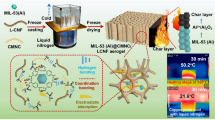
Abstract
Cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) produced from waste lignocellulosic biomass have emerged as a sustainable source material for high value-added applications. In the current study, previously unreported entangled cellulose nanofibril and nanosheet (CNF/CNS) were obtained using Agave Tequilana Weber var. Azul leaves by means of a microfluidization process. These nanomaterials were investigated as potential biosorbents of Pb2+, for which three adsorption mechanisms were identified by XPS. At low initial concentrations of Pb2+ (C0 < 100 ppm), the adsorption-mechanism is governed by electrostatic interactions between carboxylate groups and Pb2+; meanwhile, at (C0 = 1000 ppm) mono and bi-dentate complexes dominate the adsorption-mechanism. Finally, when 110 < C0 < 1000 ppm, both mechanisms co-exist. The maximum adsorption capacity was 43.55 mg/g, according to the Langmuir model, while CNF/CNS showed the characteristic diffraction peaks of cellulose type II. Our results highlight the high potential of these novel CNF/CNS biosorbents in the treatment of wastewater contaminated with toxic metals and afford new insights on adsorption mechanisms.
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alle M, Bandi R, Lee S-H, Kim J-C (2020) Recent trends in isolation of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils from various forest wood and nonwood products and their application. In: Nanomaterials for agriculture and forestry applications. Elsevier Ltd, pp 41–80
Anderson R, Biong A, Gómez-Gualdrón DA (2020) Adsorption Isotherm Predictions for multiple molecules in MOFs using the same deep learning model. J Chem Theory Comput 16:1271–1283. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.9b00940
Bala T, Prasad BLV, Sastry M et al (2007) Interaction of different metal ions with carboxylic acid group: a quantitative study. J Phys Chem A 111:6183–6190. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp067906x
Boparai HK, Joseph M, O’Carroll DM (2011) Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. J Hazard Mater 186:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.029
Chávez-Guerrero L, Sepúlveda-Guzmán S, Rodríguez-Liñan C et al (2017) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanoplatelets from the parenchyma cells of Agave salmiana. Cellulose 24:3741–3752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1376-9
Chávez-Guerrero L, Sepúlveda-Guzmán S, Silva-Mendoza J et al (2018) Eco-friendly isolation of cellulose nanoplatelets through oxidation under mild conditions. Carbohydr Polym 181:642–649
Cholico-González D, Ortiz Lara N, Fernández Macedo AM, Chavez Salas J (2020) Adsorption behavior of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) onto agave bagasse, characterization, and mechanism. ACS Omega 5:3302–3314. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03385
de Myttenaere A, Golden B, Le Grand B, Rossi F (2016) Mean absolute percentage error for regression models. Neurocomputing 192:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.12.114
El Oudiani A, Chaabouni Y, Msahli S, Sakli F (2011) Crystal transition from cellulose i to cellulose II in NaOH treated Agave americana L. fibre. Carbohydr Polym 86:1221–1229
Espino E, Cakir M, Domenek S et al (2014) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from industrial by-products of Agave tequilana and barley. Ind Crops Prod 62:552–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.09.017
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD, Santiago Cintrón M (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 20:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
Gadd GM (2009) Biosorption: critical review of scientific rationale, environmental importance and significance for pollution treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:13–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1999
Grande-Tovar CD, Vallejo W, Zuluaga F (2018) Equilibrium and kinetic study of lead and copper ion adsorption on chitosan-grafted-polyacrylic acid synthesized by surface initiated atomic transfer polymerization. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092218
Hamdaoui O, Naffrechoux E (2007) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon. Part II. Models with more than two parameters. J Hazard Mater 147:401–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.023
Hokkanen S, Repo E, Sillanpää M (2013) Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by succinic anhydride modified mercerized nanocellulose. Chem Eng J 223:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.054
Jain CK, Malik DS, Yadav AK (2016) Applicability of plant based biosorbents in the removal of heavy metals: a review. Environ Process 3:495–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0143-5
Jiang JQ, Cooper C, Ouki S (2002) Comparison of modified montmorillonite adsorbents part I: preparation, characterization and phenol adsorption. Chemosphere 47:711–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00011-5
Johansson LS, Campbell JM (2004) Reproducible XPS on biopolymers: cellulose studies. Surf Interface Anal 36:1018–1022. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.1827
Kardam A, Raj KR, Srivastava S, Srivastava MM (2014) Nanocellulose fibers for biosorption of cadmium, nickel, and lead ions from aqueous solution. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-013-0634-2
Krishnadev P, Subramanian KS, Janavi GJ et al (2020) Synthesis and characterization of nano-fibrillated cellulose derived from Green Agave americana L. Fiber. 15:2442–2458
Kumar R, Sharma RK, Singh AP (2017) Cellulose based grafted biosorbents: journey from lignocellulose biomass to toxic metal ions sorption applications—a review. J Mol Liq 232:62–93
Lee B-G, Rowell Roger M (2004) Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using lignocellulosic fibers. J Nat Fibers 1:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1300/J395v01n01
Mansikkamäki P, Lahtinen M, Rissanen K (2007) The conversion from cellulose I to cellulose II in NaOH mercerization performed in alcohol-water systems: an X-ray powder diffraction study. Carbohydr Polym 68:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.07.010
Manzoor K, Ahmad M, Ahmad S, Ikram S (2019) Removal of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii) from wastewater using arginine cross-linked chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose beads as green adsorbent. RSC Adv 9:7890–7902. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00356H
Mariano M, Cercená R, Soldi V (2016) Thermal characterization of cellulose nanocrystals isolated from sisal fibers using acid hydrolysis. Ind Crops Prod 94:454–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.011
Mondal S (2017) Preparation, properties and applications of nanocellulosic materials. Carbohydr Polym 163:301–316
Morales-Medina R, Dong D, Schalow S, Drusch S (2020) Impact of microfluidization on the microstructure and functional properties of pea hull fibre. Food Hydrocoll 103:105660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105660
Morán JI, Alvarez VA, Cyras VP, Vázquez A (2008) Extraction of cellulose and preparation of nanocellulose from sisal fibers. Cellulose 15:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9145-9
Nasir MH, Nadeem R, Akhtar K et al (2007) Efficacy of modified distillation sludge of rose (Rosa centifolia) petals for lead(II) and zinc(II) removal from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 147:1006–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.131
Palacios Hinestroza H, Hernández Diaz JA, Esquivel Alfaro M et al (2019) Isolation and characterization of nanofibrillar cellulose from Agave tequilana Weber Bagasse. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1342547
Pérez S, Samain D (2010) Structure and Engineering of Celluloses. In: Horton D (ed) Advances in carbohydrate chemistry and biochemistry, first edit. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, pp 25–116
Poletto M, Zattera AJ, Santana RMC (2012) Structural differences between wood species: evidence from chemical composition, FTIR spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 126:E337–E344. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.36991
Rajinipriya M, Nagalakshmaiah M, Robert M, Elkoun S (2018) Importance of agricultural and industrial waste in the field of nanocellulose and recent industrial developments of wood based nanocellulose: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:2807–2828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03437
Robles E, Fernández-Rodríguez J, Barbosa AM et al (2018) Production of cellulose nanoparticles from blue agave waste treated with environmentally friendly processes. Carbohydr Polym 183:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.015
Saeed A, Akhter MW, Iqbal M (2005) Removal and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solution using papaya wood as a new biosorbent. Sep Purif Technol 45:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2005.02.004
Saito T, Kimura S, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromol 8:2485–2491. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0703970
Saito T, Kuramae R, Wohlert J et al (2013) An ultrastrong nanofibrillar biomaterial: the strength of single cellulose nanofibrils revealed via sonication-induced fragmentation. Biomacromol 14:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm301674e
Sari A, Tuzen M (2009) Kinetic and equilibrium studies of biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by macrofungus (Amanita rubescens) biomass. J Hazard Mater 164:1004–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.002
Shak KPY, Pang YL, Mah SK (2018) Nanocellulose: recent advances and its prospects in environmental remediation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:2479–2498. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.232
Sharma PR, Chattopadhyay A, Sharma SK et al (2018) Nanocellulose from spinifex as an effective adsorbent to remove cadmium(II) from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:3279–3290. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03473
Suopajärvi T, Liimatainen H, Karjalainen M et al (2015) Lead adsorption with sulfonated wheat pulp nanocelluloses. J Water Process Eng 5:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.06.003
Taty-Costodes VC, Fauduet H, Porte C, Delacroix A (2003) Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J Hazard Mater 105:121–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2003.07.009
Tiemann KJ, Gamez G, Dokken K et al (2002) Chemical modification and X-ray absorption studies for lead(II) binding by Medicago sativa (alfalfa) biomass. Microchem J 71:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-265X(02)00021-8
Tran HN, You SJ, Chao HP (2016) Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: a comparison study. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2671–2682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.05.009
TRC https://www.crt.org.mx/index.php/en/. In: Tequila Regul. Counc. 2019. https://www.crt.org.mx/index.php/en/. Accessed 13 Mar 2020
Velazquez-Jimenez LH, Pavlick A, Rangel-Mendez JR (2013) Chemical characterization of raw and treated agave bagasse and its potential as adsorbent of metal cations from water. Ind Crops Prod 43:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.06.049
Vieira MC, Heinze T, Antonio-Cruz R, Mendoza-Martinez AM (2002) Cellulose derivatives from cellulosic material isolated from Agave lechuguilla and fourcroydes. Cellulose 9:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020158128506
Wan Ngah WS, Hanafiah MAKM (2008) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresour Technol 99:3935–3948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011
Yang X, Reid MS, Olsén P, Berglund LA (2020) Eco-friendly cellulose nanofibrils designed by nature: effects from preserving native state. ACS Nano 14:724–735. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b07659
Yu X, Tong S, Ge M et al (2013) Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals. J Environ Sci (China) 25:933–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60145-4
Zhang X, Zhao J, Cheng L et al (2014) Acrylic acid grafted and acrylic acid/sodium humate grafted bamboo cellulose nanofibers for Cu2+ adsorption. RSC Adv 4:55195–55201. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra08307e
Acknowledgments
E. Hernández would like to acknowledge CONACYT (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología) for providing a Ph.D. scholarship. T. Lara and C.Y. Yin would like to acknowledge CONACYT and the British Council for providing bilateral grants through the Institutional Links-FONCICYT Program (Grant No. 276243) and the British Council Institutional Links programme (Newton Fund) (Grant No. 264232317). Also, the authors would like to thank Nayely Pineda and Alejandro Arizpe for assistance in SEM characterization, Gerardo Silva for help on XPS acquisitions and Isabel Mendivil for providing sputtered-coating samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest/competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Francisco, E., Bonilla-Cruz, J., Márquez-Lamas, U. et al. Entangled cellulose nanofibrils/nanosheets derived from native mexican agave for lead(II) ion removal. Cellulose 27, 8785–8798 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03373-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03373-6