Abstract
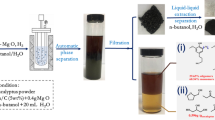
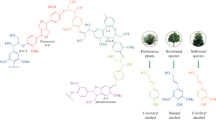
Lignocellulosic wastes obtained from vegetal residues in combination with nucleophiles were used as catalysts for carbon dioxide fixation in epoxides to form cyclic carbonates. An adequate combination of the residue and the nucleophile was essential to obtain active catalytic systems. The best binary systems were formed by olive bones, grape waste, date pit and corn leaves husk residues with tetrabutylammonium bromide (TBAB). High conversions in the cycloaddition of CO2 to propylene oxide (76–84%) and 1,2-epoxyhexane (68–79%) were achieved at very low nucleophile loading (0.47 mol % respect to the substrate) under mild conditions (95 °C and 10 atm of CO2). The vegetal wastes were stable under catalytic conditions and could be recycled after adequately supporting the nucleophile TBAB in silica gel. The mechanistic computational study carried out with Density Functional Theory calculations on model catalysts describes the contribution of individual lignin and cellulosic components to the experimental substrate conversion into cyclic carbonate. The energy barriers obtained and the experimental data suggest that the contribution of lignin to the total catalytic activity (barrier energy of 9.9 kcal/mol) may be more important than the contribution of cellulose (energy barrier 11.9 kcal/mol).
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alper E, Orhan OY (2017) CO2 utilization: developments in conversion processes. Petroleum 3:109–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petlm.2016.11.003
Aresta M (2010) Carbon dioxide: utilization options to reduce its accumulation in the atmosphere. In: Carbon dioxide as chemical feedstock, pp 1–13
Aresta M, Dibenedetto A, Quaranta E (2016) The carbon dioxide molecule. In: Reaction mechanisms in carbon dioxide conversion. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–34
Beyzavi MH, Stephenson CJ, Liu Y et al (2015) Metal–organic framework-based catalysts: chemical fixation of CO2 with epoxides leading to cyclic organic carbonates. Front Energy Res 2:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2014.00063
Bhanage BM, Arai M (2014) Transformation and utilization of carbon dioxide. Springer, Heildelberg
Caló V, Nacci A, Monopoli A, Fanizzi A (2002) Cyclic carbonate formation from carbon dioxide and oxiranes in tetrabutylammonium halides as solvents and catalysts. Org Lett 4:2561–2563. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol026189w
Caulfield DF (2005) Handbook of wood chemistry and wood composites. Handb Wood Chem Wood Compos. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203492437
Centi G, Perathoner S (2014) Green carbon dioxide, advances in CO2 utilization. Wiley, Hoboken
Chang H, Li Q, Cui X et al (2018) Conversion of carbon dioxide into cyclic carbonates using wool powder-KI as catalyst. J CO2 Util 24:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2017.12.017
Chen Y, Mu T (2019) Conversion of CO2 to value-added products mediated by ionic liquids. Green Chem 21:2544–2574. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00827F
Chen W, Zhong L, Peng X et al (2015) Chemical fixation of carbon dioxide using a green and efficient catalytic system based on sugarcane bagasse an agricultural waste. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc5006445
Claver C, Bin YeaminM, Reguero M, Masdeu-Bultó AM (2020) Recent advances in the use of catalysts based on natural products for the conversion of CO2 into cyclic carbonates. Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC01870H
Cokoja M, Wilhelm ME, Anthofer MH et al (2015) Synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and carbon dioxide by using organocatalysts. Chemsuschem 8:2436–2454. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201500161
Colmenares JC, Kuna E (2017) Photoactive Hybrid catalysts based on natural and synthetic polymers: a comparative overview. Molecules 22:790. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050790
Comerford JW, Ingram IDV, North M, Wu X (2015) Sustainable metal-based catalysts for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates containing five-membered rings. Green Chem 17:1966–1987. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc01719f
Cooper JF, Myri L (1956) Catalytic process for producing alkylene carbonates
Corma A, Iborra S, Velty A (2007) Chemical routes for the transformation of biomass into chemicals. Chem Rev 107:2411–2502. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr050989d
Cuesta-Aluja L, Campos-Carrasco A, Castilla J et al (2016) Highly active and selective Zn(II)-NN′O schiff base catalysts for the cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides. J CO2 Util 14:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2016.01.002
Decortes A, Castilla AM, Kleij AW (2010) Salen-complex-mediated formation of cyclic carbonates by cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:9822–9837. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201002087
Dong Y, Bi J, Zhu D et al (2019) Functionalized cellulose with multiple binding sites for a palladium complex catalyst: synthesis and catalyst evaluation in Suzuki-Miyaura reactions. Cellulose 26:7355–7370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02568-w
Ema T, Miyazaki Y, Shimonishi J et al (2014) Bifunctional porphyrin catalysts for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and CO2: structural optimization and mechanistic study. J Am Chem Soc 136:15270–15279. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja507665a
Foltran S, Mereau R, Tassaing T (2014) Theoretical study on the chemical fixation of carbon dioxide with propylene oxide catalyzed by ammonium and guanidinium salts. Catal Sci Technol 4:1585–1597. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cy00955f
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, et al (2016) Gaussian 16 Rev. B.01
Gennen S, Grignard B, Tassaing T et al (2017) CO2-sourced α-alkylidene cyclic carbonates: a step forward in the quest for functional regioregular poly(urethane)s and poly(carbonate)s. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:10394–10398. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201704467
Guo W, Gómez JE, Cristòfol À et al (2018) Catalytic transformations of functionalized cyclic organic carbonates. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:13735–13747. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201805009
Hatfield R, Fukushima RS (2005) Can lignin be accurately measured? Crop Sci 45:832–839. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2004.0238
He Q, O’Brien JW, Kitselman KA et al (2014) Synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and epoxides using ionic liquids and related catalysts including choline chloride-metal halide mixtures. Catal Sci Technol 4:1513–1528. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cy00998j
Hong M, Kim Y, Kim H et al (2018) Scorpionate catalysts for coupling CO2 and epoxides to cyclic carbonates: a rational design approach for organocatalysts. J Org Chem 83:9370–9380. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.8b00722
Hu T, Sun Y, Ding Y (2018) A quantum-chemical insight on chemical fixation carbon dioxide with epoxides co-catalyzed by MIL-101 and tetrabutylammonium bromide. J CO2 Util 28:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2018.09.027
Ioelovich M (2015) Methods for determination of chemical composition of plant biomass. J SITA 17:208–214
Li X, Cheetham AK, Jiang J (2019) CO2 cycloaddition with propylene oxide to form propylene carbonate on a copper metal-organic framework: a density functional theory study. Mol Catal 463:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2018.11.015
Liang S, Liu H, Jiang T et al (2011) Highly efficient synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and epoxides over cellulose/KI. Chem Commun 47:2131–2133. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc04829a
Liu N, Xie Y-F, Wang C et al (2018) Cooperative multifunctional organocatalysts for ambient conversion of carbon dioxide into cyclic carbonates. ACS Catal. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b01925
Liu M, Wang X, Jiang Y et al (2019) Hydrogen bond activation strategy for cyclic carbonates synthesis from epoxides and CO2: current state-of-the art of catalyst development and reaction analysis. Catal Rev Sci Eng 61:214–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/01614940.2018.1550243
Maeda C, Taniguchi T, Ogawa K, Ema T (2015) Bifunctional catalysts based on m-phenylene-bridged porphyrin dimer and trimer platforms: synthesis of cyclic carbonates from carbon dioxide and epoxides. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201409729
Mahmudov KT, Gurbanov AV, Guseinov FI, da Silva MFCG (2019) Noncovalent interactions in metal complex catalysis. Coord Chem Rev 387:32–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.02.011
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J Phys Chem B 113:6378–6396. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp810292n
Meléndez J, North M, Pasquale R (2007) Synthesis of cyclic carbonates from atmospheric pressure carbon dioxide using exceptionally active aluminium(salen) complexes as catalysts. Eur J Inorg Chem 2007:3323–3326. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200700521
Nguyen PTK, Nguyen HTD, Nguyen HN et al (2018) New metal-organic frameworks for chemical fixation of CO2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:733–744. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b16163
Peppel WJ (1958) Preparation and properties of the alkylene carbonates. Ind Eng Chem 50:767–770. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50581a030
Putro JN, Soetaredjo FE, Lin SY et al (2016) Pretreatment and conversion of lignocellulose biomass into valuable chemicals. RSC Adv 6:46834–46852. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra09851g
Ripple WJ, Wolf C, Newsome TM et al (2017) World scientists’ warning to humanity: a second notice. Bioscience 67:1026–1028. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/bix125
Ruiz L, Aghmiz A, Masdeu-Bultó AM et al (2017) Upgrading castor oil: from heptanal to non-isocyanate poly(amide-hydroxyurethane)s. Polymer (Guildf) 124:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.07.070
Schäffner B, Schäffner F, Verevkin SP, Börner A (2010) Organic carbonates as solvents in synthesis and catalysis. Chem Rev 110:4554–4581. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900393d
Shaikh A-AG, Sivaram S (1996) Organic carbonates. Chem Rev 96:951–976. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr950067i
Shaikh RR, Pornpraprom S, D’Elia V et al (2018) Catalytic strategies for the cycloaddition of pure, diluted, and waste CO2 to epoxides under ambient conditions. ACS Catal 8:419–450. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b03580
Sun J, Fujita S, Arai M (2005) Development in the green synthesis of cyclic carbonate from carbon dioxide using ionic liquids. J Organomet Chem 690:3490–3497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.02.011
Sun J, Cheng W, Yang Z et al (2014) Superbase/cellulose: an environmentally benign catalyst for chemical fixation of carbon dioxide into cyclic carbonates. Green Chem 16:3071–3078. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc41850b
Sun Q, Jin Y, Aguila B et al (2017) Porous ionic polymers as a robust and efficient platform for capture and chemical fixation of atmospheric CO2. Chemsuschem 10:1160–1165. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201601350
Thomas B, Raj MC et al (2018) Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications. Chem Rev 118:11575–11625. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00627
Tundo P, Selva M (2005) Continuous-flow, gas phase synthesis of 1-chlorobutane (1-bromobutane) from 1-butanol and aqueous HCl (HBr) over silica-supported quaternary phosphonium salt. Green Chem 7:464–467. https://doi.org/10.1039/b418941h
Tursi A (2019) A review on biomass: importance, chemistry, classification, and conversion. Biofuel Res J 6:962–979
Wang J (2015) Hydrogen bond donor-promoted fixation of CO2 with epoxides into cyclic carbonates: moving forward. Curr Green Chem 2:3–13. https://doi.org/10.2174/2213346101666140630164855
Watts HD, Mohamed MNA, Kubicki JD (2014) A DFT study of vibrational frequencies and 13C NMR chemical shifts of model cellulosic fragments as a function of size. Cellulose 21:53–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0128-8
Whiteoak CJ, Kielland N, Laserna V et al (2013) A powerful aluminum catalyst for the synthesis of highly functional organic carbonates. J Am Chem Soc 135:1228–1231. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja311053h
Wilhelm ME, Anthofer MH, Reich RM et al (2014) Niobium(v) chloride and imidazolium bromides as efficient dual catalyst systems for the cycloaddition of carbon dioxide and propylene oxide. Catal Sci Technol 4:1638–1643. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cy01057k
Wu Z, Xie H, Yu X, Liu E (2013) Lignin-based green catalyst for the chemical fixation of carbon dioxide with epoxides to form cyclic carbonates under solvent-free conditions. ChemCatChem 5:1328–1333. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201200894
Yamaguchi K, Ebitani K, Yoshida T et al (1999) Mg-Al mixed oxides as highly active acid-base catalysts for cycloaddition of carbon dioxide to epoxides. J Am Chem Soc 121:4526–4527. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9902165
Yang Y, Tilman D (2020) Soil and root carbon storage is key to climate benefits of bioenergy crops. Biofuel Res J 7:1143–1148. https://doi.org/10.18331/BRJ2020.7.2.2
Yang H, Watts HD, Gibilterra V et al (2019) Quantum calculations on plant cell wall component interactions. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 11:485–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-018-0293-4
Yingcharoen P, Kongtes C, Arayachukiat S et al (2019) Assessing the pKa-dependent activity of hydroxyl hydrogen bond donors in the organocatalyzed cycloaddition of carbon dioxide to epoxides: experimental and theoretical study. Adv Synth Catal 361:366–373. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201801093
Yu JL, Zhang SQ, Hong X (2017) Mechanisms and origins of chemo- and regioselectivities of Ru(II)-catalyzed decarboxylative C–H alkenylation of aryl carboxylic acids with alkynes: a computational study. J Am Chem Soc 139:7224–7243. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b00714
Zhao H, Park SJ, Shi F et al (2014) Propylene carbonate (PC)-based electrolytes with high coulombic efficiency for lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 161:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.095401jes
Zhou Z, He C, Xiu J et al (2015) Metal–organic polymers containing discrete single-walled nanotube as a heterogeneous catalyst for the cycloaddition of carbon dioxide to epoxides. J Am Chem Soc 137:15066–15069. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b07925
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad and AEI/FEDER UE (CTQ2016-75016-R and CTQ2017-83566-P), Departament d’Economia i Coneixement (2017 SGR 1472 and 2017 SGR 629) and Xarxa d’R + D + I en Química Computacional (XRQTC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10570_2020_3522_MOESM1_ESM.docx
The xyz coordinates of the DFT calculations of this article can be found in a figshare data repository (See at https://figshare.com/s/84bc57f3018e66bf3618). (DOCX 6970 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Ouahabi, M.S., Yeamin, M.B., Rivas, R. et al. Lignocellulosic residues as catalysts for CO2 fixation: complementary experimental and computational approaches. Cellulose 28, 359–375 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03522-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03522-x