Abstract
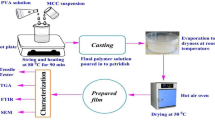
In this study, all-cellulose nanocomposites were developed by depositing one-dimensional jute cellulose nanowhiskers on a hydrolyzed two dimensional electrospun nanofibrous membrane via an immersion-drying process. The prepared nanocomposites were characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared, field emission scanning electron microscope, thermal gravimetric analysis, Brunauer, Emmett and Teller specific surface area, and mechanical properties. The versatile all-cellulose nanocomposites have the potential to be used in ultrafiltration, medical application, catalyst supports, etc.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aparecido JDM, Daniel P, Antonio ASC et al (2009) Self-reinforced composites obtained by the partial oxypropylation of cellulose fibers. 1. Characterization of the materials obtained with different types of fibers. Carbohydr Polym 76(3):437–442
Bismarck A, Mishra S, Lampke T (2005) In natural fibers, biopolymers, and biocomposites. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton
Cao X, Ding B, Yu J, Al-Deyab SS (2012) Cellulose nanowhiskers extracted from TEMPO-oxidized jute fibers. Carbohydr Polym 90(2):1075–1080
Cao X, Ding B, Yu J, Al-Deyab SS (2013) In situ growth of silver nanoparticles on TEMPO-oxidized jute fibers by microwave heating. Carbohydr Polym 92(1):571–576
Chen Q, Nattakan S, Ni XY et al (2008) The effect of fibre volume fraction and mercerization on the properties of all-cellulose composites. Carbohydr Polym 71(3):458–467
Chen QJ, Zhou LL, Zou JQ, Gao X (2019) The preparation and characterization of nanocomposite film reinforced by modified cellulose nanocrystals. Int J Biol Macromol 132(1):1155–1162
Gindl W, Jozef K (2007) Drawing of self-reinforced cellulose films. J Appl Polym Sci 103(4):2703–2708
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85
Lu X, Zhang MQ, Rong MZ et al (2004a) Environmental degradability of self-reinforced composites made from sisal. Compos Sci Technol 64(9):1301–1310
Lu X, Zhang MQ, Rong MZ, Yue DL, Yang GC (2004b) The preparation of self-reinforced sisal fiber composites. Polym Polym Compos 12(4):297–307
Ma H, Burger C, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2011) Ultrafine polysaccharide nanofibrous membranes for water purification. Biomacromolecules 12(4):970–976
Mao X, Ding B, Wang M, Yin Y (2010) Self-assembly of phthalocyanine and polyacrylic acid composite multilayers on cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 80(3):839–844
Nattakan S, Chandeep S (2009) All cellulose nanocomposites by surface selective dissolution of bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 16(3):435–444
Nattakan S, Takashi N, Ton P (2009) All-cellulose composites of regenerated cellulose fibres by surface selective dissolution. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 40(4):321–328
Nishino T, Matsuda I, Koichi H (2004) All cellulose composite. Macromolecules 37(20):7683–7687
Yao Ch, Yin X, Yu Y, Cai Zh, Wang X (2017) Chemically functionalized natural cellulose materials for effective triboelectric nanogenerator development. Ad Funct Mater 27:1700794
Zhang MQ, Rong MZ, Lu X (2005) Fully biodegradable natural fiber composites from renewable resources: all-plant fiber composites. Compos Sci Technol 65(15–16):2514–2525
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51503162), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant No. 2016CFB459) and Hubei province technical innovation special Project (No. 2019AAA005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Zhu, M., Fan, F. et al. All-cellulose composites based on jute cellulose nanowhiskers and electrospun cellulose acetate (CA) fibrous membranes. Cellulose 27, 1385–1391 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02880-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02880-5