Abstract
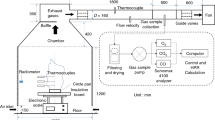
Ethanol is often used as a humectant during the storage of nitrocellulose (NC). To mitigate the fire hazard of NC, which is a highly flammable compound, during storage, and to understand the fire hazards of NC–ethanol mixtures, it is imperative to study the thermal behavior of NC–ethanol mixtures and determine the optimal range of ethanol content in the mixture. In this study, the decomposition and burning behaviors of NC–ethanol mixtures with different ethanol contents (0–100%) were studied via thermogravimetric (TG) analysis and cone calorimetry (ISO 5660), respectively. The results of TG/differential TG analyses suggested that NC samples with a low ethanol content are more prone to thermal runaway such as burning or explosion during their decomposition under a constant temperature increase. Furthermore, ignition and burning characteristics of the mixtures, which were analyzed by cone calorimetry, revealed that the ignition of the sample is mainly caused by the volatilization of ethanol. According to the results, an ethanol content of ~ 30–50% helps reduce the thermal hazard of NC during fire. This study provides a perspective on ensuring the safe storage of NC, and elucidates effective fire suppression and rescue measures for fires caused by such materials.
Graphic abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakhtiyari S, Taghi-Akbari L, Ashtiani MJ (2015) Evaluation of thermal fire hazard of 10 polymeric building materials and proposing a classification method based on cone calorimeter results. Fire Mater 39:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.2219
Benhammada A, Trache D (2020) Thermal decomposition of energetic materials using TG-FTIR and TG-MS: a state-of-the-art review. Appl Spectrosc Rev 55:724–777
Chai H, Duan Q, Jiang L et al (2019) Theoretical and experimental study on the effect of nitrogen content on the thermal characteristics of nitrocellulose under low heating rates. Cellulose 26:763–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2100-0
Chai H, Duan Q, Cao H et al (2020) Effects of nitrogen content on pyrolysis behavior of nitrocellulose. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116853
Fu G, Wang J, Yan M (2016) Anatomy of Tianjin Port fire and explosion: process and causes. Process Saf Prog 35:216–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/prs.11837
Gao X, Jiang L, Xu Q (2020a) Experimental and theoretical study on thermal kinetics and reactive mechanism of nitrocellulose pyrolysis by traditional multi kinetics and modeling reconstruction. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121645
Gao X, Jiang L, Xu Q et al (2020b) Thermal kinetics and reactive mechanism of cellulose nitrate decomposition by traditional multi kinetics and modeling calculation under isothermal and non-isothermal conditions. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112085
He Y, He Y, Liu J et al (2017) Experimental study on the thermal decomposition and combustion characteristics of nitrocellulose with different alcohol humectants. J Hazard Mater 340:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.029
ISO 5660–1 (2002) Reaction-to-fire tests -- Heat release, smoke production and mass loss rate -- Part 1: Heat Release rate (cone calorimeter method). Int Stand
Liu J, Chen M (2018) A simplified method to predict the heat release rate of industrial nitrocellulose materials. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060910
Liu J, He Y, Wang J et al (2019) Investigation on the combustion efficiency and residual of nitrocellulose–alcohol humectant mixtures. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:1807–1816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7817-3
Mi W, Wei R, Zhou T et al (2019) Experimental study on the thermal decomposition of two nitrocellulose mixtures in different forms. Medziagotyra 25:60–65. https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.ms.25.1.18907
Petrella RV (1994) The assessment of full-scale fire hazards from cone calorimeter data. J Fire Sci 12:14–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/073490419401200102
Pourmortazavi SM, Hosseini SG, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M et al (2009) Effect of nitrate content on thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. J Hazard Mater 162:1141–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.161
Sovizi MR, Hajimirsadeghi SS, Naderizadeh B (2009) Effect of particle size on thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. J Hazard Mater 168:1134–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.146
Tarchoun AF, Trache D, Klapötke TM et al (2020a) Synthesis, characterization, and thermal decomposition kinetics of Nitrogen-rich energetic biopolymers from aminated giant reed cellulosic fibers. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:22677–22689. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05448
Tarchoun AF, Trache D, Klapötke TM et al (2020b) A promising energetic biopolymer based on azide-functionalized microcrystalline cellulose: synthesis and characterization. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116820
Tarchoun AF, Trache D, Klapötke TM, Khimeche K (2020c) Tetrazole-functionalized microcrystalline cellulose: a promising biopolymer for advanced energetic materials. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125960
Tarchoun AF, Trache D, Klapoetke TM et al (2021a) New insensitive high-energy dense biopolymers from giant reed cellulosic fibers: synthesis, characterization, and non-isothermal decomposition kinetics. New J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ05484D
Tarchoun AF, Trache D, Klapötke TM et al (2021b) Synthesis and characterization of new insensitive and high-energy dense cellulosic biopolymers. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120347
Trache D, Tarchoun AF (2019) Analytical methods for stability assessment of Nitrate Esters-based propellants. Crit Rev Anal Chem 49:415–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2018.1540921
Wang X, He Y, Zhou T et al (2018) Experimental study on fire behaviors of Kerosene/additive blends. Fire Technol 54:1841–1869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-018-0776-1
Wei R, He Y, Liu J et al (2017) Experimental study on the fire properties of nitrocellulose with different structures. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030316
Wei R, He Y, Zhang Z et al (2018a) Effect of different humectants on the thermal stability and fire hazard of nitrocellulose. J Therm Anal Calorim 133:1291–1307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7235-6
Wei R, Huang S, Huang Q et al (2018b) Experimental study on the fire characteristics of typical nitrocellulose mixtures using a cone calorimeter. J Therm Anal Calorim 134:1471–1480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7410-9
Wei R, Huang S, Wang Z et al (2018c) Effect of plasticizer dibutyl phthalate on the thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. J Therm Anal Calorim 134:953–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7521-3
Wei R, Huang S, Wang Z et al (2019) Thermal behavior of nitrocellulose with different aging periods. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:651–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7653-5
Xiao J, Das O, Mensah RA et al (2021) Ablation behavior studies of charring materials with different thickness and heat flux intensity. Case Stud Therm Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2020.100814
Xie T, Wei R, Wang Z, Wang J (2020) Comparative analysis of thermal oxidative decomposition and fire characteristics for different straw powders via thermogravimetry and cone calorimetry. Process Saf Environ Prot 134:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.11.028
Zhang X, Weeks BL (2014) Preparation of sub-micron nitrocellulose particles for improved combustion behavior. J Hazard Mater 268:224–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.019
Zhao B (2016) Facts and lessons related to the explosion accident in Tianjin Port, China. Nat Hazards 84:707–713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2403-0
Acknowledgments
The experimental materials were provided by Sichuan Nitrocell Co., Ltd. (Luzhou, China). The experiments were carried out with the assistance of the Physical and Chemical Center of the University of Science and Technology of China and the Engineering Experiment Center of the City University of Hong Kong. We, the authors, express our sincere gratitude for this.
Funding
This work was supported by the National key Research and Development Program [Grant No. 2018YFC0808600].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH: Methodology, Writing–review & editing. RW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing–original draft. JW: Data curation, Investigation. JW: Resources; Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Human or animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Wei, R., Weng, J. et al. An experimental study on the effects of ethanol content on the decomposition and burning risks of nitrocellulose. Cellulose 28, 4595–4609 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03837-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03837-3