from two different case studies to predict the WI of cotton. The predictive accuracy of the MLSSVR model was measured by root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). The obtained results were compared with other regression models including partial least square regression, predictive fuzzy model, locally weighted partial least square regression, and locally weighted kernel partial least square regression. Our findings indicate that the proposed MLSSVR model performed better than other models in predicting the WI as it showed significantly lower values of RMSE and MAE. Furthermore, it provided the highest R2 values which are up to 0.9999.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
A matrix consisting Lagrange multipliers
- \(b\) :
-
A threshold value
- bk :
-
Kernel parameter for locally weighted kernel partial least square
- CIE:
-
Commission on Illumination
- CPU:
-
Central processing unit (CPU)
- H, P, Q, K, \(\Omega\), \(0\),\(S\) :
-
A definite matrix
- H2O2 :
-
Hydroxide peroxide
- LSSVR:
-
Least squares support vector regression
- LOO:
-
Leave-one-out
- LW-KPLSR:
-
Locally weighted Kernel partial least square regression
- LW-PLSR:
-
Locally weighted partial least square regression
- LV:
-
Latent variable
- MAE:
-
Mean absolute error
- p:
-
A positive hyperparameter of radial basis function kernel function
- PE:
-
Prediction error
- PLSR:
-
Partial least square regression
- MLSSVR:
-
Multi-output least square support vector regression
- NT :
-
Total number of data sets
- N1 :
-
Number of training data sets
- N2 :
-
Number of testing data sets
- R2 :
-
R-squared or the coefficient of determination
- RBF:
-
Radial basis function
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- T:
-
Temperature of bleaching process
- t:
-
Time of bleaching process
- \(V\),\(v_{i}\) :
-
A vector in multi-output least square support vector regression
- WI:
-
Whiteness index
- W:
-
Weighed value vector
- \(x_{i}\), \(x\) :
-
Input vector
- \(x_{c}\) and \(y_{c}\) :
-
Chromaticity coordinates of the bleached cotton fabric samples
- \(x_{n}\) and \(y_{n}\) :
-
Chromaticity coordinates of the illuminant
- \(y^{i}\),\(y\), \(Y\) :
-
Output vector
- \(Y_{L}\) :
-
Lightness
- Z:
-
A mapping to some high or even unlimited/infinite dimensional Hilbert space or feature space via the nonlinear mapping function \(\phi\) with \(n_{h}\) dimensions
- \(\gamma\),\(\lambda\) :
-
Two positive real regularised parameters in the multi-output least square support vector regression
- \(\phi (x)\) :
-
A nonlinear mapping function
- \(\xi\) :
-
A vector containing slack variables
- \(\Xi\) :
-
A matrix consisting of slack variables with an order of \(l \times m\)
- \(\alpha\) :
-
A vector consisting of Lagrange multipliers
- \(\ell\) :
-
The Lagrangian function
References
Abdul S, Narendra G (2013) Accelerated bleaching of cotton material with hydrogen peroxide. J Text Sci Eng 3:1000140. https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-8064.1000140
Ahmad S, Huifang W, Akhtar S, Imran S, Yousaf H, Wang C, Akhtar MS (2021) Impact assessment of better management practices of cotton: a sociological study of southern Punjab, Pakistan. Pak J Agric Sci 58:291–300. https://doi.org/10.21162/PAKJAS/21.227
An X, Xu S, Zhang L-D, Su S-G (2009) Multiple dependent variables LS-SVM regression algorithm and its application in NIR spectral quantitative analysis. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 29:127–130. https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)01-0127-04
Bajpai D (2007) Laundry detergents: an overview. J Oleo Sci 56:327–340. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.56.327
Ferdush J, Nahar K, Akter T, Ferdoush MJ, Jahan N, Iqbal SF (2019) Effect of hydrogen peroxide concentration on 100% cotton knit fabric bleaching. ESJ 15:254–263. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2019.v15n33p254
Ferreira ILS, Medeiros I, Steffens F, Oliveira FR (2019) Cotton fabric bleached with seawater: mechanical and coloristic properties. Mater Res 22:e20190085. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2019-0085
Guang W, Baraldo M, Furlanut M (1995) Calculating percentage prediction error: a user’s note. Pharmacol Res 32:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1043-6618(05)80029-5
Gültekin BC (2016) Bleaching of SeaCell® active fabrics with hydrogen peroxide. Fibers Polym 17:1175–1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6181-9
Haque A, Islam MA (2015) Optimization of bleaching parameters by whiteness index and bursting strength of knitted cotton fabric. Int J Sci Technol Res 4:40–43
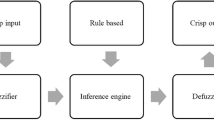
Haque ANMA, Smriti SA, Hussain M, Farzana N, Siddiqa F, Islam MA (2018) Prediction of whiteness index of cotton using bleaching process variables by fuzzy inference system. Fash Text 5:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40691-017-0118-9
Harmel RD, Smith PK, Migliaccio KW (2010) Modifying goodness-of-fit indicators to incorporate both measurement and model uncertainty in model calibration and validation. Trans ASABE 53:55–63. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.29502
Hocaoğlu FO, Gerek ÖN, Kurban M (2008) Hourly solar radiation forecasting using optimal coefficient 2-D linear filters and feed-forward neural networks. Solar energ 82:714–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2008.02.003
Jaeger BC, Edwards LJ, Das K, Sen PK (2017) An R 2 statistic for fixed effects in the generalized linear mixed model. J Appl Stat 44:1086–1105. https://doi.org/10.1080/02664763.2016.1193725
Jafari R, Amirshahi S (2008) Variation in the decisions of observers regarding the ordering of white samples. Color Technol 124:127–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-4408.2008.00132.x
Jung H, Sato T (2013) Comparison between the color properties of whiteness index and yellowness index on the CIELAB. Text Coloration Finish 25:241–246. https://doi.org/10.5764/TCF.2013.25.4.241
Kabir SF, Iqbal MI, Sikdar PP, Rahman MM, Akhter S (2014) Optimization of parameters of cotton fabric whiteness. Eur Sci J 10:200–210
Kaneko H, Funatsu K (2016) Ensemble locally weighted partial least squares as a just-in-time modeling method. AIChE J 62:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15090
Keerthi SS, Lin C-J (2003) Asymptotic behaviors of support vector machines with Gaussian kernel. Neural Comput 15:1667–1689. https://doi.org/10.1162/089976603321891855
Kovac P, Rodic D, Pucovsky V, Savkovic B, Gostimirovic M (2013) Application of fuzzy logic and regression analysis for modeling surface roughness in face milliing. J Intell Manuf 24:755–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-012-0623-z
Liu H, Yoo C (2016) A robust localized soft sensor for particulate matter modeling in Seoul metro systems. J Hazard Mater 305:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.11.051
Moosavi SR, Vaferi B, Wood DA (2021) Auto-characterization of naturally fractured reservoirs drilled by horizontal well using multi-output least squares support vector regression. Arab J Geosci 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06559-9
Oliveira BPd, Moriyama LT, Bagnato VS (2018) Colorimetric analysis of cotton textile bleaching through H2O2 activated by UV light. J Braz Chem Soc 29:1360–1365. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20170235
Tang P, Ji B, Sun G (2016) Whiteness improvement of citric acid crosslinked cotton fabrics: H2O2 bleaching under alkaline condition. Carbohydr polym 147:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.007
Tang F, Tiňo P, Gutiérrez PA, Chen H (2015) The benefits of modeling slack variables in svms. Neural Comput 27:954–981. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO_a_00714
Topalovic T, Nierstrasz VA, Bautista L, Jocic D, Navarro A, Warmoeskerken MM (2007) Analysis of the effects of catalytic bleaching on cotton. Cellulose 14:385–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9120-5
Vapnik V (1992) Principles of risk minimization for learning theory. In: NIPS'91: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on neural information processing systems, pp 831–838. https://doi.org/10.5555/2986916.2987018
Wang X, Hu P, Zhen L, Peng D (2021) Drsl: deep relational similarity learning for cross-modal retrieval. Inf Sci 546:298–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.009
Wang D, Zhong L, Zhang C, Zhang F, Zhang G (2018) A novel reactive phosphorous flame retardant for cotton fabrics with durable flame retardancy and high whiteness due to self-buffering. Cellulose 25:5479–5497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1964-3
Wexler J, Pushkarna M, Bolukbasi T, Wattenberg M, Viégas F, Wilson J (2019) The What-If Tool: interactive probing of machine learning models. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Gr 26:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2019.2934619
Xie K, Gao A, Zhang Y (2013) Flame retardant finishing of cotton fabric based on synergistic compounds containing boron and nitrogen. Carbohydr Polym 98:706–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.014
Xu C, Hinks D, Sun C, Wei Q (2015) Establishment of an activated peroxide system for low-temperature cotton bleaching using N-[4-(triethylammoniomethyl) benzoyl] butyrolactam chloride. Carbohydr Polym 119:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.054
Xu S, An X, Qiao X, Zhu L, Li L (2013) Multi-output least-squares support vector regression machines. Pattern Recogn Lett 34:1078–1084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2013.01.015
Yeo WS, Saptoro A, Kumar P (2017) Development of adaptive soft sensor using locally weighted Kernel partial least square model. Chem Prod Process Model 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1515/cppm-2017-0022
Zhang J, Wang Y (2021) Evaluating the bond strength of FRP-to-concrete composite joints using metaheuristic-optimized least-squares support vector regression. Neural Comput Appl 33:3621–3635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05191-0
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Curtin University Malaysia and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia for providing the support for this paper.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This research program does not involve testing to be done on humans or animals. It also does not involve any potentially dangerous equipment and hazardous substance of any kind. Therefore, no ethical issue will be expected in this research project.
Human or animal rights
No animal studies or human participants involvement in the study, hence this research project is compliance with ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeo, W.S., Lau, W.J. Predicting the whiteness index of cotton fabric with a least squares model. Cellulose 28, 8841–8854 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04096-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04096-y