Abstract
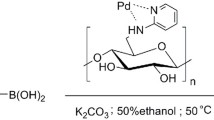
Biowaste resources are the promising renewable raw materials for green and economical purpose. In this context, usage of cellulose fibers as linear and flexible bio-polymer derived from waste lignocellulosic biomass has gained much attention in various applications due to their extensive properties such as eco-friendly, low cost, easy availability, low energy consumption, bio-degradability, high tensile strength and could be recyclable compared to other synthetic fibers those are expensive and non-decomposable in nature. In the present work, biogenically prepared palladium nanoparticles from waste banana pseudostem extract are immobilized on cellulose fibers, isolated from waste banana pseudostem as dip catalyst through green protocol for the first time. The synthesized new dip catalyst was characterized by ATR-IR, FE-SEM, EDS, ICP-OES, HR-TEM, p-XRD, TG/DTA, UV–Vis, GC–MS, XPS and BET surface area analysis. Catalytic potential and reusability of newly developed dip catalyst has been studied in Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions for the synthesis of various functional groups tolerated biaryls for practical applications. In addition, an analgesic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug molecule Felbinac was synthesized in greener reaction conditions by using dip catalyst with good yield.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Reziq R, Wang D, Post M, Alper H (2008) Separable catalysts in one-pot syntheses for greener chemistry. Chem Mater 20:2544–2550
áP Vinod M (1997) Pd–Cu–Exchanged montmorillonite K10 clay: an efficient and reusable heterogeneous catalyst for vinylation of aryl halides. ChemComm 21:2071–2072
Arafat K, Nayeem J, Quadery A, Quaiyyum M, Jahan MS (2018) Handmade paper from waste banana fibre. Bangladesh J Sci Ind Res 53:83–88
Balou J, Khalilzadeh MA, Zareyee D (2019) An efficient and reusable nano catalyst for the synthesis of benzoxanthene and chromene derivatives. Sci Rep 9:3605
Bankar A, Joshi B, Kumar AR, Zinjarde S (2010) Banana peel extract mediated novel route for the synthesis of palladium nanoparticles. Mater Lett 64:1951–1953
Biffis A, Zecca M, Basato M (2001) Palladium metal catalysts in Heck C–C coupling reactions. J Mol Catal A Chem 173:249–274
Boruah PR, Ali AA, Saikia B, Sarma D (2015) A novel green protocol for ligand free Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions in WEB at room temperature. Green Chem 17:1442–1445
Budtova T, Navard P (2016) Cellulose in NaOH–water based solvents: a review. Cellulose 23:5–55
Cordeiro N, Belgacem M, Torres I, Moura J (2004) Chemical composition and pulping of banana pseudo-stems. Ind Crops Prod 19:147–154
Deshmukh AA, Ul Islam R, Witcomb MJ, van Otterlo WA, Coville NJ (2010) Catalytic activity of metal nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon spheres. ChemCatChem 2:51–54
Dewan A, Sarmah M, Thakur AJ, Bharali P, Bora U (2018) Greener Biogenic approach for the synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using papaya peel: an eco-friendly catalyst for C–C coupling reaction. ACS Omega 3:5327–5335
Dhakshinamoorthy A, Garcia H (2012) Catalysis by metal nanoparticles embedded on metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 41:5262–5284
Djakovitch L, Koehler K (2001) Heck reaction catalyzed by Pd-modified zeolites. J Am Chem Soc 123:5990–5999
Doke DS, Advani JH, Naikwadi DR, Gawande MB, Walke P, Umbarkar SB et al (2019) Utilization of waste biomass for the synthesis of functionalizable support for covalent anchoring of active organo catalyst. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:3018–3026
Du Q, Zhang W, Ma H, Zheng J, Zhou B, Li Y (2012) Immobilized palladium on surface-modified Fe3O4/SiO2 nanoparticles: as a magnetically separable and stable recyclable high-performance catalyst for Suzuki and Heck cross-coupling reactions. Tetrahedron 68:3577–3584
Dubey AV, Kumar AV (2016) A biomimetic magnetically recoverable palladium nanocatalyst for the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. RSC Adv 6:46864–46870
Durap F, Rakap M, Aydemir M, Özkar S (2010) Room temperature aerobic Suzuki cross-coupling reactions in DMF/water mixture using zeolite confined palladium (0) nanoclusters as efficient and recyclable catalyst. Appl Catal A 382:339–344
Edwards GA, Trafford MA, Hamilton AE, Buxton AM, Bardeaux MC, Chalker JM (2014) Melamine and melamine-formaldehyde polymers as ligands for palladium and application to Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions in sustainable solvents. J Org Chem 79:2094–2104
Ezhilan BP, Neelamegam R (2012) GC–MS analysis of phytocomponents in the ethanol extract of Polygonum chinense L. Pharmacogn Res 4:11
Faria VW, Oliveira DG, Kurz MH, Gonçalves FF, Scheeren CW, Rosa GR (2014) Palladium nanoparticles supported in a polymeric membrane: an efficient phosphine-free “green” catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura reactions in water. RSC Adv 4:13446–13452
Frindy S, Primo A, Lahcini M, Bousmina M, Garcia H, El Kadib A (2015) Pd embedded in chitosan microspheres as tunable soft-materials for Sonogashira cross-coupling in water–ethanol mixture. Green Chem 17:1893–1898
Gong J, Li J, Xu J, Xiang Z, Mo L (2017) Research on cellulose nanocrystals produced from cellulose sources with various polymorphs. RSC Adv 7:33486–33493
Gurunathan S, Kim E, Han J, Park J, Kim J-H (2015) Green chemistry approach for synthesis of effective anticancer palladium nanoparticles. Molecules 20:22476–22498
Haleemkhan A, Naseem B, Vardhini B (2015) Synthesis of nanoparticles from plant extracts. Int J Mod Chem Appl Sci 2:195–203
Hariprasad E, Radhakrishnan TP (2012) Palladium nanoparticle-embedded polymer thin film “dip catalyst” for Suzuki-Miyaura reaction. ACS Catal 2:1179–1186
He J, Kunitake T, Nakao A (2003) Facile in situ synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles in porous cellulose fibers. Chem Mater 15:4401–4406
Hussain I, Singh N, Singh A, Singh H, Singh S (2016) Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol Lett 38:545–560
Jönsson LJ, Martín C (2016) Pretreatment of lignocellulose: formation of inhibitory by-products and strategies for minimizing their effects. Bioresour Technol 199:103–112
Jústiz-Smith NG, Virgo GJ, Buchanan VE (2008) Potential of Jamaican banana, coconut coir and bagasse fibres as composite materials. Mater Charact 59:1273–1278
Kandathil V, Fahlman BD, Sasidhar B, Patil SA, Patil SA (2017) A convenient, efficient and reusable N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium (ii) based catalyst supported on magnetite for Suzuki-Miyaura and Mizoroki-Heck cross-coupling reactions. New J Chem 41:9531–9545
Kandathil V, Dateer RB, Sasidhar B, Patil SA, Patil SA (2018a) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: applications in aryl halide cyanation and hiyama cross-coupling reaction under ligand free conditions. Catal Lett 148:1562–1578
Kandathil V, Koley TS, Manjunatha K, Dateer RB, Keri RS, Sasidhar B et al (2018b) A new magnetically recyclable heterogeneous palladium (II) as a green catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling and reduction of nitroarenes in aqueous medium at room temperature. Inorg Chim Acta 478:195–210
Kandathil V, Kempasiddaiah M, Sasidhar B, Patil SA (2019) From agriculture residue to catalyst support; A green and sustainable cellulose-based dip catalyst for CC coupling and direct arylation. Carbohydr Polym 223:115060
Keipour H, Hosseini A, Afsari A, Oladee R, Khalilzadeh MA, Ollevier T (2015) CsF/clinoptilolite: an efficient solid base in SNAr and copper-catalyzed Ullmann reactions. Can J Chem 94:95–104
Kempasiddhaiah M, Kandathil V, Dateer RB, Sasidhar BS, Patil SA, Patil SA (2019) Magnetite tethered mesoionic carbene-palladium (II): an efficient and reusable nanomagnetic catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and Mizoroki-Heck cross-coupling reactions in aqueous medium. Appl Organomet Chem 33:e4846
Khalilzadeh MA, Hosseini A, Pilevar A (2011) Potassium fluoride supported on natural nanoporous zeolite: a new solid base for the synthesis of diaryl ethers. Eur J Org Chem 2011:1587–1592
Khalilzadeh MA, Keipour H, Hosseini A, Zareyee D (2014) KF/Clinoptilolite, an effective solid base in Ullmann ether synthesis catalyzed by CuO nanoparticles. New J Chem 38:42–45
Khalilzadeh MA, Sadeghifar H, Venditti RA (2019) Natural clinoptilolite/KOH: an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for carboxymethylation of hemicellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:11680–11688
Kim JS, Lee Y, Kim TH (2016) A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 199:42–48
Köhler K, Wagner M, Djakovitch L (2001) Supported palladium as catalyst for carbon–carbon bond construction (Heck reaction) in organic synthesis. Catal Today 66:105–114
Kylmälä T, Tois J, Xu Y, Franzén R (2009) One step synthesis of Diflunisal using a Pd-diamine complex. Cent Eur J Chem 7:818–826
Lakshmipathy R, Reddy BP, Sarada N, Chidambaram K, Pasha SK (2015) Watermelon rind-mediated green synthesis of noble palladium nanoparticles: catalytic application. Appl Nanosci 5:223–228
Li K, Fu S, Zhan H, Zhan Y, Lucia L (2010) Analysis of the chemical composition and morphological structure of banana pseudo-stem. BioResources 5:576–585
Li Y, Xu L, Xu B, Mao Z, Xu H, Zhong Y et al (2017) Cellulose sponge supported palladium nanoparticles as recyclable cross-coupling catalysts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:17155–17162
Ling Z, Wang T, Makarem M, Cintrón MS, Cheng HN, Kang X, Bacher M, Potthast A, Rosenau T, King H, Delhom CD (2019) Effects of ball milling on the structure of cotton cellulose. Cellulose 26:305–328
Lu Z, Jasinski JB, Handa S, Hammond GB (2018) Recyclable cellulose-palladium nanoparticles for clean cross-coupling chemistry. Org Biomol Chem 16:2748–2752
Manjunatha K, Koley TS, Kandathil V, Dateer RB, Balakrishna G, Sasidhar B et al (2018) Magnetic nanoparticle-tethered Schiff base–palladium (II): highly active and reusable heterogeneous catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling and reduction of nitroarenes in aqueous medium at room temperature. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e4266
Maryan AS, Gorji M (2016) Synthesize of nano silver using cellulose or glucose as a reduction agent: the study of their antibacterial activity on polyurethan fibers. Bulg Chem Commun 47:151–155
Mohapatra D, Mishra S, Sutar N (2010) Banana and its by-product utilisation: an overview. J Sci Ind Res 69:323–329
Nishikata T, Tsutsumi H, Gao L, Kojima K, Chikama K, Nagashima H (2014) Adhesive catalyst immobilization of palladium nanoparticles on cotton and filter Paper: applications to reusable catalysts for sequential catalytic reactions. Adv Synth Catal 356:951–960
Park JN, Forman AJ, Tang W, Cheng J, Hu YS, Lin H et al (2008) Highly active and sinter-resistant Pd-nanoparticle catalysts encapsulated in silica. Small 4:1694–1697
Paul SA, Boudenne A, Ibos L, Candau Y, Joseph K, Thomas S (2008) Effect of fiber loading and chemical treatments on thermophysical properties of banana fiber/polypropylene commingled composite materials. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 39:1582–1588
Reynolds WR, Plucinski P, Frost CG (2014) Robust and reusable supported palladium catalysts for cross-coupling reactions in flow. Catal Sci Technol 4:948–954
Rezayat M, Blundell RK, Camp JE, Walsh DA, Thielemans W (2014) Green one-step synthesis of catalytically active palladium nanoparticles supported on cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1241–1250
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Shin HS, Jacob JM, Pugazhendhi A, Bhaisare M et al (2018) New insights on the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant and waste biomaterials: current knowledge, their agricultural and environmental applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:10164–10183
Schröfel A, Kratošová G, Šafařík I, Šafaříková M, Raška I, Shor LM (2014) Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles–a review. Acta Biomater 10:4023–4042
Sermakkani M, Thangapandian V (2012) GC–MS analysis of Cassia italica leaf methanol extract. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 5:90–94
Seyednejhad S, Khalilzadeh MA, Zareyee D, Sadeghifar H, Venditti R (2019) Cellulose nanocrystal supported palladium as a novel recyclable catalyst for Ullmann coupling reactions. Cellulose 26:5015–5031
Sharma V, Bahuguna A, Krishnan V (2017) Bioinspired dip catalysts for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions: effect of scaffold architecture on the performance of the catalyst. Adv Mater Interfaces 4:1700604
Shiyong L, Qizhong Z, Zhengneng J, Jiang H, Jiang X (2010) Dodecylsulfate anion embedded layered double hydroxide supported nanopalladium catalyst for the Suzuki reaction. Chin J Catal 31:557–561
Shylesh S, Schünemann V, Thiel WR (2010) Magnetically separable nanocatalysts: bridges between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:3428–3459
Sukirtha R, Krishnan M, Ramachandran R, Kamalakkannan S, Kokilavani P, SankarGanesh D et al (2011) Areca catechu Linn.–Derived silver nanoparticles: a novel antitumor agent against Dalton’s ascites lymphoma. Int J Green Nanotechnol 3:1–12
Sun T, Zhang Z, Xiao J, Chen C, Xiao F, Wang S et al (2013) Facile and green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles-graphene-carbon nanotube material with high catalytic activity. Sci Rep 3:2527
Veisi H, Ghorbani M, Hemmati S (2019) Sonochemical in situ immobilization of Pd nanoparticles on green tea extract coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles: an efficient and magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst for synthesis of biphenyl compounds under ultrasound irradiations. Mater Sci Eng C 98:584–593
Vishal K, Fahlman BD, Sasidhar B, Patil SA, Patil SA (2017) Magnetic nanoparticle-supported N-heterocyclic carbene-palladium (II): a convenient, efficient and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. Catal Lett 147:900–918
Xiang Z, Chen Y, Liu Q, Lu F (2018) A highly recyclable dip-catalyst produced from palladium nanoparticle-embedded bacterial cellulose and plant fibers. Green Chem 20:1085–1094
Xiao J, Lu Z, Li Y (2015) Carboxymethylcellulose-supported palladium nanoparticles generated in situ from palladium (II) carboxymethylcellulose: an efficient and reusable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Mizoroki–Heck reactions. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:790–797
Zhao F, Bhanage BM, Shirai M, Arai M (2000) Heck reactions of iodobenzene and methyl acrylate with conventional supported palladium catalysts in the presence of organic and/and inorganic bases without ligands. Chem Eur J 6:843–848
Zheng G, Kaefer K, Mourdikoudis S, Polavarapu L, Vaz B, Cartmell SE et al (2014) Palladium nanoparticle-loaded cellulose paper: a highly efficient, robust, and recyclable self-assembled composite catalytic system. J Phys Chem Lett 6:230–238
Zheng G, Polavarapu L, Liz-Marzán LM, Pastoriza-Santos I, Pérez-Juste J (2015) Gold nanoparticle-loaded filter paper: a recyclable dip-catalyst for real-time reaction monitoring by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem Commun 51:4572–4575
Zin M, Abdan K, Norizan M, Mazlan N (2018) The effects of alkali treatment on the mechanical and chemical properties of banana fibre and adhesion to epoxy resin. Partanika J Sci Technol 26:161–176
Acknowledgments
The authors thank DST-SERB, India [SERB/F/1423/2017–18 (File No. YSS/2015/000010)], DST-Nanomission, India (SR/NM/NS-20/2014) and Jain University, India for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10570_2020_3001_MOESM1_ESM.docx
All the analysis data and 1H NMR spectra of cross-coupled products are available in the supplementary data (DOCX 7356 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kempasiddaiah, M., Kandathil, V., Dateer, R.B. et al. Immobilizing biogenically synthesized palladium nanoparticles on cellulose support as a green and sustainable dip catalyst for cross-coupling reaction. Cellulose 27, 3335–3357 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03001-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03001-3