Abstract
A greener processing route to replace the current environmentally-unfriendly esterification technique to produce biofuels such as pentyl valerate (PeVa) was explored. This study statistically optimized the covalent immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase (CRL) onto biomass-based nanocellulose-silica (NC-SiO2) reinforced polyethersulfone (PES) membrane to synthesize PeVa. Raman spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and atomic force microscopy of NC-SiO2-PES/CRL proved that CRL was successfully conjugated to the membrane. The optimized Taguchi Design-assisted immobilization of CRL onto NC-SiO2-PES membrane (5% glutaraldehyde, 4 h of immobilization, 20 mg/mL CRL concentration, 40 °C and pH 5) gave 90% yield of PeVa in 3 h. The thermal stability of NC-SiO2-PES/CRL was ~ 30% greater over the free CRL, with reusability for up to 14 successive esterification cycles. In a nutshell, the greener NC-SiO2-PES membrane effectively hyperactivated and stabilized the CRL for the esterification production of PeVa. This research provides a promising approach for expanding the use of sustainably sourced NC and SiO2 nanoparticles, as fillers in a PES for improving CRL activity and durability for an extended catalytic process.
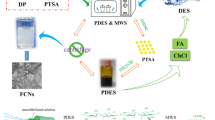
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Manan FM, Attan N, Widodo N, Aboul-Enein HY, Wahab RA (2018) Rhizomucor miehei lipase immobilized on reinforced chitosan–chitin nanowhiskers support for synthesis of eugenyl benzoate. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 48:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2017.1405021
Ameri A, Shakibaie M, Khoobi M, Faramarzi MA, Ameri A, Forootanfar H (2019) Immobilization of thermoalkalophilic lipase from Bacillus atrophaeus FSHM2 on amine-modified graphene oxide nanostructures: statistical optimization and its application for pentyl valerate synthesis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03180-1
Amin F, Bhatti HN, Bilal M, Asgher M (2017) Improvement of activity, thermo-stability and fruit juice clarification characteristics of fungal exo-polygalacturonase. Int J Biol Macromol 95:974–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.086
Ashnani MHM, Johari A, Hashim H, Hasani E (2014) A source of renewable energy in Malaysia, why biodiesel? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 35:244–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.04.001
Bassi JJ et al (2016) Interfacial activation of lipases on hydrophobic support and application in the synthesis of a lubricant ester. Int J Biol Macromol 92:900–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.097
Bayramoğlu G, Hazer B, Altıntaş B, Arıca MY (2011) Covalent immobilization of lipase onto amine functionalized polypropylene membrane and its application in green apple flavor (ethyl valerate) synthesis. Process Biochem 46:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.09.014
Bedade DK, Sutar YB, Singhal RS (2019) Chitosan coated calcium alginate beads for covalent immobilization of acrylamidase: process parameters and removal of acrylamide from coffee. Food Chem 275:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.090
Bisswanger H (2014) Enzyme assays. Perspect Sci 1:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pisc.2014.02.005
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brito MJP, Veloso CM, Bonomo RCF, Fontan RdCI, Santos LS, Monteiro KA (2017) Activated carbons preparation from yellow mombin fruit stones for lipase immobilization. Fuel Process Technol 156:421–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.10.003
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhang H, Wang K (2012) Preparation and antibacterial property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration hybrid membrane containing halloysite nanotubes loaded with copper ions. Chem Eng J 210:298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.100
Chen H, Zhang Q, Dang Y, Shu G (2013) The effect of glutaraldehyde cross-linking on the enzyme activity of immobilized β-galactosidase on chitosan bead. Adv J Food Sci Technol 5:932–935
Chylińska M, Szymańska-Chargot M, Zdunek A (2014) Imaging of polysaccharides in the tomato cell wall with Raman microspectroscopy. Plant Methods 10:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-10-14
Corradini MCC, Costa BM, Bressani APP, Garcia KC, Pereira EB, Mendes AA (2017) Improvement of the enzymatic synthesis of ethyl valerate by esterification reaction in a solvent system. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2016.1181084
Coşkun G, Çıplak Z, Yıldız N, Mehmetoğlu Ü (2020) Immobilization of Candida antarctica lipase on nanomaterials and investigation of the enzyme activity and enantioselectivity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03443-2
Dhawane SH, Kumar T, Halder G (2016a) Biodiesel synthesis from Hevea brasiliensis oil employing carbon supported heterogeneous catalyst: optimization by Taguchi method. Renew Energy 89:506–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.12.027
Dhawane SH, Kumar T, Halder G (2016b) Parametric effects and optimization on synthesis of iron (II) doped carbonaceous catalyst for the production of biodiesel. Energy Convers Manage 122:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.06.005
dos Santos MMO et al (2020) Application of lipase immobilized on a hydrophobic support for the synthesis of aromatic esters. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1959
Elias N, Chandren S, Attan N, Mahat NA, Razak FIA, Jamalis J, Wahab RA (2017) Structure and properties of oil palm-based nanocellulose reinforced chitosan nanocomposite for efficient synthesis of butyl butyrate. Carbohydr Polym 176:281–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.097
Elias N, Chandren S, Razak FIA, Jamalis J, Widodo N, Wahab RA (2018) Characterization, optimization and stability studies on Candida rugosa lipase supported on nanocellulose reinforced chitosan prepared from oil palm biomass. Int J Biol Macromol 114:306–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.095
Elias N, Wahab RA, Chandren S, Jamalis J, Mahat NA, Jye LW (2020) Structure and properties of lipase activated by cellulose-silica polyethersulfone membrane for production of pentyl valerate. Carbohydr Polym 245:116549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116549
Engliman NS, Jahim JM, Abdul PM, Ling TP, Tan JP, Ong CB (2020) Effectiveness of fouling mechanism for bacterial immobilization in polyvinylidene fluoride membranes for biohydrogen fermentation. Food Bioprod Process 120:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2019.12.004
Eş I, Vieira JDG, Amaral AC (2015) Principles, techniques, and applications of biocatalyst immobilization for industrial application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2065–2082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6390-y
Fediuk R, Timokhin R, Mochalov A, Otsokov K, Lashina I (2019) Performance properties of high-density impermeable cementitious paste. J Mater Civ Eng 31:04019013. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002633
Fernandez-Lorente G, Rocha-Martín J, Guisan JM (2020) Immobilization of lipases by adsorption on hydrophobic supports: modulation of enzyme properties in biotransformations in anhydrous media. In: Guisan J, Bolivar J, López-Gallego F, Rocha-Martín J (eds) Immobilization of enzymes and cells: methods in molecular biology, vol 2100. Springer, New York, pp 143–158
Golbaha N, Ramli Z, Endud S (2016) Immobilization of lipase onto mesoporous silica KIT-6 and montmorillonite K10 for enzymatic hydrolysis of tributyrin. Malay J Fundam Appl Sci https://doi.org/10.11113/mjfas.v12n1.419
Gumbi NN, Hu M, Mamba BB, Li J, Nxumalo EN (2018) Macrovoid-free PES/SPSf/O-MWCNT ultrafiltration membranes with improved mechanical strength, antifouling and antibacterial properties. J Membr Sci 566:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.09.009
Gupta S, Mazumder P, Scott D, Ashokkumar M (2020) Ultrasound-assisted production of biodiesel using engineered methanol tolerant Proteus vulgaris lipase immobilized on functionalized polysulfone beads. Ultrason Sonochem 68:105211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105211
Huang X-J, Yu A-G, Xu Z-K (2008) Covalent immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa onto poly (acrylonitrile-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) electrospun fibrous membranes for potential bioreactor application. Bioresour Technol 99:5459–5465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.009
Hussin FNNM, Attan N, Wahab RA (2020) Taguchi design-assisted immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase onto a ternary alginate/nanocellulose/montmorillonite composite: physicochemical characterization, thermal stability and reusability studies. Enzyme Microb Technol 136:109506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109506
Isah AA, Mahat NA, Jamalis J, Attan N, Zakaria II, Huyop F, Wahab RA (2017) Synthesis of geranyl propionate in a solvent-free medium using Rhizomucor miehei lipase covalently immobilized on chitosan–graphene oxide beads. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2016.1201681
Jafarian F, Bordbar A-K, Razmjou A, Zare A (2020) The fabrication of a high performance enzymatic hybrid membrane reactor (EHMR) containing immobilized Candida rugosa lipase (CRL) onto graphene oxide nanosheets-blended polyethersulfone membrane. J Membr Sci 613:118435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118435
Jambulingam R, Shalma M, Shankar V (2019) Biodiesel production using lipase immobilised functionalized magnetic nanocatalyst from oleaginous fungal lipid. J Clean Prod 215:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.146
Jun LY et al (2020) Modelling of methylene blue adsorption using peroxidase immobilized functionalized Buckypaper/polyvinyl alcohol membrane via ant colony optimization. Environ Pollut 259:113940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113940
Kumar D, Das T, Giri BS, Verma B (2020) Optimization of biodiesel synthesis from nonedible oil using immobilized bio-support catalysts in jacketed packed bed bioreactor by response surface methodology. J Clean Prod 244:118700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118700
Lage FA, Bassi JJ, Corradini MC, Todero LM, Luiz JH, Mendes AA (2016) Preparation of a biocatalyst via physical adsorption of lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus on hydrophobic support to catalyze biolubricant synthesis by esterification reaction in a solvent-free system. Enzyme Microb Technol 84:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2015.12.007
Lai J-Q, Li Z, Lü Y-H, Yang Z (2011) Specific ion effects of ionic liquids on enzyme activity and stability. Green Chem 13:1860–1868. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1GC15140A
Lee J-W, Trinh CT (2020) Towards renewable flavors, fragrances, and beyond. Curr Opin Biotechnol 61:168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2019.12.017
Li K, Fan Y, He Y, Zeng L, Han X, Yan Y (2017) Burkholderia cepacia lipase immobilized on heterofunctional magnetic nanoparticles and its application in biodiesel synthesis. Sci Rep 7:16473. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16626-5
Manan FMA, Rahman INA, Marzuki NHC, Mahat NA, Huyop F, Wahab RA (2016) Statistical modelling of eugenol benzoate synthesis using Rhizomucor miehei lipase reinforced nanobioconjugates. Process Biochem 51:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.12.002
Matuoog N, Li K, Yan Y (2018) Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles and its application in the hydrolysis of fish oil. J Food Biochem 42:e12549. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12549
Mazlan SZ, Hanifah SA (2017) Effects of temperature and pH on immobilized laccase activity in conjugated methacrylate-acrylate microspheres. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5657271
Mendes AA, Freitas L, de Carvalho AK, de Oliveira PC, de Castro HF (2011) Immobilization of a commercial lipase from Penicillium camembertii (Lipase G) by different strategies. Enzyme Res 2011:967239. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/967239
Migneault I, Dartiguenave C, Bertrand MJ, Waldron KC (2004) Glutaraldehyde: behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 37:790–802. https://doi.org/10.2144/04375RV01
Mishra A, Ghosh S (2019) Bioethanol production from various lignocellulosic feedstocks by a novel “fractional hydrolysis” technique with different inorganic acids and co-culture fermentation. Fuel 236:544–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.09.024
Mohamad N, Buang NA, Mahat NA, Jamalis J, Huyop F, Aboul-Enein HY, Wahab RA (2015) Simple adsorption of Candida rugosa lipase onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes for sustainable production of the flavor ester geranyl propionate. J Ind Eng Chem 32:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.08.001
Onoja E, Wahab RA (2020) Robust magnetized oil palm leaves ash nanosilica composite as lipase support: Immobilization protocol and efficacy study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03348-0
Onoja E, Chandren S, Razak FIA, Wahab RA (2018) Extraction of nanosilica from oil palm leaves and its application as support for lipase immobilization. J Biotechnol 283:81–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.07.036
Osuna Y et al (2015) Immobilization of Aspergillus niger lipase on chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles using two covalent-binding methods. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:1437–1445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1385-8
Pérez-Silva I, Galán-Vidal CA, Ramírez-Silva MT, Romero GAÁ, Páez-Hernández ME (2018) Evaluation of activated composite membranes for the facilitated transport of phenol. E-Polymers 18:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1515/epoly-2018-0002
Plan EM (2015) Pursuing green growth for sustainability and resilience
Radovanović M, Jugović B, Gvozdenović M, Jokić B, Grgur B, Bugarski B, Knežević-Jugović Z (2016) Immobilization of α-amylase via adsorption on magnetic particles coated with polyaniline. Starch-Stärke 68:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201500161
Rahman INA, Attan N, Mahat NA, Jamalis J, Keyon ASA, Kurniawan C, Wahab RA (2018) Statistical optimization and operational stability of Rhizomucor miehei lipase supported on magnetic chitosan/chitin nanoparticles for synthesis of pentyl valerate. Int J Biol Macromol 115:680–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.111
Razmjou A, Mansouri J, Chen V (2011) The effects of mechanical and chemical modification of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface chemistry, structure and fouling performance of PES ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 378:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.10.019
Ren M-Y, Bai S, Zhang D-H, Sun Y (2008) pH memory of immobilized lipase for (±)-menthol resolution in ionic liquid. J Agric Food Chem 56:2388–2391. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf073067f
Sahin S, Ozmen I (2020) Immobilization of pectinase on Zr-treated pumice for fruit juice industry. J Food Process Preserv 44:e14661. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14661
Soemphol W, Charee P, Audtarat S, Sompech S, Hongsachart P, Dasri T (2020) Characterization of a bacterial cellulose-silica nanocomposite prepared from agricultural waste products. Mater Res Express 7:015085. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6c25
Subtil EL et al (2020) Preparation and characterization of a new composite conductive polyethersulfone membrane using polyaniline (PANI) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO). Chem Eng J 390:124612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124612
Torres MdPG, Foresti ML, Ferreira ML (2013) Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) of selected lipases: a procedure for the proper calculation of their recovered activity. AMB Express 3:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-0855-3-25
Vatanpour V, Madaeni SS, Rajabi L, Zinadini S, Derakhshan AA (2012) Boehmite nanoparticles as a new nanofiller for preparation of antifouling mixed matrix membranes. J Membr Sci 401:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.01.040
Wang J, Li K, He Y, Wang Y, Han X, Yan Y (2019) Enhanced performance of lipase immobilized onto Co2+-chelated magnetic nanoparticles and its application in biodiesel production. Fuel 255:115794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115794
Xie W, Ma N (2010) Enzymatic transesterification of soybean oil by using immobilized lipase on magnetic nano-particles. Biomass Bioenergy 34:890–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.01.034
Xie W, Huang M (2020) Fabrication of immobilized Candida rugosa lipase on magnetic Fe3O4-poly (glycidyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) composite as an efficient and recyclable biocatalyst for enzymatic production of biodiesel. Renew Energy 158:474–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.172
Yi S, Dai F, Zhao C, Si Y (2017) A reverse micelle strategy for fabricating magnetic lipase-immobilized nanoparticles with robust enzymatic activity. Sci Rep 7:9806. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10453-4
Yuan B, Zhang J, Mi Q, Yu J, Song R, Zhang J (2017) Transparent cellulose–silica composite aerogels with excellent flame retardancy via an in situ sol–gel process. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:11117–11123. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03211
Zhang D-H, Peng L-J, Wang Y, Li Y-Q (2015) Lipase immobilization on epoxy-activated poly(vinyl acetate-acrylamide) microspheres. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 129:206–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.03.056
Zhao X, Qi F, Yuan C, Du W, Liu D (2015) Lipase-catalyzed process for biodiesel production: enzyme immobilization, process simulation and optimization. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 44:182–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.12.021
Zhu J, Sun G (2012) Lipase immobilization on glutaraldehyde-activated nanofibrous membranes for improved enzyme stabilities and activities. React Funct Polym 72:839–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2012.08.001
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia for their facilities. This work was funded by Yayasan Sultan Iskandar, Johor and the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) (R.J130000.7854.5F013) awarded by Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: RAW. Methodology: NE. Formal analysis and investigation: NE. Writing—original draft preparation: NE. Writing—review and editing: RAW, LWJ, NAM, SC and JJ. Funding acquisition: RAW. Resources: RAW and LWJ. Supervision: RAW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human or animal rights
Human or animal rights applicable to influence the outcomes of the present research.
Informed consent
Informed consent applicable to influence the outcomes of the present research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elias, N., Wahab, R.A., Jye, L.W. et al. Taguchi orthogonal design assisted immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase onto nanocellulose-silica reinforced polyethersulfone membrane: physicochemical characterization and operational stability. Cellulose 28, 5669–5691 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03886-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03886-8